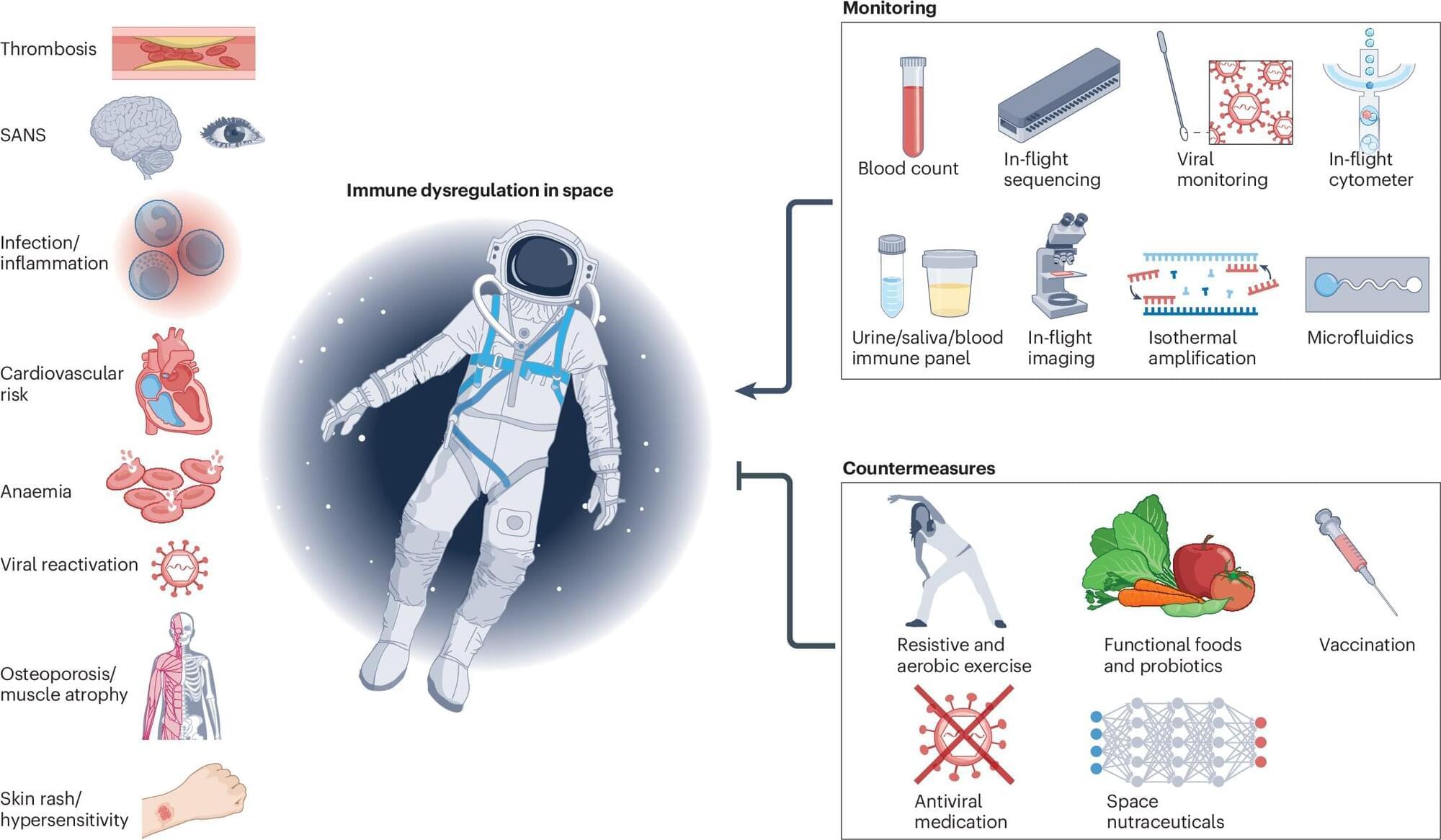
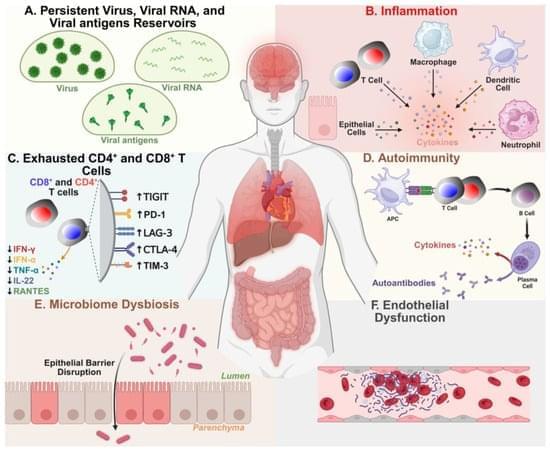
With the advent of commercial spaceflight, an increasing number of people may be heading into space in the coming years. Some will even get a chance to fly to the moon or live on Mars.
One of the major health risks associated with spaceflight involves the immune system, which normally fights off viruses and cancer. It’s already established that spaceflight weakens immunity; current and past astronauts report clinical issues such as respiratory illnesses and skin rashes. These issues may become even more serious on longer-term flights, such as to Mars.
To better understand the full scope of immunology during spaceflight, Buck Associate Professor Dan Winer, MD, working with colleagues linked to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), Cornell University, the University of Pittsburgh, the University of Toronto, Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, and others, have put together a comprehensive guide describing a full array of science linking spaceflight and the immune system.