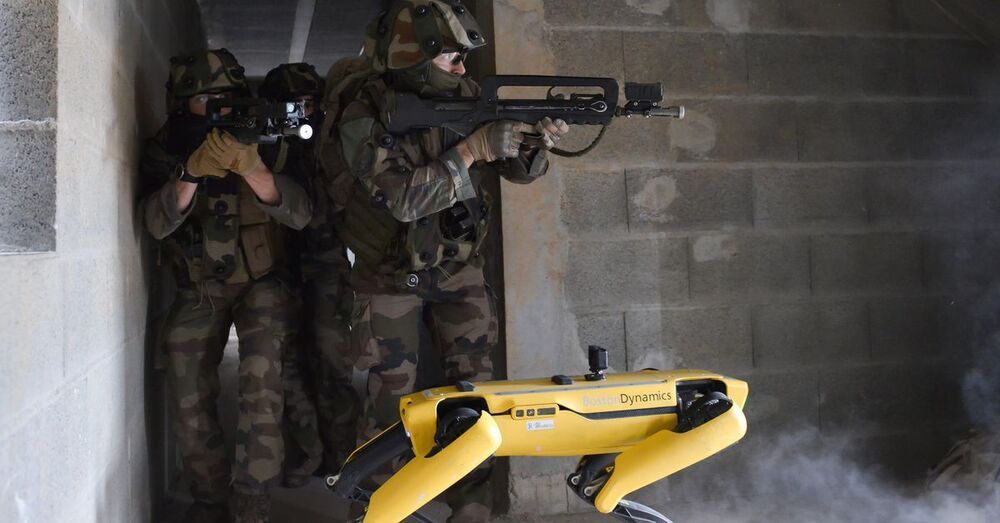
But the latest work has divided developmental biologists. Some question the need for such experiments using closely related primates — these animals are not likely to be used as model animals in the way that mice and rodents are. Nonhuman primates are protected by stricter research ethics rules than are rodents, and they worry such work is likely to stoke public opposition.
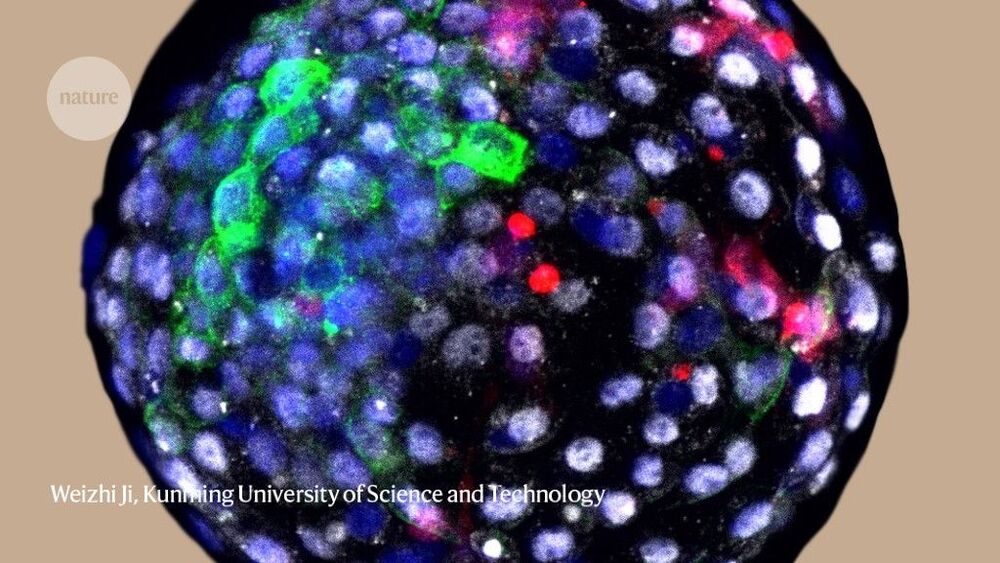
The chimaeras lived up to 19 days — but some scientists question the need for such research.