Circa 2015 face_with_colon_three
Scientific Reports volume 5, Article number: 12,488 (2015) Cite this article.
Circa 2015 face_with_colon_three
Scientific Reports volume 5, Article number: 12,488 (2015) Cite this article.

Circa 2020 face_with_colon_three
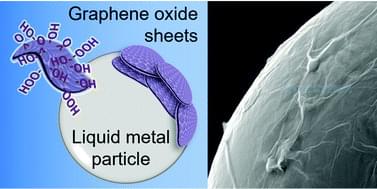
Liquid metals are a promising functional material due to their unique combination of metallic properties and fluidity at room temperature. They are of interest in wide-ranging fields including stretchable and flexible electronics, reconfigurable devices, microfluidics, biomedicine, material synthesis, and catalysis. Transformation of bulk liquid metal into particles has enabled further advances by allowing access to a broader palette of fabrication techniques for device manufacture or by increasing area available for surface-based applications. For gallium-based liquid metal alloys, particle stabilization is typically achieved by the oxide that forms spontaneously on the surface, even when only trace amounts of oxygen are present. The utility of the particles formed is governed by the chemical, electrical, and mechanical properties of this oxide. To overcome some of the intrinsic limitations of the native oxide, it is demonstrated here for the first time that 2D graphene-based materials can encapsulate liquid metal particles during fabrication and imbue them with previously unattainable properties. This outer encapsulation layer is used to physically stabilize particles in a broad range of pH environments, modify the particles’ mechanical behavior, and control the electrical behavior of resulting films. This demonstration of graphene-based encapsulation of liquid metal particles represents a first foray into the creation of a suite of hybridized 2D material coated liquid metal particles.

Circa 2020 face_with_colon_three
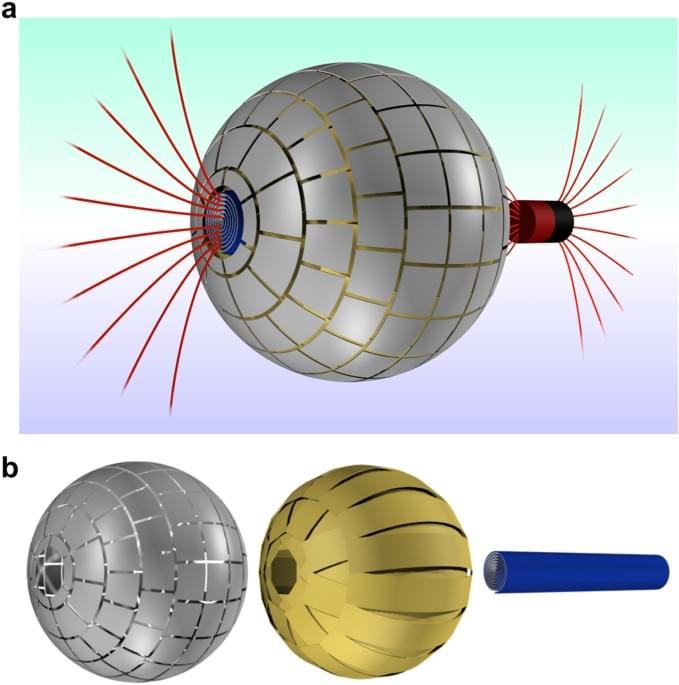
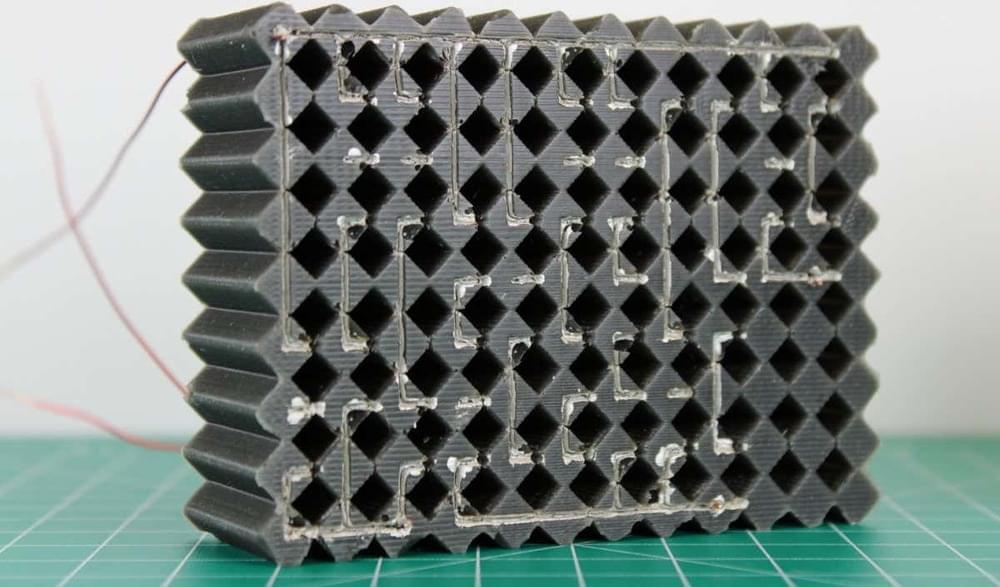
UNSW researchers have overcome a major design challenge on the path to controlling the dimensions of so-called DNA nanobots—structures that assemble themselves from DNA components.
Self-assembling nanorobots may sound like science fiction, but new research in DNA nanotechnology has brought them a step closer to reality. Future nanobot use cases won’t just play out on the tiny scale, but include larger applications in the health and medical field, such as wound healing and unclogging of arteries.
Researchers from UNSW, with colleagues in the UK, have published a new design theory in ACS Nano on how to control the length of self-assembling nanobots in the absence of a mould, or template.

Circa 2020 face_with_colon_three
Light-activated molecular nanomachines (MNMs) can be used to drill holes into prokaryotic (bacterial) cell walls and the membrane of eukaryotic cells, including mammalian cancer cells, by their fast rotational movement, leading to cell death. We examined how these MNMs function in multicellular organisms and investigated their use for treatment and eradication of specific diseases by causing damage to certain tissues and small organisms. Three model eukaryotic species, Caenorhabditis elegans, Daphnia pulex, and Mus musculus (mouse), were evaluated. These organisms were exposed to light-activated fast-rotating MNMs and their physiological and pathological changes were studied in detail. Slow rotating MNMs were used to control for the effects of rotation rate. We demonstrate that fast-rotating MNMs caused depigmentation and 70% mortality in C.

Say hello to ronnagrams and quettameters: International scientists gathered in France voted on Friday for new metric prefixes to express the world’s largest and smallest measurements, prompted by an ever-growing amount of data.
It marks the first time in more than three decades that new prefixes have been added to the International System of Units (SI), the agreed global standard for the metric system.
Joining the ranks of well-known prefixes like kilo and milli are ronna and quetta for the largest numbers – and ronto and quecto for the smallest.
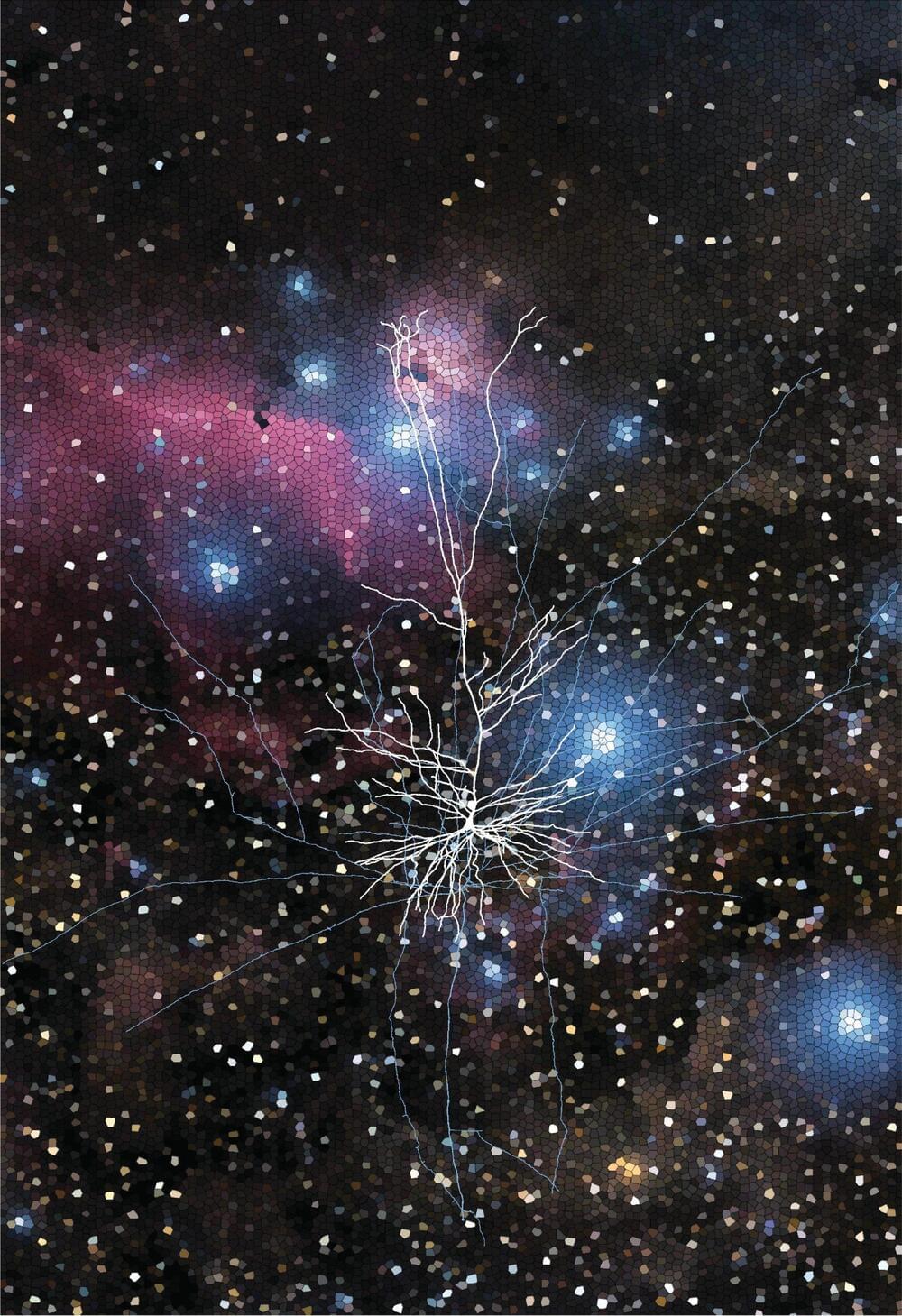
Researchers have discovered the human brain’s enhanced processing power may stem from differences in the structure and function of our neurons. Credit: Queensland Brain Institute / Professor Stephen Williams.
The human brain’s function is remarkable, driving all aspects of our creativity and thoughts. However, the neocortex, a region of the human brain responsible for these cognitive functions, has a similar overall structure to other mammals.
Researchers from The University of Queensland (UQ), The Mater Hospital, and the Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital have shown that changes in the structure and function of our neurons may be the cause of the human brain’s increased processing power.
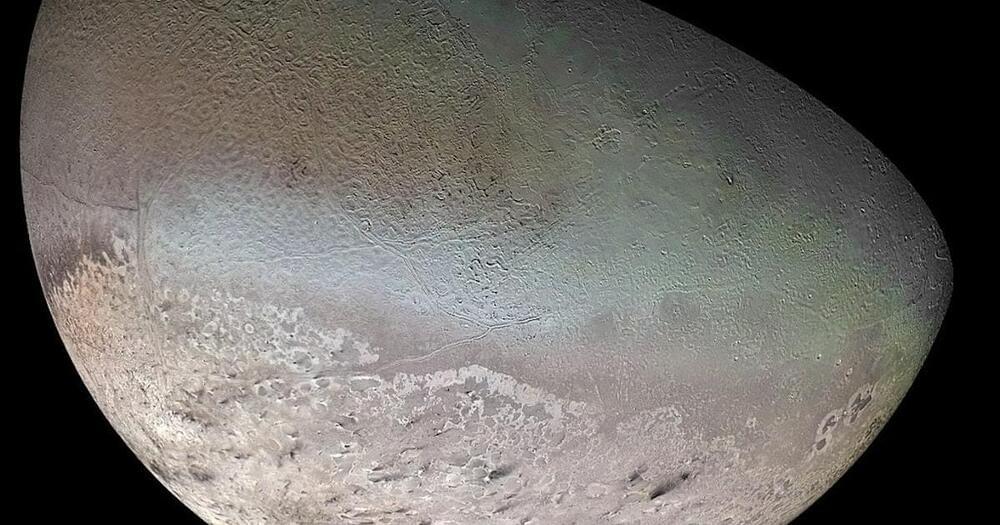

It’s frigid and strange and orbits its home planet backward.
But Enceladus isn’t the only location in our solar system with active geysers, as another small moon near the edge of the solar system shares similar characteristics, as well. This is Neptune’s largest moon, Triton, which has been visited only once by NASA’s Voyager 2 in 1989. But are Triton’s geysers the only characteristics that make it a good target for astrobiology and finding life beyond Earth?
“Triton may be an ‘ocean world’, a moon that has a solid ice crust over a liquid water subsurface ocean,” said Candice Hansen-Koharchek, a planetary scientist who was a Voyager Imaging Team Assistant Experiment Representative during the Voyager missions. “If that is the case, and if we are able someday to reach that ocean and find life, that would extend the habitable zone to the Kuiper Belt, not just the inner solar system. That has profound implications, both in our solar system and at exoplanets.”
Due to its geysers, which Voyager 2 identified as dark streaks, Triton is only the third known planetary body in the Solar System to be volcanically active, aside from Earth and Jupiter’s innermost Galilean moon, Io.