Researchers from the group of Hans Clevers (Hubrecht Institute) corrected mutations that cause cystic fibrosis in cultured human stem cells. In collaboration with the UMC Utrecht and Oncode Institute, they used a technique called prime editing to replace the ‘faulty’ piece of DNA with a healthy piece. The study, published in Life Science Alliance on August 9 shows that prime editing is safer than the conventional CRISPR/Cas9 technique. “We have for the first time demonstrated that this technique really works and can be safely applied in human stem cells to correct cystic fibrosis.”
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is one of the most prevalent genetic diseases worldwide and has grave consequences for the patient. The mucus in the lungs, throat and intestines is sticky and thick, which causes blockages in organs. Although treatments are available to dilute the mucus and prevent inflammations, CF is not yet curable. However, a new study from the group of Hans Clevers (Hubrecht Institute) in collaboration with the UMC Utrecht and Oncode Institute offers new hope.
Correcting CF mutations
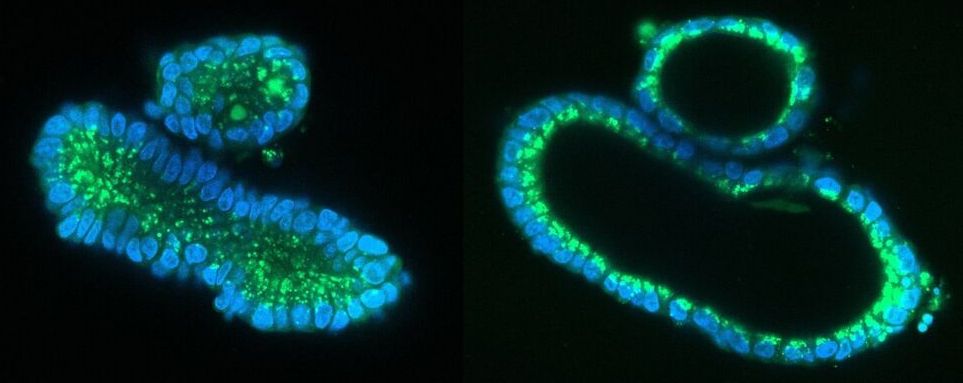
The researchers succeeded in correcting the mutations that cause CF in human intestinal organoids. These organoids, also called mini-organs, are tiny 3D structures that mimic the intestinal function of patients with CF. They were previously developed by the same research group from stem cells of patients with CF and stored in a biobank in Utrecht. For the study, published in Life Science Alliance, a technique named prime editing was used to replace the piece of mutated DNA that causes CF with a healthy piece of DNA in these organoids.