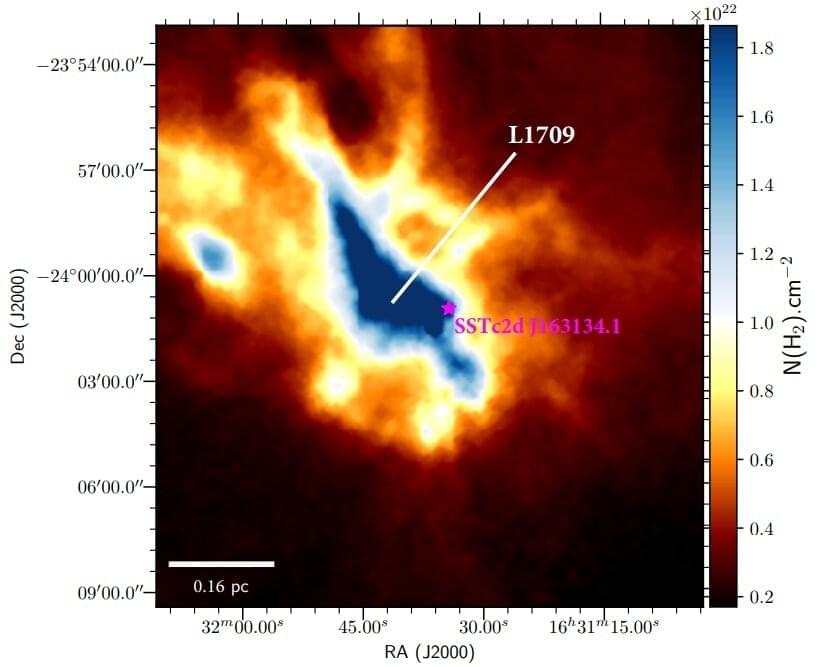
Astronomers report the detection of a new brown dwarf as part of the Ophiuchus Disk Survey Employing ALMA (ODISEA) program. The newfound object, designated SSTc2d J163134.1–24006, appears to be experiencing a quasi-spherical mass loss. The discovery was detailed in a paper published September 2 on the arXiv pre-print repository.
Brown dwarfs are intermediate objects between planets and stars, occupying the mass range between 13 and 80 Jupiter masses (0.012 and 0.076 solar masses). They can burn deuterium but are unable to burn regular hydrogen, which requires a minimum mass of at least 80 Jupiter masses and a core temperature of about 3 million K.
A team of astronomers led by Dary Ruiz-Rodriguez of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) in Charlottesville, Virginia, have investigated SSTc2d J163134.1–24006, initially identified as a faint stellar object, under the ODISEA project, which is dedicated to study the entire population of protoplanetary disks in the Ophiuchus Molecular Cloud. They found that SSTc2d J163134.1–24006 is most likely a brown dwarf with a mass of about 0.05 solar masses, and an elliptical shell of carbon monoxide (CO).