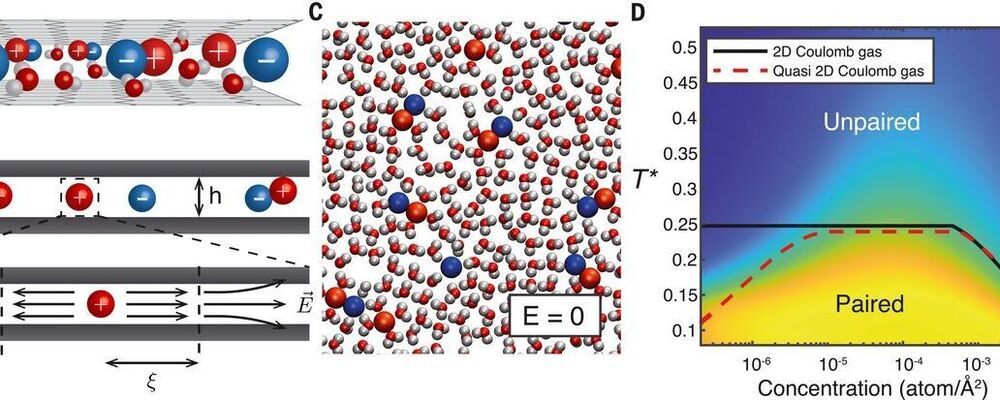
Most memory resistor (“memristor”) systems use electrons as the charge carrier, but it may also be possible to use ionic carriers, similar to the way that neurons work. Robin et al. studied an aqueous electrolyte confined into a pseudo two-dimensional gap between two graphite layers (see the Perspective by Hou and Hou). The authors observed a current–voltage relation that exhibits hysteresis, and the conductance depends on the history of the system, also known as the memresistor effect. Using simulations of their system, they can model the emission of voltage spikes characteristic of neuromorphic activity.
Science, abf7923, this issue p. 687; see also abj0437, p. 628
Recent advances in nanofluidics have enabled the confinement of water down to a single molecular layer. Such monolayer electrolytes show promise in achieving bioinspired functionalities through molecular control of ion transport. However, the understanding of ion dynamics in these systems is still scarce. Here, we develop an analytical theory, backed up by molecular dynamics simulations, that predicts strongly nonlinear effects in ion transport across quasi–two-dimensional slits. We show that under an electric field, ions assemble into elongated clusters, whose slow dynamics result in hysteretic conduction. This phenomenon, known as the memristor effect, can be harnessed to build an elementary neuron. As a proof of concept, we carry out molecular simulations of two nanofluidic slits that reproduce the Hodgkin-Huxley model and observe spontaneous emission of voltage spikes characteristic of neuromorphic activity.