By redesigning how fluids are simulated, researchers have demonstrated an order of magnitude speed increase on the previous state-of-the-art for slow-flowing viscous liquids.



UNSW engineers have built a new high-speed motor which has the potential to increase the range of electric vehicles.
The design of the prototype IPMSM type motor was inspired by the shape of the longest railroad bridge in South Korea and has achieved speeds of 100,000 revolutions per minute.
The maximum power and speed achieved by this novel motor have successfully exceeded and doubled the existing high-speed record of laminated IPMSMs (Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor), making it the world’s fastest IPMSM ever built with commercialized lamination materials.
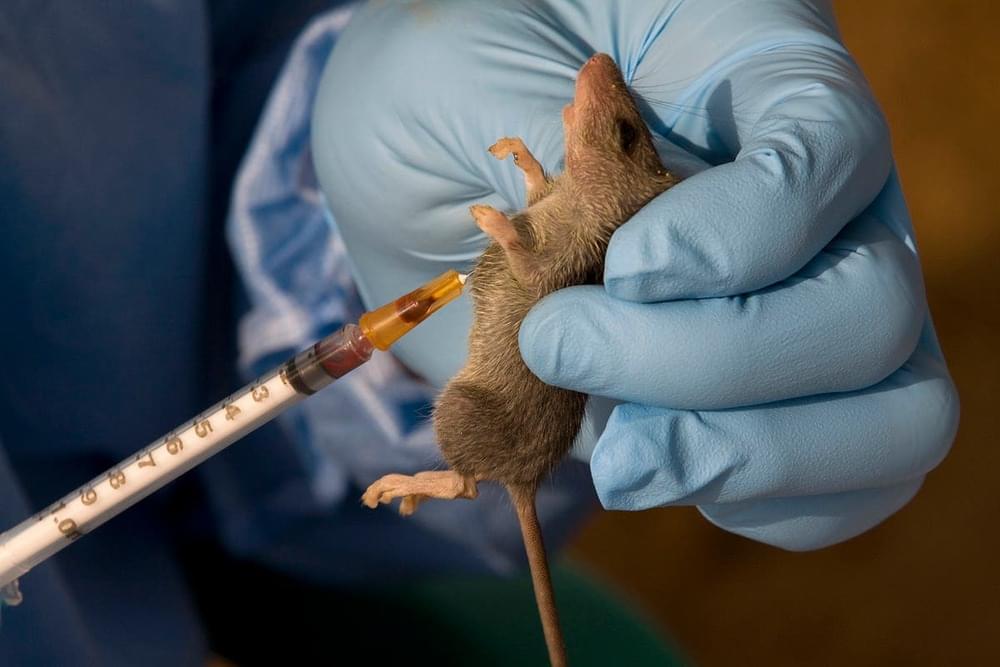
Lassa fever is like ebola and there is an outbreak in Nigeria. It is transmissible through inhalation.
The death of a patient in the UK suffering from Lassa fever has heightened concern around the illness after a third case was reported.
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) said it was contacting individuals who had been in close contact with the infected patients after the death was confirmed last week.
Commenting on the recent cases detected in the UK, which were linked to travel to west Africa, Dr Susan Hopkins, chief medical advisor at UKHSA, said: Cases of Lassa fever are rare in the UK and it does not spread easily between people.

NPR’s Ayesha Rascoe speaks to Nsikan Akpan, health and science editor at WNYC/Gothamist, about the poliovirus emergecy disaster declaration in New York state.
AYESHA RASCOE, HOST:
New York Governor Kathy Hochul declared polio a state disaster emergency on Friday. The first polio case in nearly a decade was identified back in July. The virus can cause paralysis. Nsikan Akpan runs the health and science desk at WNYC/Gothamist. He joins us now. Welcome to the program.

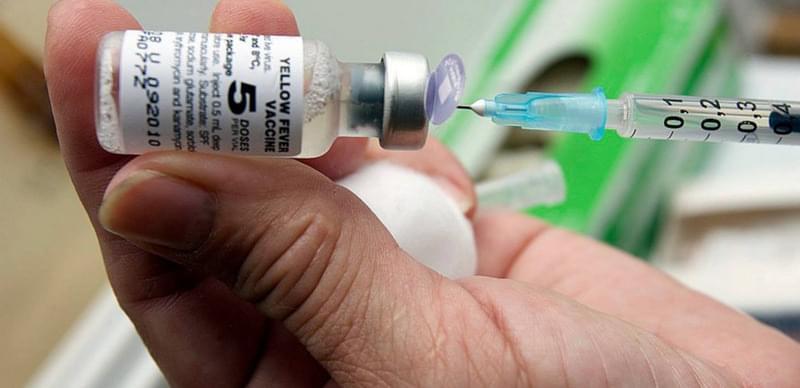
Yellow fever epidemics are happening across Nigeria spreading state by state. The yellow fever is another haemorgic disease like ebola.
Over 160 million people, more than half of Nigeria’s current estimated population, are at risk of yellow fever in the country, reports by the World Health Organisation Africa Region have recently highlighted. Lately, the yellow fever virus has become of serious global health concern more because the wakes of its historic outbreaks are trailed by devastating outcomes.
The WHO says the virus is spreading rapidly across Africa, warning that the rising trend could cause an epidemic in Nigeria particularly, mainly because of its large population. Consequently, it issued an advisory for travellers to and out of Nigeria to consult their healthcare provider on precautionary measures required against the virus if need be.
The Yellow fever virus is endemic in tropical areas of Africa and Central and South America. The disease is a potentially fatal disease, as half of its patients in the toxic phase die within seven to 10 days.
Alcohol Fermentation or ethanol fermentation is a biological method wherein the sugar gets transformed into carbon dioxide and alcohol.
This Video Explains Alcoholic Fermentation.
Ethanol fermentation, also called alcoholic fermentation, is a biological process which converts sugars such as glucose into cellular energy under anaerobic conditions and producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as by-products.
Thank You For Watching.
Please Like And Subscribe to Our Channel: https://www.youtube.com/EasyPeasyLearning.
Like Our Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/learningeasypeasy/
Join Our Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/460057834950033
Support Our Channel: https://www.patreon.com/supereasypeasy
Recent technological advancements have paved the way for the creation of increasingly sophisticated robotic systems designed to autonomously complete missions in different familiar and unfamiliar environments. Robots meant to operate in uncertain or remote environments could greatly benefit from the ability to actively acquire electrical power from their surroundings.
Researchers at Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Imperial College London, and University of Illinois Urbana Champaign have recently developed a new robotic system that can visually rearrange its surroundings to receive the maximum amount of energy from a given power source. This robot, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv and set to be presented at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, works by drawing electrical circuits using conductive ink.
“Our PLOS ONE work started off as a quite philosophical thought experiment,” Andre Rosendo, the professor who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “Nietzsche claims that human’s primal instinct is power, and survival is just a condition sine qua non we couldn’t reach that final goal. Based on this idea, we started to devise experimental settings where our robot could not only act to survive, but to thrive.”
What if humans were gods instead?? Join us… and find out more!
Subscribe for more from Unveiled ► https://wmojo.com/unveiled-subscribe.
In this video, Unveiled takes a closer look at one of the ultimate what if scenarios — what if humans became GODS? According to some predictions, science and technology will one day lead us to godlike power… so what will we do with that responsibility? Will we use it for good or for bad?
This is Unveiled, giving you incredible answers to extraordinary questions!
Find more amazing videos for your curiosity here:
Can Science Solve the God Equation? — https://youtu.be/YPgKH-adjik.
Are Ancient Civilisations Still Hidden on Earth? — https://youtu.be/cbtPJmJErmc.
0:00 Intro.
