In nature, wood, shells, and other structural materials are lightweight, strong, and tough. Significantly, these materials are made at the ambient temperature in the local environment – not at the high temperatures at which human-made structural materials are generally processed. Similar materials are difficult to make synthetically. In a review article in Nature Materials, a team of scientists assessed the common design motifs of a range of natural structural materials and determined what it would take to design and fabricate structures that mimic nature. They considered the remaining challenges to include the need for comprehensive characterization of strength and toughness to identify underlying multiscale mechanisms.
This comprehensive assessment provides new inspiration and understanding of design principles that may lead to more efficient synthetic approaches for advanced, lightweight structural materials for transportation, buildings, batteries, and energy conversion.
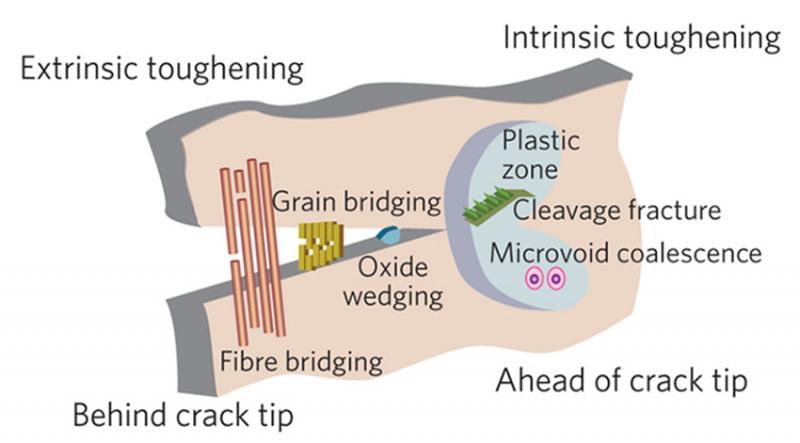
In the natural world, many of the structural materials (wood, shells, bones, etc.) are hybrid materials made up of simple constituents that are assembled at ambient temperatures and often have remarkable properties. Even though the constituent materials generally have poor intrinsic properties, the superior extrinsic properties of the hybrid materials are the result of the arrangement of hard and soft phases in complex hierarchical architectures, with dimensions spanning from the nanoscale to the macroscale. The resulting materials are lightweight and usually show interesting combinations of strength and toughness, even though these two key structural properties tend to be mutually exclusive. It is relatively easy to make materials that are strong or tough, but difficult to make materials that are both.