View insights.
Intel’s Raptor Lake CPU has been benchmarked in Geekbench, and the results are quite impressive.

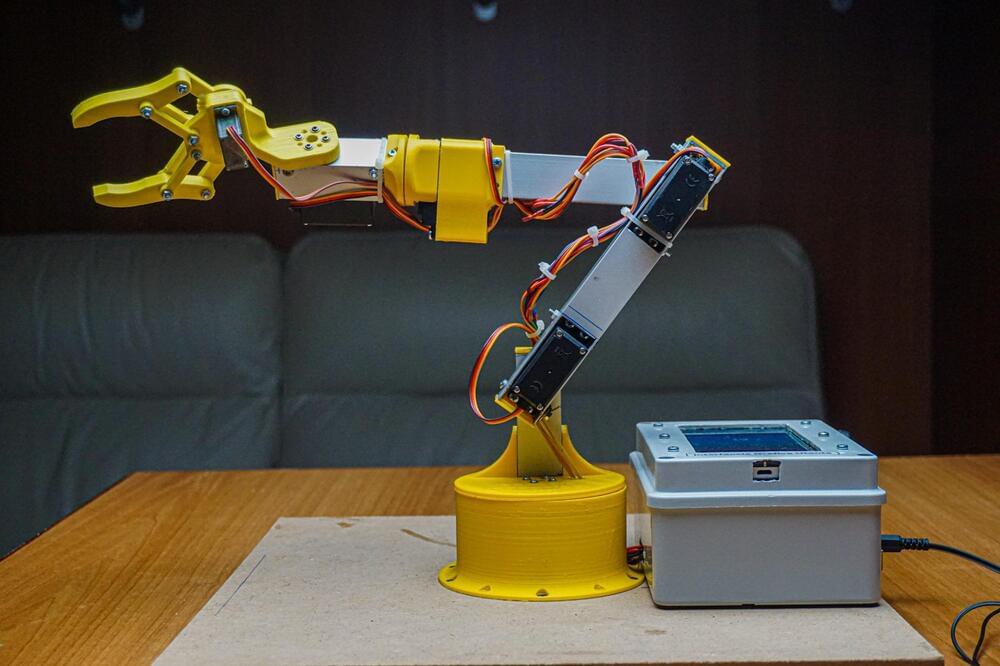
Normally, robotic arms are controlled by a GUI running on a host PC, or with some kind of analog system that maps human inputs to various degrees of rotation. However, Maurizio Miscio was able to build a custom robotic arm that is completely self-contained — thanks to a companion mobile app that resides on an old smartphone housed inside a control box.
Miscio started his project by making 3D models of each piece, most of which were 3D-printed. These included the gripper, various joints that each give a single axis of rotation, and a large circular base that acts as a stable platform on which the arm can spin. He then set to work attaching five servo motors onto each rotational axis, along with a single SG90 micro servo motor for the gripper. These motors were connected to an Arduino Uno that also had an HC-05 Bluetooth® serial module for external communication.
In order to operate the arm, Miscio developed a mobile app with the help of MIT App Inventor, which presents the user with a series of buttons that rotate a particular servo motor to the desired degree. The app even lets a series of motion be recorded and “played back” to the Uno over Bluetooth for repeated, accurate movements.
A research partnership between Penn State and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) could enable an improved method to make a new type of semiconductor that is a few atoms thin and interacts with light in an unusual way. This new semiconductor could lead to new computing and communications technologies that use lower amounts of energy than current electronics.
The new type of semiconductor, tin selenide (SnSe), would be useful for developing a new type of electronics known as “photonics” that use particles of light, or photons, to store, manipulate and transmit information. Traditional electronics use electrons to do this, while photonics use photons. Tin selenide is a binary compound consisting of tin and selenium in a 1:1 ratio.
The material has a peculiar interaction with light that gives it great potential for use in electronics.
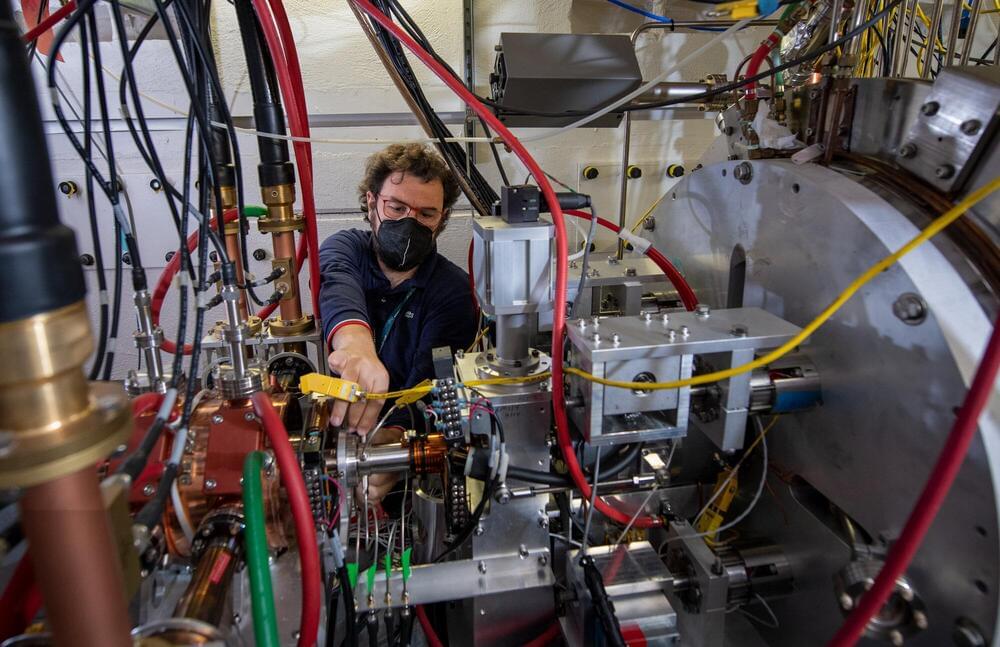

Scientists have developed a new machine-learning platform that makes the algorithms that control particle beams and lasers smarter than ever before. Their work could help lead to the development of new and improved particle accelerators that will help scientists unlock the secrets of the subatomic world.
Daniele Filippetto and colleagues at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) developed the setup to automatically compensate for real-time changes to accelerator beams and other components, such as magnets. Their machine learning approach is also better than contemporary beam control systems at both understanding why things fail, and then using physics to formulate a response. A paper describing the research was published late last year in Nature Scientific Reports.
“We are trying to teach physics to a chip, while at the same time providing it with the wisdom and experience of a senior scientist operating the machine,” said Filippetto, a staff scientist at the Accelerator Technology & Applied Physics Division (ATAP) at Berkeley Lab and deputy director of the Berkeley Accelerator Controls and Instrumentation Program (BACI) program.
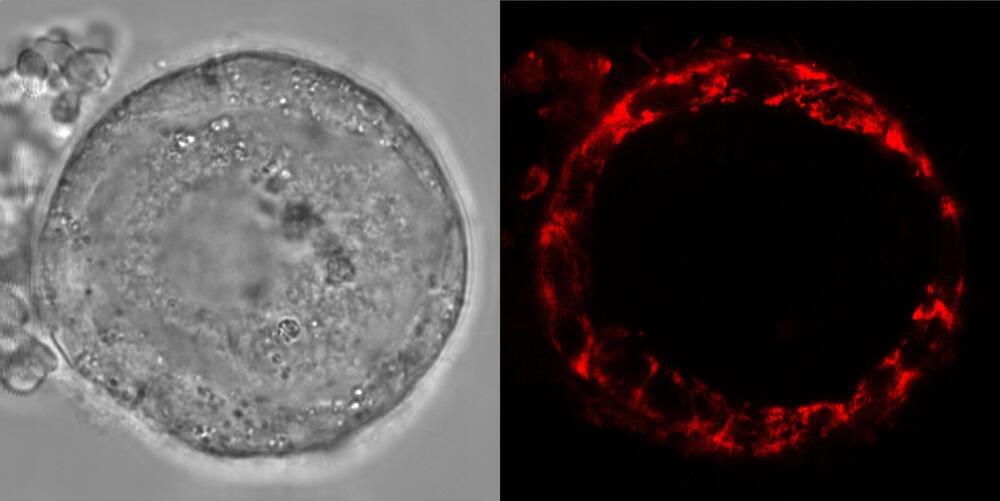
Immature human egg cells skip a fundamental metabolic reaction thought to be essential for generating energy, according to the findings of a study by researchers at the Center for Genomic Regulation (CRG) published today in the journal Nature.
By altering their metabolic activity, the cells avoid creating reactive oxygen species, harmful molecules that can accumulate, damage DNA and cause cell death. The findings explain how human egg cells remain dormant in ovaries for up to 50 years without losing their reproductive capacity.
“Humans are born with all the supply of egg cells they have in life. As humans are also the longest-lived terrestrial mammal, egg cells have to maintain pristine conditions while avoiding decades of wear-and-tear. We show this problem is solved by skipping a fundamental metabolic reaction that is also the main source of damage for the cell. As a long-term maintenance strategy, its like putting batteries on standby mode. This represents a brand new paradigm never before seen in animal cells,” says Dr. Aida Rodriguez, postdoctoral researcher at the CRG and first author of the study.
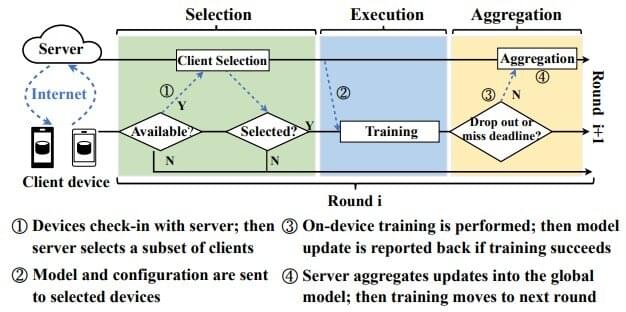
The biggest benchmarking data set to date for a machine learning technique designed with data privacy in mind has been released open source by researchers at the University of Michigan.
Called federated learning, the approach trains learning models on end-user devices, like smartphones and laptops, rather than requiring the transfer of private data to central servers.
“By training in-situ on data where it is generated, we can train on larger real-world data,” explained Fan Lai, U-M doctoral student in computer science and engineering, who presents the FedScale training environment at the International Conference on Machine Learning this week.

The results of the study by Wells Fargo Foundation and NREL initiative showed that PV-coated windows can appreciably lower the solar heat gain coefficient.
From pv magazine USA
In the IN2 NEXT project, PV-coated windows from NEXT Energy Technologies were tested against traditional commercial windows, tracking performance based on their respective solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), an industry-standard performance metric for commercial windows. The results show that NEXT Energy’s technology could lower the SHGC from an otherwise equal window to below .20.

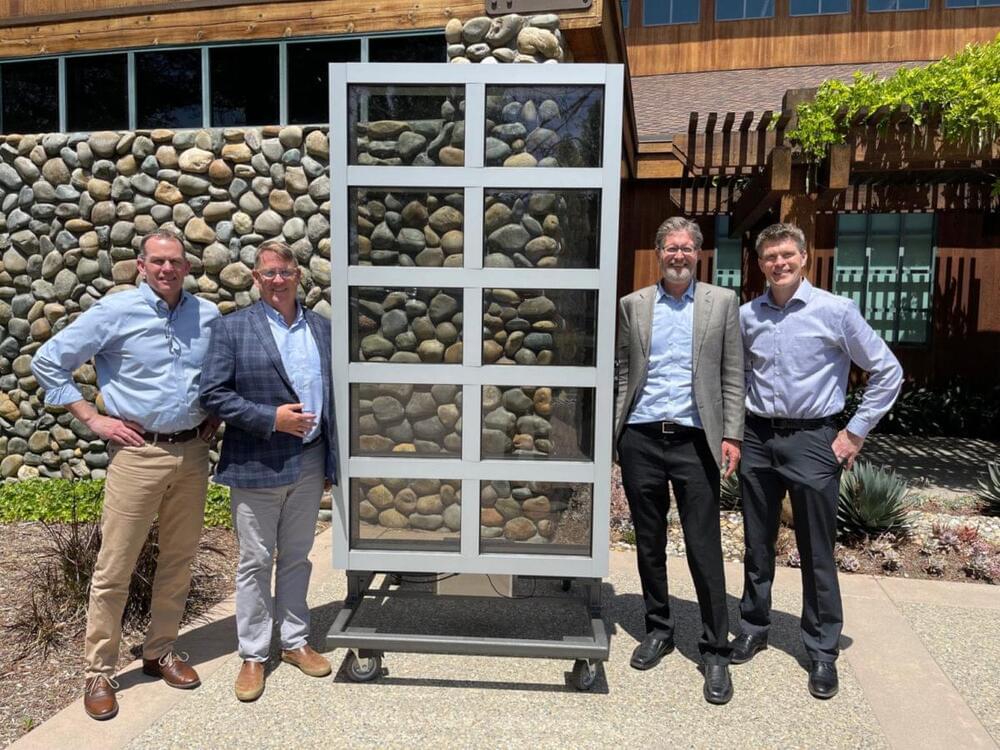
Digital information is everywhere in the era of smart technology, where data is continuously generated by and communicated among cell phones, smart watches, cameras, smart speakers and other devices. Securing digital data on handheld devices requires massive amounts of energy, according to an interdisciplinary group of Penn State researchers, who warn that securing these devices from bad actors is becoming a greater concern than ever before.
Led by Saptarshi Das, Penn State associate professor of engineering science and mechanics, researchers developed a smart hardware platform, or chip, to mitigate energy consumption while adding a layer of security. The researchers published their results on June 23 in Nature Communications.
“Information from our devices is currently stored in one location, the cloud, which is shared and stored in large servers,” said Das, who also is affiliated with the Penn State School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, the Materials Research Institute and the College of Earth and Mineral Sciences’ Department of Materials Science and Engineering. “The security strategies employed to store this information are extremely energy inefficient and are vulnerable to data breaches and hacking.”

China’s dependence on foreign suppliers of computer chips could undermine the country’s transition to electric vehicles, tech traders and researchers say.
The shortage of chips, or semiconductors, is more acute in China than elsewhere and could hit the nation’s EV momentum, according to CATARC, the China Automotive Technology and Research Center, because its fledgling domestic chipmaking industry is unlikely to be in a position to cope with demand within the next two to three years, it says.
With delivery delays of up to a year, that means carmakers in China are occasionally being forced to pay expensive premiums to chip brokers in cities like Shenzhen, where there is a “grey market” trade in semiconductors.
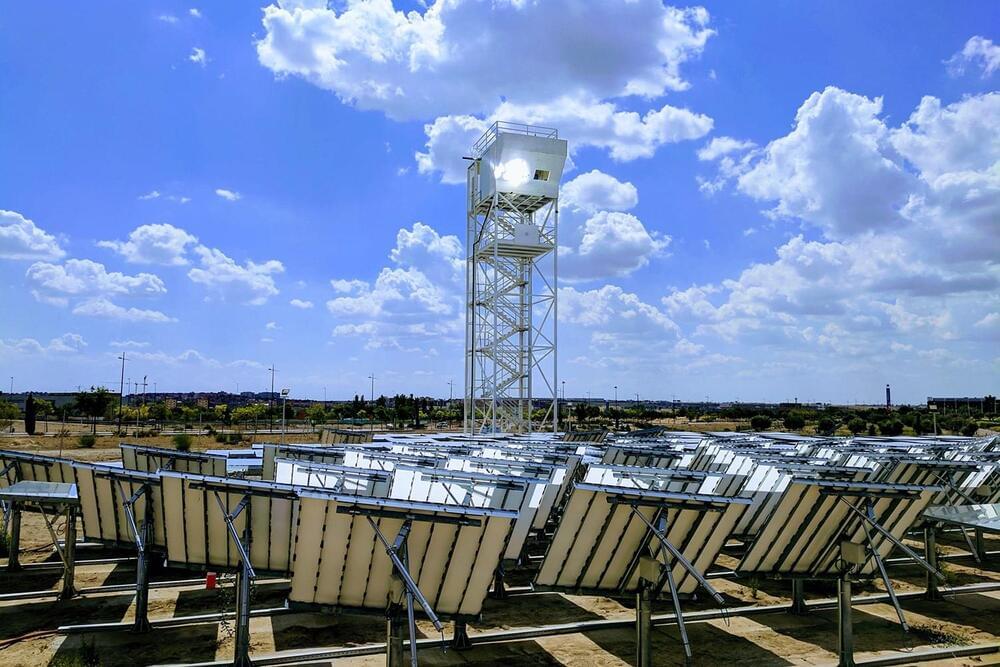

Now, an international team of researchers has developed a tower that uses solar energy to produce a synthetic alternative to fossil-derived fuels like kerosene and diesel. The fuel production system uses water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and sunlight to produce aviation fuel. The team has implemented the system in the field, and the design could help the aviation industry become carbon neutral.
The solar-made kerosene is fully compatible with the existing aviation infrastructure for fuel storage, distribution, and end use in jet engines. It can also be blended with fossil-derived kerosene, says Aldo Steinfeld, a professor from ETH Zurich and the corresponding author of the paper.
The solar fuel production plant consists of 169 sun-tracking reflective panels that redirect and concentrate solar radiation into a solar reactor mounted on top of a tower. The concentrated solar energy then drives oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction cycles in the solar reactor, which contains a reticulated porous ceramic structure made of ceria. The ceria – which is not consumed but can be used over and over – convert water and CO2 injected into the reactor into syngas, a tailored mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Subsequently, syngas is sent into a gas-to-liquid converter, where it is finally processed into liquid hydrocarbon fuels that include kerosene and diesel.