A conversation with Astera Resident Edwin Kite on applied planetary science, applied astrobiology, and what it would take to terraform Mars




A new cancer drug candidate developed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BBOT (BridgeBio Oncology Therapeutics) and the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research (FNLCR) has demonstrated the ability to block tumor growth without triggering a common and debilitating side effect. In early clinical trials, the compound, known as BBO-10203, has shown promise in disrupting a key interaction between two cancer-driving proteins — RAS and PI3Kα — without causing hyperglycemia (high blood-sugar levels), which has historically hindered similar treatments. Published in Science

Matthew Berman
Can artificial intelligence (AI) potentially transform health care for the better?
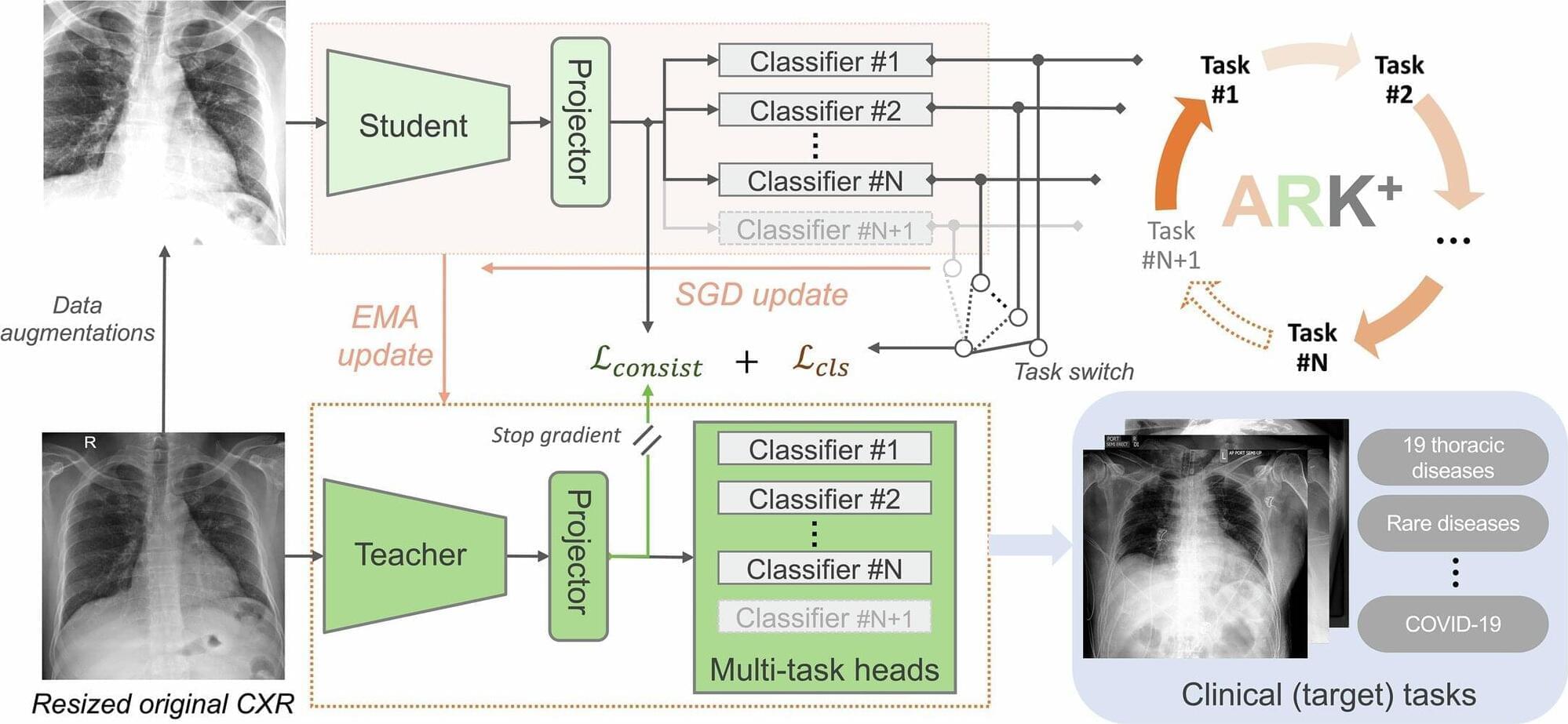
Now, rising to the challenge, an Arizona State University team of researchers has built a powerful new AI tool, called Ark+, to help doctors read chest X‑rays better and improve health care outcomes.
“Ark+ is designed to be an open, reliable and ultimately useful tool in real‑world health care systems,” said Jianming “Jimmy” Liang, an ASU professor from the College of Health Solutions, and lead author of the study recently published in Nature.
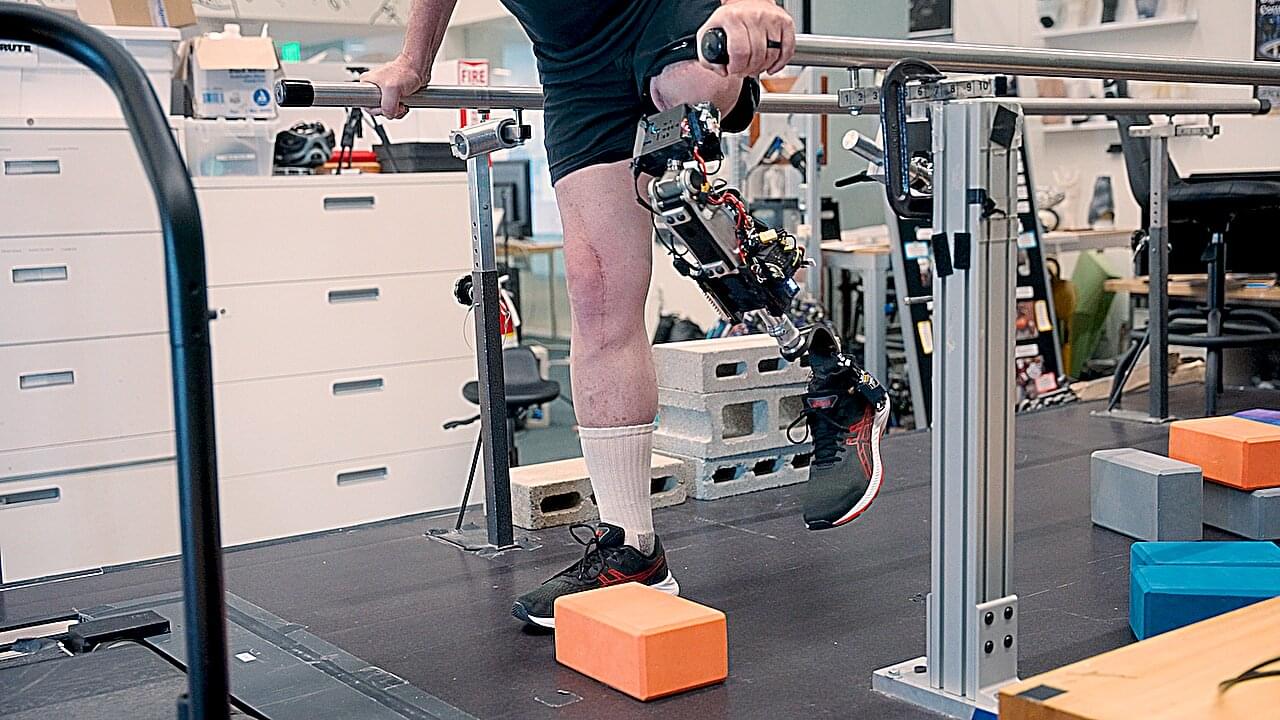

A new bionic knee allows amputees to walk faster, climb stairs more easily, and adroitly avoid obstacles, researchers reported in the journal Science.
The new prothesis is directly integrated with the person’s muscle and bone tissue, enabling greater stability and providing more control over its movement, researchers said.
Two people equipped with the prosthetic said the limb felt more like a part of their own body, the study says.
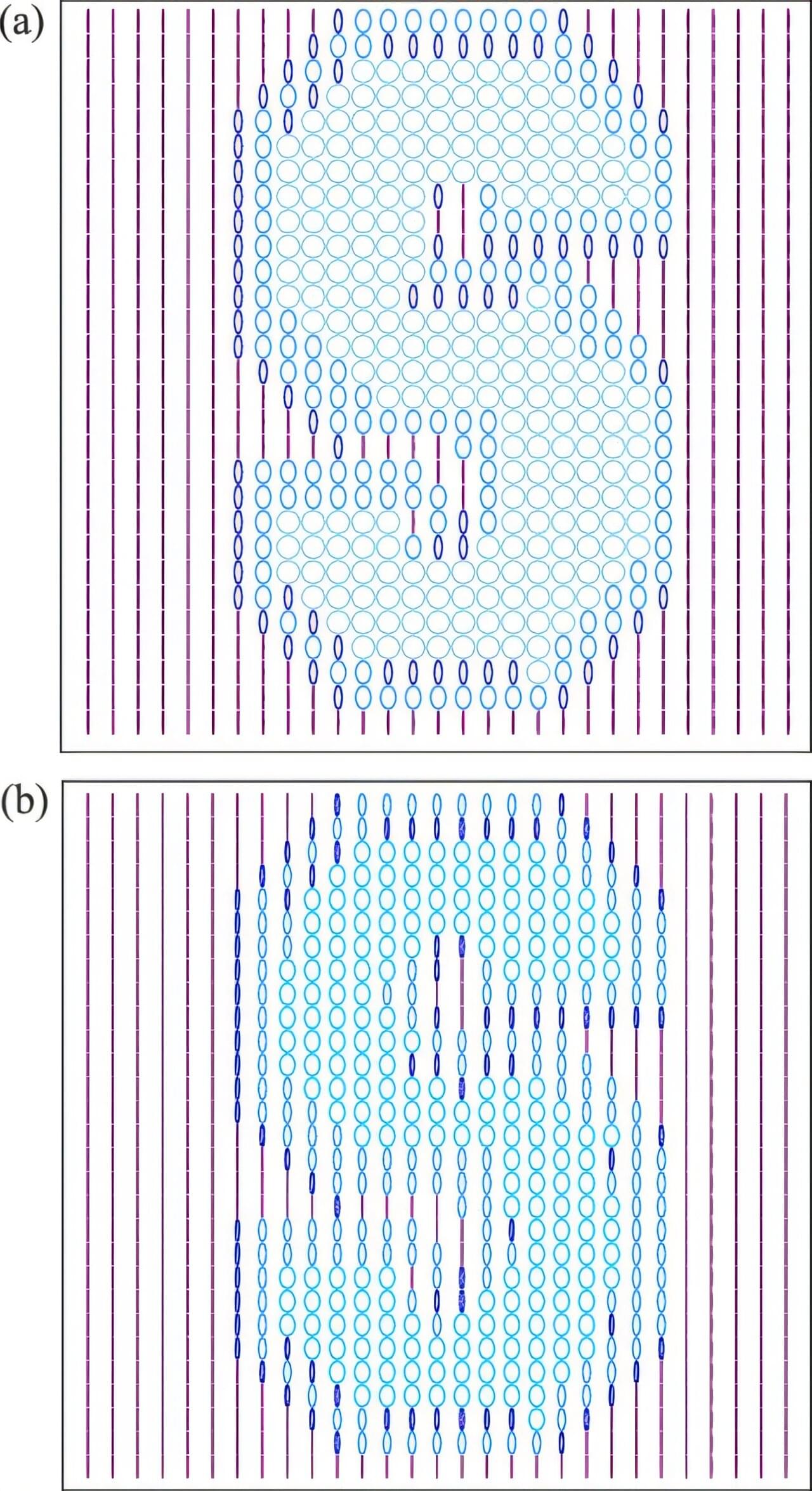
Since its development 100 years ago, quantum mechanics has revolutionized our understanding of nature, revealing a bizarre world in which an object can act like both waves and particles, and behave differently depending on whether it is being watched.
In recent decades, researchers exploring this wave-particle duality have learned to measure the relative “wave-ness” and “particle-ness” of quantum objects, helping to explain how and when they veer between wave-like or particle-like behaviors.
Now, in a paper for Physical Review Research, researchers at the Stevens Institute of Technology report an important new breakthrough: a simple but powerful formula that describes the precise closed mathematical relationship between a quantum object’s “wave-ness” and “particle-ness.”