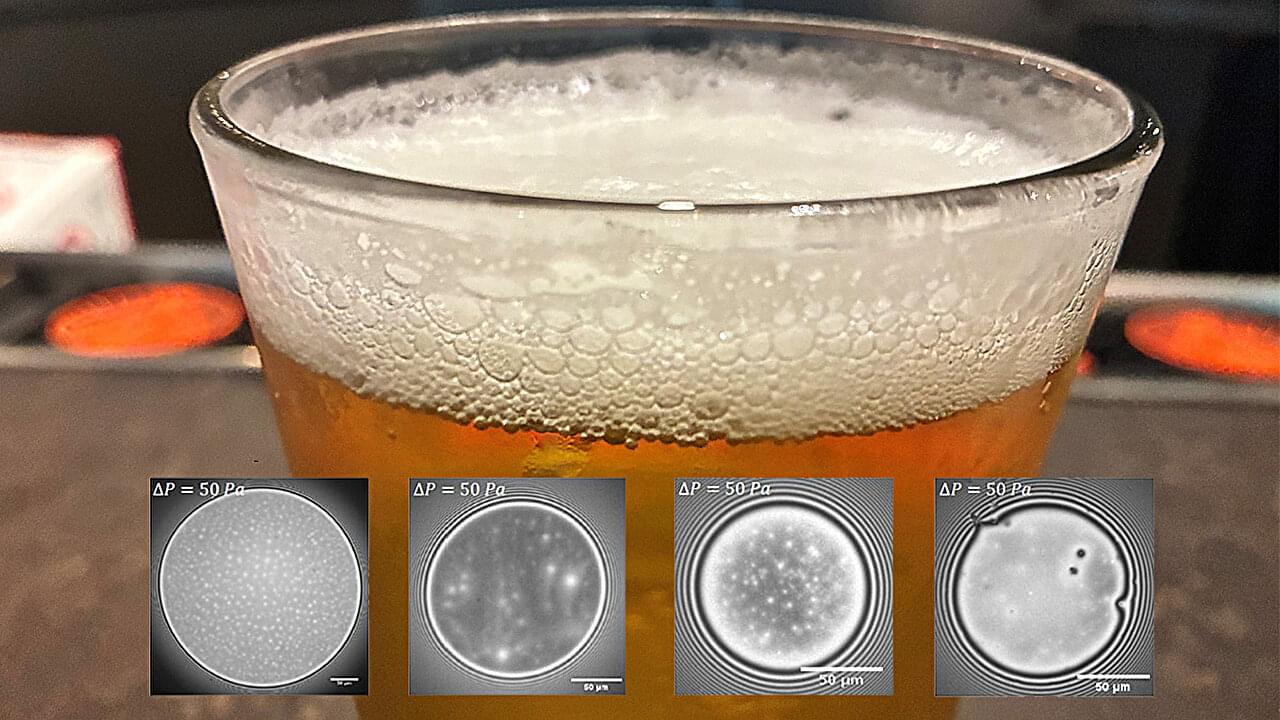
Beer is one of the world’s most popular drinks, and one of the clearest signs of a good brew is a big head of foam at the top of a poured glass. Even brewers will use the quality of foam as an indicator of a beer having completed the fermentation process. However, despite its importance, what makes a large, stable foam is not entirely understood.
In Physics of Fluids, researchers from ETH Zurich and Eindhoven University of Technology investigated the stability of beer foams, examining multiple types of beer at different stages of the fermentation process.
Like any other foam, beer foam is made of many small bubbles of air, separated from each other by thin films of liquid. These thin films must remain stable, or the bubbles will pop, and the foam will collapse. What holds these thin films together may be conglomerates of proteins, surface viscosity, or the presence of surfactants, which are molecules that can reduce surface tension and are found in soaps and detergents.