Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


Taking Earth with us: Is space exploration “sustainable”?
Space colonization requires us to better understand how Earth sustains us.
In the coming decades, space agencies from around the world will be venturing farther out into space than ever before. This includes returning to the Moon (perhaps to stay this time), exploring Mars, and maybe even establishing human settlements on both. Beyond that, there are even proposals for establishing habitats in space that could accommodate millions. These plans build on decades of planning that go back to the dawn of the Space Age. In some cases, the plans are inspired by proposals made over half a century prior to that. While these grand visions for space exploration and colonization present many challenges, they also inspire innovative solutions. In particular, missions to deep-space require fresh thinking about environmental control and life-support systems (ECLSS) that can provide self-sufficiency in terms of air, water, food, and protection from radiation and the dangers of space. These are essential since missions that take astronauts far from Earth cannot depend upon resupply missions from the surface to Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Full Story:
Creating sustainability in space means we need a better understanding of how Earth sustains us.
Nvidia reportedly spent $10 billion for a chunk of TSMC’s 5nm manufacturing capacity
To show how bad the chip shortage is, Nvidia just spent about $10 billion in bribes (prepayments) to get TSMC to build some chips for it!
Why it matters: Securing enough manufacturing capacity is going to be critical to the success of Nvidia’s RTX 4,000 GPUs, which are expected to land as soon as this summer. The RTX 3,000 series were regarded by gamers as paper launches, but the company is said to have paid through the nose so that wouldn’t be the case for its upcoming GPUs.
Back in November 2021, the rumor mill was abuzz with hints that Nvidia was planning to use TSMC’s 5nm process node for its upcoming GeForce RTX 4,000 series (Ada Lovelace) GPUs. These are widely expected to be significantly faster and more power-hungry when compared to the current Ampere lineup, but a much bigger issue for the Jensen Huang-powered company is securing enough manufacturing capacity.
According to a report from Hardware Times, Nvidia is prepared to pay dearly for the ability to meet growing demand for increasingly powerful graphics cards. Specifically, it may be offering up to $10 billion to TSMC for a significant chunk of its 5nm manufacturing capacity. Other companies tapping TSMC’s N5 process node are Bitmain, AMD, and Apple.

Elon Musk’s Starlink Satellite Dishes Are Attracting Cats
The heat from Starlink’s receiver dishes is helping felines and other small animals stay warm through the cold winters.
Starlink is an important project of SpaceX and Elon Musk to provide high-speed satellite Internet to mankind. Although it is not yet clear how we humans will benefit, this project is definitely being extremely popular with cats, at least for the time being. The reason is because Starlink’s receiver dishes are becoming the ideal place for cats to rest and warm up in the cold winter.
Specifically, on a Twitter post on New Year’s Eve, one user named Aaron Taylor captured an image of 5 cats cuddled up on one of Starlink satellite dishes. Meanwhile, though the outdoor temperature seemed quite low and the ground was still covered with snow, the heat emitted from the receiver dishes appeared to be enough to warm the kittens, making them continue to lie there.

Key Protein Identified That Could Be Harnessed to Extend Healthy Lifespan in Humans
Decades of research has shown that limits on calorie intake by flies, worms, and mice can enhance life span in laboratory conditions. But whether such calorie restriction can do the same for humans remains unclear. Now a new study led by Yale researchers confirms the health benefits of moderate calorie restrictions in humans — and identifies a key protein that could be harnessed to extend health in humans.
The findings were published on February 10, 2022, in Science.
The research was based on results from the Comprehensive Assessment of Long-term Effects of Reducing Intake of Energy (CALERIE) clinical trial, the first controlled study of calorie restriction in healthy humans. For the trial, researchers first established baseline calorie intake among more than 200 study participants. The researchers then asked a share of those participants to reduce their calorie intake by 14% while the rest continued to eat as usual, and analyzed the long-term health effects of calorie restriction over the next two years.
Brain’s Ability To Clear Protein Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease Controlled by Circadian Cycle
Ability of immune system to destroy Alzheimer’s-related protein oscillates with daily circadian rhythm.
The brain’s ability to clear a protein closely linked to Alzheimer’s disease is tied to our circadian cycle, according to research published recently in PLOS Genetics. The research underscores the importance of healthy sleep habits in preventing the protein Amyloid-Beta 42 (AB42) from forming clumps in the brain, and opens a path to potential Alzheimer’s therapies.
“Circadian regulation of immune cells plays a role in the intricate relationship between the circadian clock and Alzheimer’s disease,” said Jennifer Hurley, an expert in circadian rhythms, and associate professor of biological science at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. “This tells us a healthy sleep pattern might be important to alleviate some of the symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease, and this beneficial effect might be imparted by an immune cell type called macrophages/microglia.”

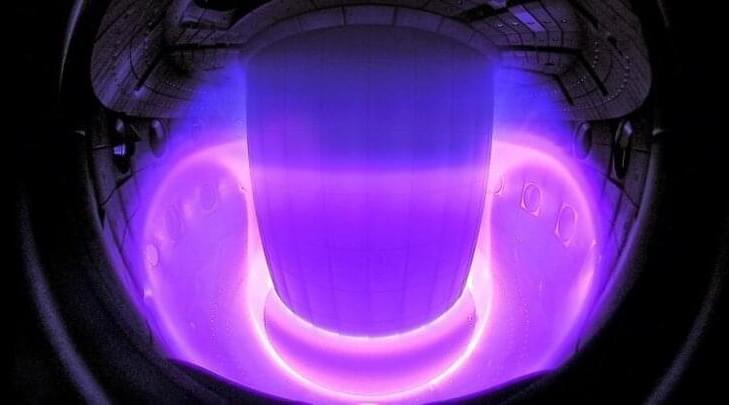
Physics Breakthrough as AI Successfully Controls Plasma in Nuclear Fusion Experiment
Successfully achieving nuclear fusion holds the promise of delivering a limitless, sustainable source of clean energy, but we can only realize this incredible dream if we can master the complex physics taking place inside the reactor.
For decades, scientists have been taking incremental steps towards this goal, but many challenges remain. One of the core obstacles is successfully controlling the unstable and super-heated plasma in the reactor – but a new approach reveals how we can do this.
In a joint effort by EPFL’s Swiss Plasma Center (SPC) and artificial intelligence (AI) research company DeepMind, scientists used a deep reinforcement learning (RL) system to study the nuances of plasma behavior and control inside a fusion tokamak – a donut-shaped device that uses a series of magnetic coils placed around the reactor to control and manipulate the plasma inside it.
“Self-Destruct” Switches Engineered Into GM Microbes
Tae Seok Moon, associate professor of energy, environmental and chemical engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has taken a big step forward in his quest to design a modular, genetically engineered kill switch that integrates into any genetically engineered microbe, causing it to self-destruct under certain defined conditions.
His research was published Feb. 3 in the journal Nature Communications.
Moon’s lab understands microbes in a way that only engineers would, as systems made up of sensors, circuits and actuators. These are the components that allow microbes to sense the world around them, interpret it and then act on the interpretation.