What is the difference between vitamin D2 and D3? Read on to learn the differences, including which foods are high in vitamin D2 and D3.
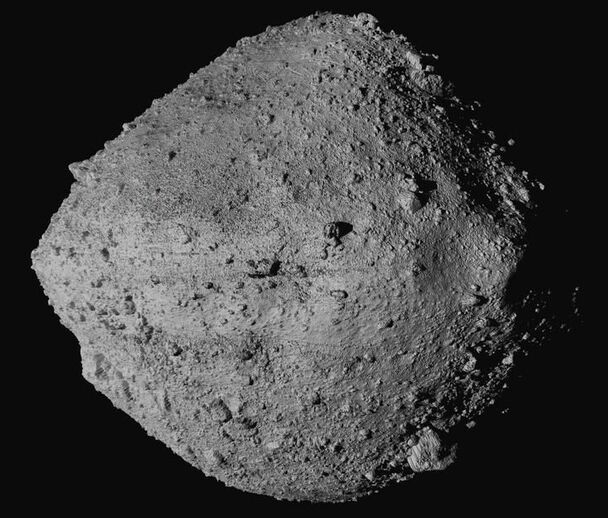
After nearly five years in space, a NASA spacecraft is nearing the end of its historic mission, beginning its journey home to Earth with a plethora of asteroid samples.
NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) spacecraft began its journey back to Earth on Monday — a trip that’s expected to take around two-and-a-half years. It’s returning from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu, and it marks NASA’s first-ever asteroid sample return mission.
The spacecraft is only about 200 million miles away, but it will have to circle the sun twice to catch up to Earth — making the journey a total of 1.4 billion miles.
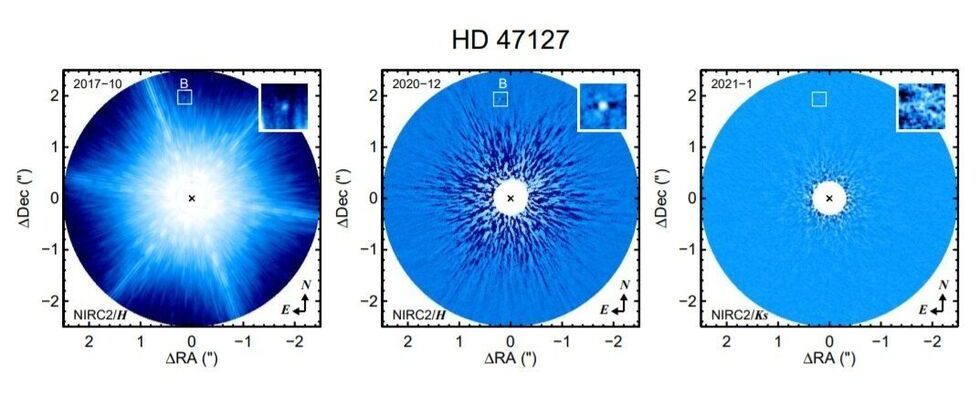
Using the Harlan J. Smith Telescope, astronomers have discovered that the star HD 47127 has a substellar companion. The newly identified object, designated HD 47127 B, appears to be a brown dwarf or a brown dwarf binary. The finding is reported in a paper published May 4 on arXiv.org.
Brown dwarfs are intermediate objects between planets and stars. Astronomers generally agree that they are substellar objects occupying the mass range between 13 and 80 Jupiter masses. One subclass of brown dwarfs (with effective temperatures between 500 and 1500K) is known as T dwarfs, and represents the coolest and least luminous substellar objects so far detected.
Located some 86.8 light years away, HD 47127 is an old sun-like main sequence star of spectral type G5. The star is slightly metal-rich and has a mass of about 1.02 solar masses. Its age is estimated to be between 7 and 10 billion years.
Watch Jupiter’s famous superstorm disappear in infrared images from NOIRLab.
A comparison of images captured in different wavelengths by the Hubble Space Telescope and a ground-based observatory in Hawaii helps shed light on how Jupiter’s massive storms formed.
The results of a new muon experiment are stirring up particle physics.
The results of a Fermilab experiment might open up the standard model of particle physics.
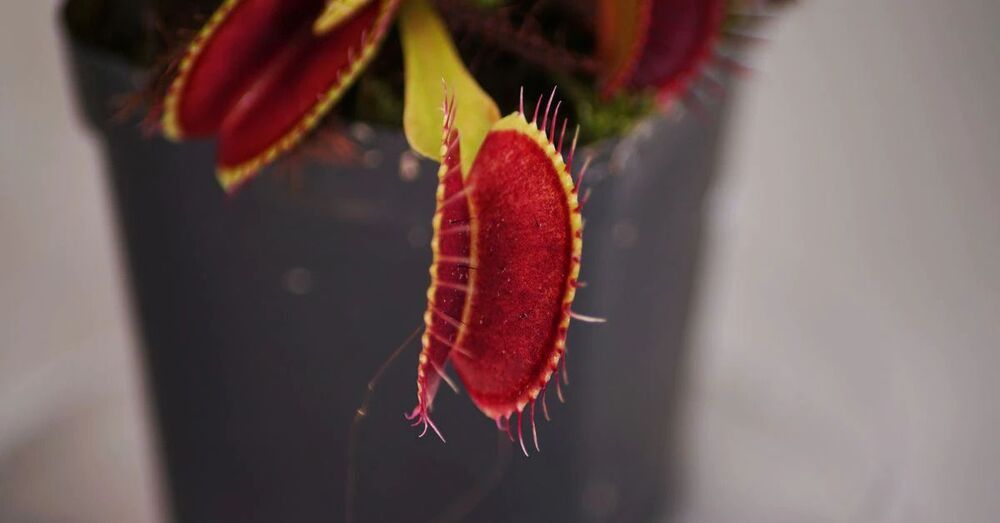
Researchers in Singapore have found a way of controlling a Venus flytrap using electric signals from a smartphone, an innovation they hope will have a range of uses from robotics to employing the plants as environmental sensors.
Luo Yifei, a researcher at Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University (NTU), showed in a demonstration how a signal from a smartphone app sent to tiny electrodes attached to the plant could make its trap close as it does when catching a fly.
“Plants are like humans, they generate electric signals, like the ECG (electrocardiogram) from our hearts,” said Luo, who works at NTU’s School of Materials Science and Engineering.
A COVID-19 vaccine that could provide protection against existing and future strains of the COVID-19 coronavirus, and other coronaviruses, and costs about $1 a dose has shown promising results in early animal testing.
Vaccines created by UVA Health’s Steven L. Zeichner, MD, PhD, and Virginia Tech’s Xiang-Jin Meng, MD, PhD, prevented pigs from being becoming ill with a pig model coronavirus, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV). The vaccine was developed using an innovative approach that Zeichner says might one day open the door to a universal vaccine for coronaviruses, including coronaviruses that previously threatened pandemics or perhaps even coronaviruses that cause some cases of the common cold.
Their coronavirus vaccine offers several advantages that could overcome major obstacles to global vaccination efforts. It would be easy to store and transport, even in remote areas of the world, and could be produced in mass quantities using existing vaccine-manufacturing factories.
A clinical-stage leader in immune-stimulatory vaccines for cancer announced the publication of its favorable long-term Overall Survival (OS) data from a Phase I trial evaluating a universal cancer vaccine candidate, UV1, in combination with checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab, in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma.
UV1 is a peptide-based vaccine inducing a specific T cell response against the universal cancer antigen telomerase.
Published in the Frontiers in Immunology journal on May 11, 2021, Norway-based Ultimovacs ASA’s UV1 vaccine candidate achieved the primary endpoints of safety and tolerability.
Influenza, commonly known as the flu virus, places a substantial burden on public health in the United States. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that influenza has resulted in about 9 million to 45 million diseases, 140000 to 810000 hospitalizations, and 12000 to 61000 deaths each year over the past decade.
Though flu vaccines are readily available to the public, they need to be remodeled and administered every year to combat new viral variants, which can undermine vaccine efficacy. Because of this, scientists have aimed to develop a universal vaccine that can protect against all influenza strains, and that can last for many years.
Now, researchers at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)’s Vaccine Research Center (VRC) and the University of Washington School of Medicine’s Institute for Protein Design (IPD) developed a universal flu vaccine candidate using small particles (nanoparticles), which can induce a long-lasting immune response.
Despite years of hype, virtual reality headsets have yet to topple TV or computer screens as the go-to devices for video viewing.
One reason: VR can make users feel sick. Nausea and eye strain can result because VR creates an illusion of 3D viewing although the user is in fact staring at a fixed-distance 2D display. The solution for better 3D visualization could lie in a 60-year-old technology remade for the digital world: holograms.
Holograms deliver an exceptional representation of 3D world around us. Plus, they’re beautiful. (Go ahead — check out the holographic dove on your Visa card.) Holograms offer a shifting perspective based on the viewer’s position, and they allow the eye to adjust focal depth to alternately focus on foreground and background.