Web Platform


Some interpretations of quantum mechanics propose that our entire universe is described by a single universal wave function that constantly splits and multiplies, producing a new reality for every possible quantum interaction. That’s quite a bold statement. So how do we get there?
One of the earliest realizations in the history of quantum mechanics is that matter has a wave-like property. The first to propose this was French physicist Louis de Broglie, who argued that every subatomic particle has a wave associated with it, just like light can behave like both a particle and a wave.
Iran’s priority in entering the Ukrainian war arena was to test NATO’s defenses against its drones, to assess the strength of these defenses in the face of Iranian offensive capabilities. It can be said that in the initial stages, the Shahed-136 drone actually managed to achieve exceptional success against NATO air defense employed by the Ukrainian army. This marks a victory for Tehran.
However, the ultimate evaluation of the Shahed-136 drone’s capability against NATO defenses will have to wait until NATO supplies Ukraine with more air defenses in the days ahead. The implications of these advances for the balance of power between Russian and Ukrainian forces, as well as the reputation of the types of weapons supplied to the Ukrainian military, were certainly realized by NATO’s leadership in the wake of these drone attacks. NATO swiftly rushed to implement additional air defense systems designed to deal with such small, drones that are capable of flying at low altitudes.
As with all armed conflicts, the war in Ukraine is being profited from by a variety of peripheral parties, especially those involved in the sale and manufacture of weapons. Attaining these goals comes with a cost in the form of material losses and casualties brought on by reckless military testing. Russia’s use of Iranian drones during the Ukraine War, which resulted in the destruction of 30% of Ukraine’s power plants without obviously advancing any military objectives is an adequate example.
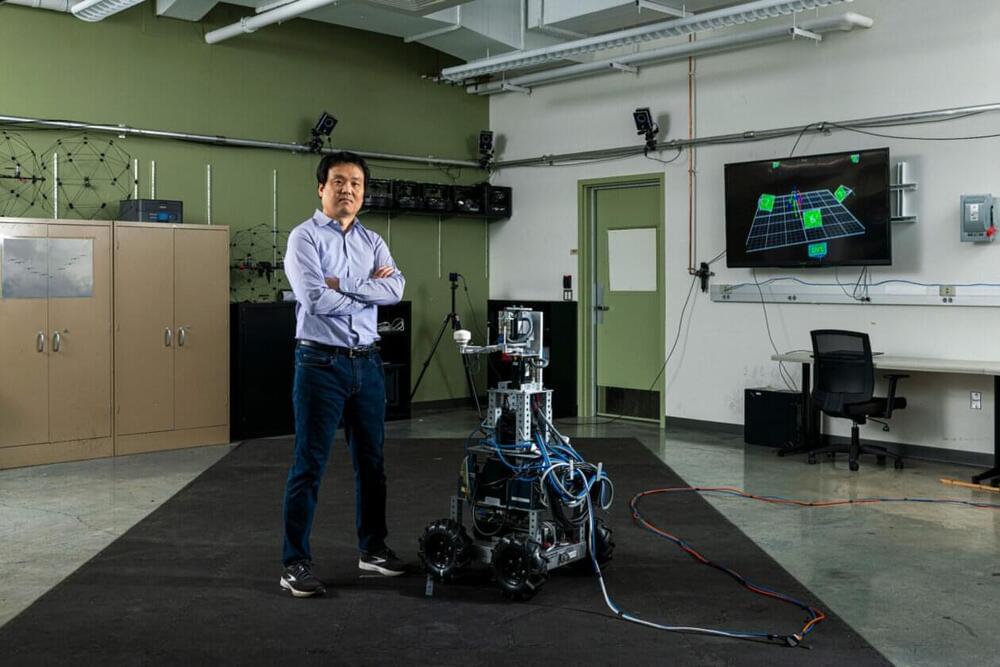

A new study by Missouri S&T researchers shows how human subjects, walking hand-in-hand with a robot guide, stiffen or relax their arms at different times during the walk. The researchers’ analysis of these movements could aid in the design of smarter, more humanlike robot guides and assistants.
“This work presents the first measurement and analysis of human arm stiffness during overground physical interaction between a robot leader and a human follower,” the Missouri S&T researchers write in a paper recently published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The lead researcher, Dr. Yun Seong Song, assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at Missouri S&T, describes the findings as “an early step in developing a robot that is humanlike when it physically interacts with a human partner.”

Hyderabad-based private space startup, Skyroot Aerospace, is set to launch its, and India’s first private rocket between November 12 and 16 from the Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) Sriharikota launchpad. The rocket, named Vikram-S, will be the first space launch vehicle manufactured and operated entirely by a private company in the country — making this the first launch of its kind since the union government opened up the space sector for private industry participation in June 2020.
The final date of the launch mission will be confirmed depending on the prevalent weather conditions during the mentioned launch window. Naga Bharath Daka, chief operating officer of Skyroot, confirmed in a statement that the launch mission will be a suborbital spaceflight, and will carry three customer payloads to the intended orbit.
Typically, a suborbital spaceflight refers to a height of around 100km from the Earth surface, and is done at a lower altitude than an orbital flight, which reaches at least a low-Earth orbit — between around 200km to 2,000km from Earth.

I’ve funded Ukraine media, the Ukraine army, and now I just funded the Ukraine navy. The navy part is extra interesting because it is “the world’s first naval fleet of drones”. That is pretty futuristic!
As Elon Musk said, “Future wars are all about the drones.”
Small and fast unmanned ships 3 russian vessels were damaged, including the Admiral Makarov, flagship of the russian Black Sea Fleet. This is the first case in history where the attack was carried out exclusively by unmanned vessels.
The result of this daring operation was incredible — russia has lost its undeniable advantage on the water. The killers of Ukrainian civilians — warships armed with missiles — became targets themselves.
Today, Ukraine starts assembling the world’s first Naval Fleet of Drones!
This theolocution has been released early in an ad-free audio version for TOE members at http://theoriesofeverything.org.
Sponsors:
- Drink Trade: https://www.drinktrade.com/everything for 30% off.
- Ro Man: https://ro.co/curt for 20% off first order.
- Masterworks: https://masterworks.art/toe.
*New* TOE Website (early access to episodes): https://theoriesofeverything.org/
Patreon: https://patreon.com/curtjaimungal.
Crypto: https://tinyurl.com/cryptoTOE
PayPal: https://tinyurl.com/paypalTOE
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TOEwithCurt.
Discord Invite: https://discord.com/invite/kBcnfNVwqs.
iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/ca/podcast/better-left-unsaid-wit…1521758802
Pandora: https://pdora.co/33b9lfP
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b92xAErofYQA7bU4e.
Subreddit r/TheoriesOfEverything: https://reddit.com/r/theoriesofeverything.
LINKS MENTIONED:
- Michael Levin (Solo TOE podcast): https://youtu.be/Z0TNfysTazc.
- Michael Levin Theolocution With Chris Fields & Karl Friston: https://youtu.be/J6eJ44Jq_pw.
- Joscha Bach Theolocution With John Vervaeke: https://youtu.be/rK7ux_JhHM4
- Joscha Bach Theolocution With Donald Hoffman: https://youtu.be/bhSlYfVtgww.
- Joscha Bach (Solo TOE podcast): https://youtu.be/3MNBxfrmfmI
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00:00 Introduction.
00:01:55 Bach and Levin speak about each other’s work.
00:03:34 The cell functions as a neuron.
00:07:15 Software as a control pattern.
00:10:55 Disciplinary boundaries in academia.
00:14:38 The perceptron is a “toy model” of the brain.
00:18:44 How do you identify yourself as a researcher?
00:20:10 The benefits of podcasts vs. academia.
00:30:04 Beliefs of Bach’s and Levin’s that have drastically changed.
00:38:54 Memory moves outside the brain structure.
00:45:06 Engrams and memory storage.
00:47:30 The implications of transferring memory between species.
00:55:25 Weissman’s barrier.
00:59:25 The notion of “competence” (Bach’s and Levin’s largest insight)
01:12:10 Virtualization for unreliable hardware.
01:16:02 Defining “competence“
01:22:35 Bach’s issues with goals (for and against teleology)
01:27:34 Planarian goals and explicitly encoded instructions.
01:34:55 Navigation in “Morphic Space“
01:36:11 One species’ birth defect can be another’s benefit.
01:37:42 The “Intelligence Trap” and bias.
01:39:05 Application of each others’ work to their own.
01:52:25 Necessities of general intelligence in cells.

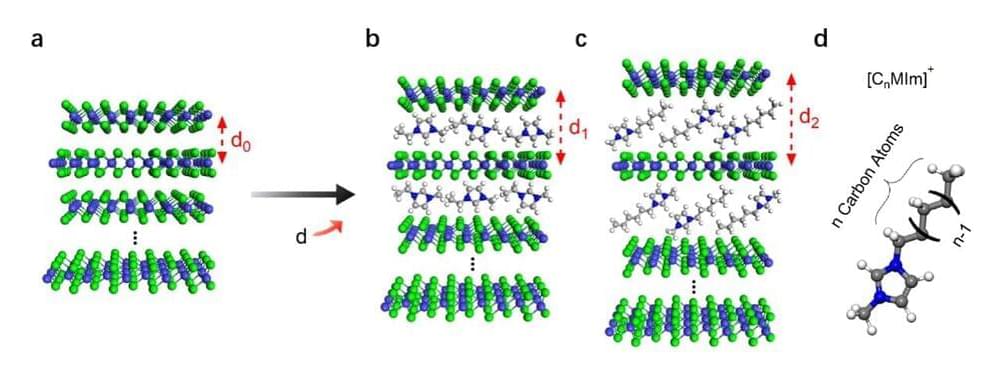
When 2D layered materials are made thinner (i.e., at the atomic scale), their properties can dramatically change, sometimes resulting in the emergence of entirely new features and in the loss of others. While new or emerging properties can be very advantageous for the development of new technologies, retaining some of the material’s original properties is often equally important.
Researchers at Tsinghua University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Frontier Science Center for Quantum Information have recently been able to realize tailored Ising superconductivity in a sample of intercalated bulk niobium diselenide (NbSe2), a characteristic of bulk NbSe2 that is typically compromised in atomically thin layers. The methods they used, outlined in a paper published in Nature Physics, could pave the way towards the fabrication of 2D thin-layered superconducting materials.
“Atomically thin 2D materials exhibit interesting properties that are often distinct from their bulk materials, which consist of hundreds and thousands of layers,” Shuyun Zhou, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “However, atomically thin films/flakes are difficult to fabricate, and the emerging new properties are sometimes achieved by sacrificing some other important properties.”
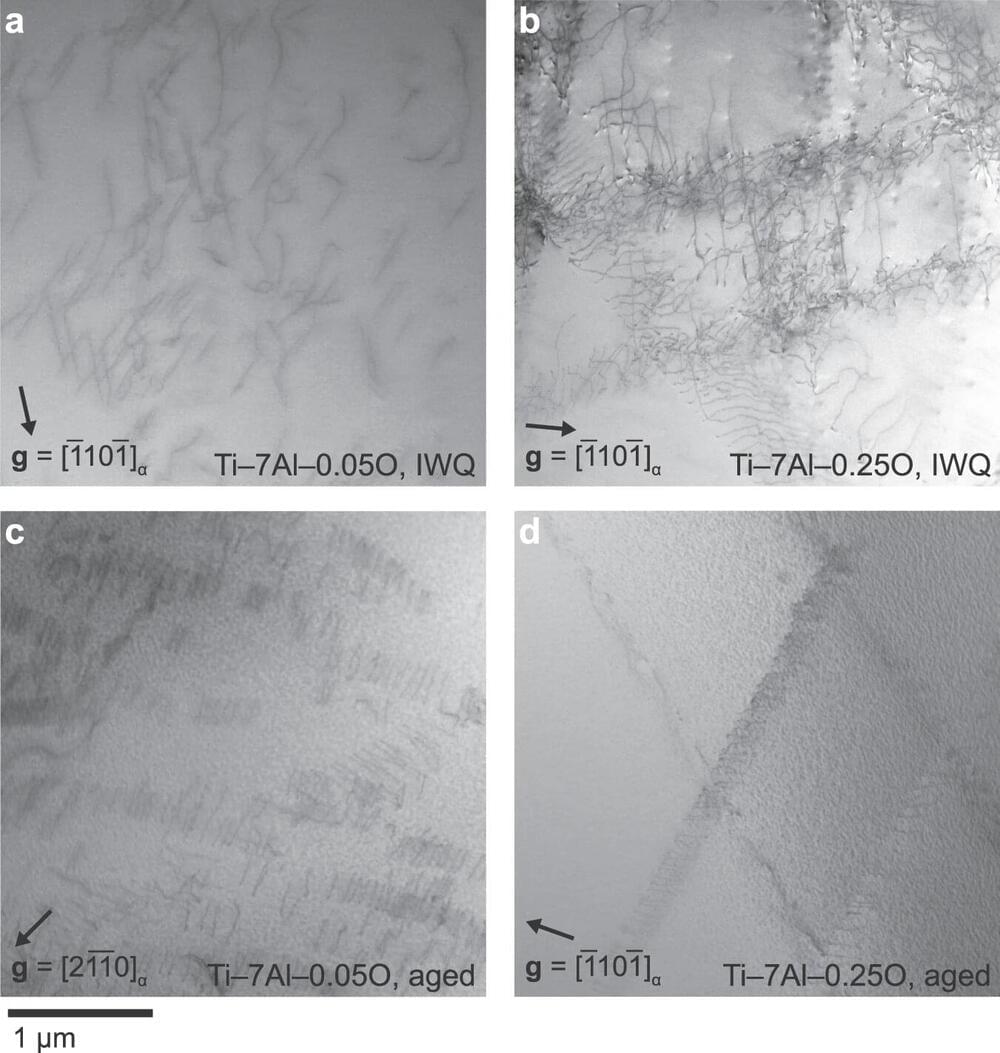
“Dwell fatigue” is a phenomenon that can occur in titanium alloys when held under stress, such as a jet engine’s fan disc during takeoff. This peculiar failure mode can initiate microscopic cracks that drastically reduce a component’s lifetime.
The most widely used titanium alloy, Ti-6Al-4V, was not believed to exhibit dwell fatigue before the 2017 Air France Flight 66 incident, in which an Airbus en route from Paris to Los Angeles suffered fan disc failure over Greenland that forced an emergency landing. The analysis of that incident and several more recent concerns prompted the Federal Aviation Administration and European Union Aviation Safety Agency to coordinate work across the aerospace industry to determine the root causes of dwell fatigue.
According to experts, metals deform predominantly via dislocation slip—the movement of line defects in the underlying crystal lattice. Researchers hold that dwell fatigue can initiate when slip is restricted to narrow bands instead of occurring more homogenously in three dimensions. The presence of nanometer-scale intermetallic Ti3Al precipitates promotes band formation, particularly when processing conditions allow for their long-range ordering.