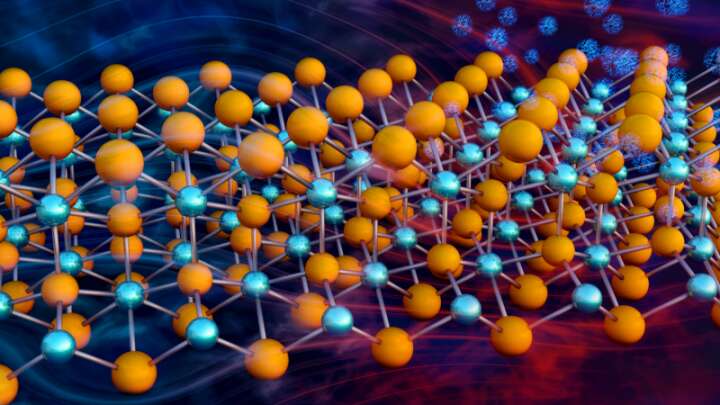
Engineers usually regard heat as “waste energy” since it is hard to efficiently turn into anything useful. However, a new class of thermoelectric materials could change that after researchers opted to try the exact opposite of the usual approach. A paper in Science Advances explains why, speeding the search for even better versions.
As the name suggests, thermoelectric materials turn heat into electricity, skipping the boiling water stage used in most bulk electricity production. However, cost and inefficiency have kept thermoelectric generators restricted to niche applications, such as powering spacecraft like the Mars Perseverance rover where lightweight, reliable energy production matters more than price.
Thermoelectric materials are too expensive and polluting for more widespread use, but new versions that replace heavier elements with magnesium could change that, opening the door to even better options that could find widespread uses.