Being called birdbrained should be a compliment. bigsmile
In cognitive tests for recognizing certain types of patterns, crows outperformed monkeys.

Flying car startup Airspeeder has completed what it’s referring to as the “world’s first electric flying car race” in the South Australian desert.
While the two competing pilots were steering the two full-scale flying cars remotely, it still made for an epic launch of a brand new kind of motorsport, as seen in a promotional video of the event.
“This is just the start, this first race offers only a glimpse of our promise to deliver the most progressive, transformative and exciting motorsport in the world,” Airspeeder founder Matt Pearson said in a press release.

To design better rechargeable ion batteries, engineers and chemists from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign collaborated to combine a powerful new electron microscopy technique and data mining to visually pinpoint areas of chemical and physical alteration within ion batteries.
A study led by materials science and engineering professors Qian Chen and Jian-Min Zuo is the first to map out altered domains inside rechargeable ion batteries at the nanoscale—a 10-fold or more increase in resolution over current X-ray and optical methods.
The findings are published in the journal Nature Materials.
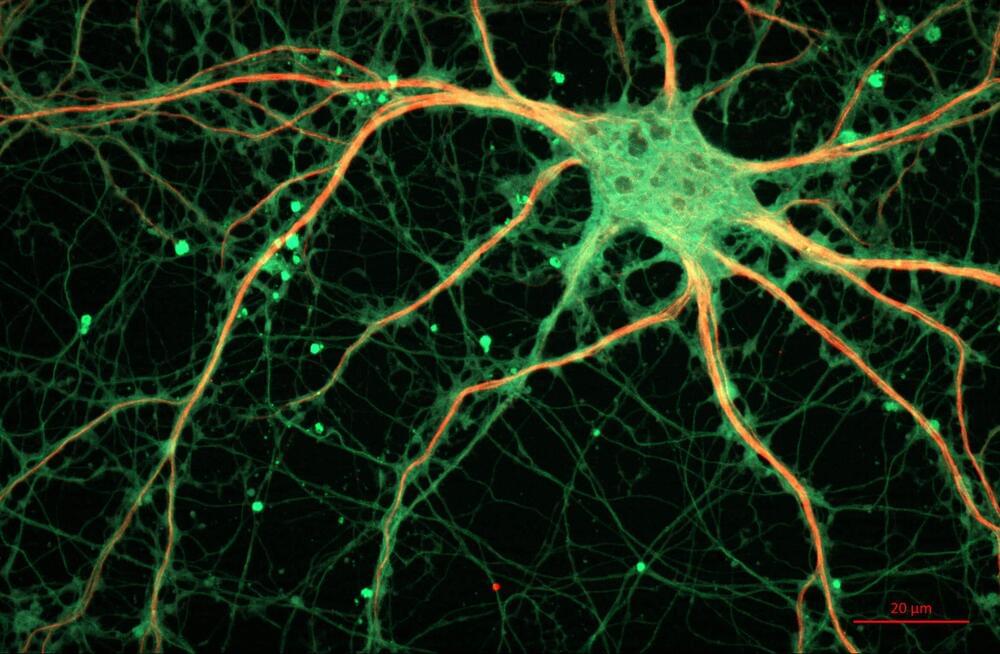
For a portion of people who get COVID, symptoms continue for months or even years after the initial infection. This is commonly referred to as “long COVID”.
Some people with long COVID complain of “brain fog”, which includes a wide variety of cognitive symptoms affecting memory, concentration, sleep and speech. There’s also growing concern about findings that people who have had COVID are at increased risk of developing brain disorders, such as dementia.
Scientists are working to understand how exactly a COVID infection affects the human brain. But this is difficult to study, because we can’t experiment on living people’s brains. One way around this is to create organoids, which are miniature organs grown from stem cells.
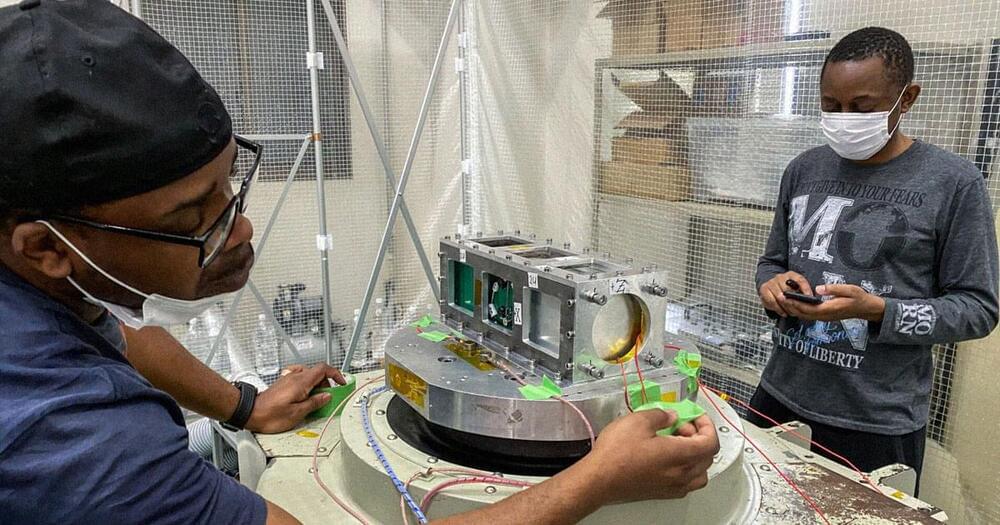


With the help of NASA and Japan, Uganda has officially become a spacefaring nation — and its newly-launched PearlAfricaSat-1 craft has some pretty nifty tech onboard.
As the Uganda-based Nile Post reports, the satellite launched out of NASA’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport facility in Virginia on the morning of November 7 will not only provide important agricultural and security monitoring features for the developing nation, but will also conduct experiments involving the 3D printing of human tissue.
Per the Ugandan news site, the tissues printed on PearlAfricaSat-1 will be used in research into the effects microgravity has on ovary function — and as Quartz notes in its write-up of the NASA and Japan-supported mission, the microgravity aspect of the experiments is key because “bioprinting” human organs is difficult to achieve with Earth’s gravity.
Circa 2016 face_with_colon_three
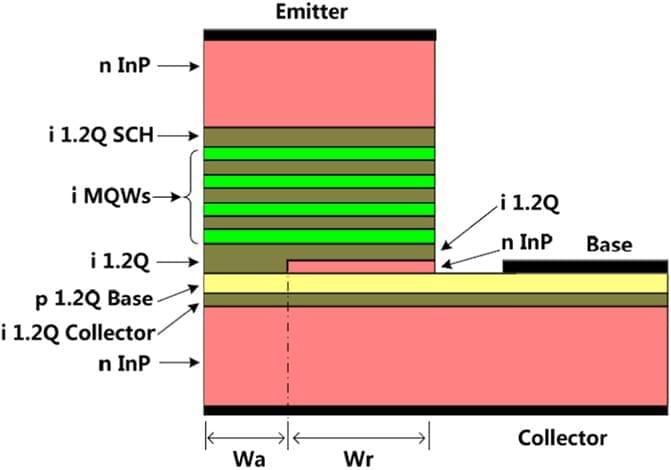
A transistor laser (TL)1,2,3, having the structure of a transistor with multi-quantum wells (MQWs) near its base region, bridges the functionality gap between lasers and transistors. From a TL, an electrical signal can be outputted simultaneously with a light signal by inputting one electrical signal, making it suitable for future high performance optoelectronic integrated device applications4. As a new kind of semiconductor laser or transistor, TLs have aroused many interests since its invention. For example, in 2006, the paper2 reporting the first room temperature operation of TLs was voted as one of the five most important papers published by Applied Physics Letters in over 40 years5. Because of the transistor structure, many interesting characters have been demonstrated, including resonance free frequency response, large direct modulation band width6, voltage controlled mode of operation7, low relative intensity noise (RIN) close to the shot-noise limit8 and low 3rd order intermodulation distortion (IMD)9.
However, light emission for all the TLs reported up to now is produced at the expense of current gain. Taking npn TLs as an example, in the devices, electrons injected from the emitter into the base layer first recombine with holes radiatively before the left being collected by the collector4. The majority of the electrons are consumed by stimulated light emissions, leading to a current gain which is a lot lower than the gain of a traditional transistor. The common emitter (CE) mode current gain (collector current/base current) is lower than 5 for most, if not all, of the TLs studied, either experimentally1,2,3,6,7,8,9,10 or numerically11,12,13. The low current gain may limit the performance of systems that use TLs. For example, it is much easier to integrate monolithically a heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) and a TL than to integrate an HBT with a laser diode (LD) because of the dual functionality of TLs. For such applications, a large current gain of TL (used as HBT) is desired for the amplification of electrical signal to drive the laser.
In this work, we propose a novel TL structure which has an n-doped InP layer inserted in the emitter ridge, forming a flow aperture in the center of the emitter ridge for only holes. Here after, the TLs having the hole current aperture is designated as a-TLs. The properties of the a-TLs are systematically studied numerically. It is shown that while the light emission power of a-TLs is comparable with that of TLs without the aperture at the same base current, the CE current gain of a-TLs can be over 15 times larger.
Organic electronic-based gas sensors hold great potential for portable healthcare-and environment-monitoring applications. It has recently been shown that introducing a porous structure into an organic semiconductor (OSC) film is an efficient way to improve the gas-sensing performance because it facilitates the interaction between the gaseous analyte and the active layer. Although several methods have been used to generate porous structures, the development of a robust approach that can facilely engineer the porous OSC film with a uniform pore pattern remains a challenge. Here, we demonstrate a robust approach to fabricate porous OSC films by using a femtosecond laser-processed porous dielectric layer template. With this laser-assisted strategy, various polymeric OSC layers with controllable pore size and well-defined pore patterns were achieved.