Integrating robots into walls, ceilings, furniture, and appliances could radically change our indoor spaces.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Elon Musk LAUGHS at a Silly Question and Then Gives a BRUTAL but BRILLIANT Answer!
This is how you do it.
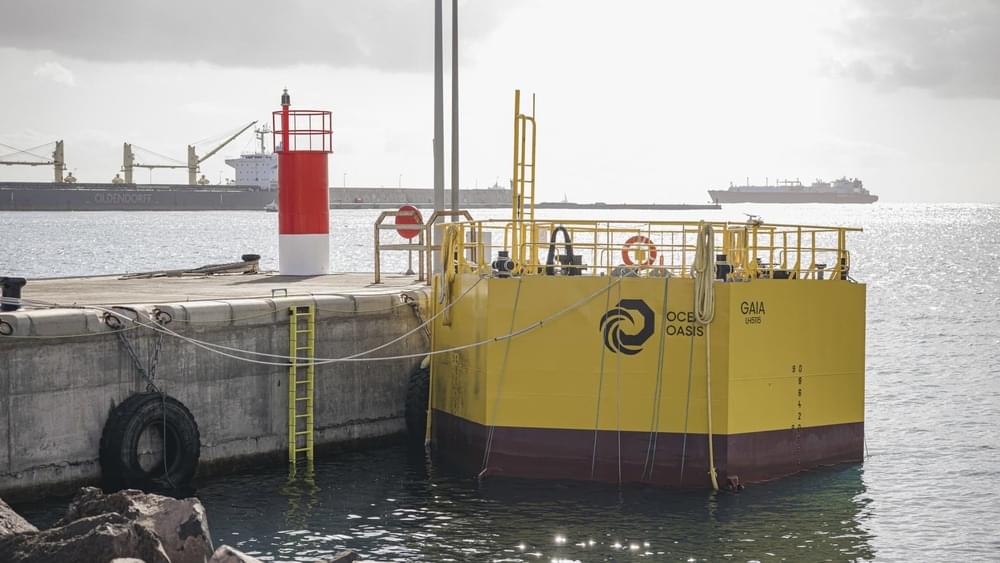

A wave-powered prototype device is aiming to produce drinking water from the ocean
With the above in mind, projects looking to desalinate water in a more sustainable way will become increasingly important in the years ahead.
The idea of using waves to power desalination is not unique to the project being undertaken in the Canaries. In April, for example, the U.S. Department of Energy revealed the winners of the last stage of a competition focused on wave-powered desalination.
Back on the Canary Islands, Ocean Oasis said it would be looking to construct a second installation after testing at the PLOCAN facility had taken place. “In this phase, the prototype will be scaled with the capacity to produce water for consumption,” the company said.
Reasons To Be Optimistic About The Future
Ground News Black Friday Sale: Compare news coverage. Spot media bias. Avoid algorithms. Download the free Ground News app to get 40% off a Ground News Vantage membership by going to https://ground.news/isaacarthur.
As we head through hard times things can seem rather bleak, but there’s lots of amazing and beneficial technologies on the horizon.
Checkout the World’s Fair Posters: https://worldsfair.co/gallery.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-arthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/reasons-to-be-…the-future.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/reasons-to-be-…ation-only.
Credits:
Reasons To Be Optimistic About The Future.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 372, November 24, 2022
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
Alex Civitello.
Konstantin Sokerin.
David McFarlane.
Cover Art:
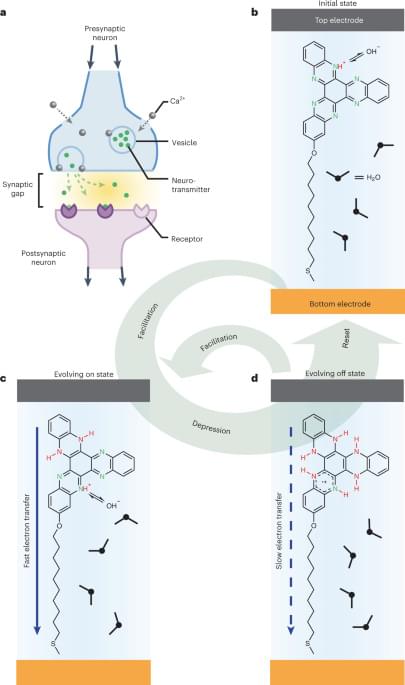
Dynamic molecular switches with hysteretic negative differential conductance emulating synaptic behaviour
To realize electronic operations beyond the von Neumann bottleneck, a new type of switch that can mimic self-learning is needed. Here, the authors demonstrate all-in-one-place logic and memory operations based on dynamic molecular switch that can emulate brain-like synaptic and Pavlovian response, bringing the field a step closer to molecular-scale hardware.
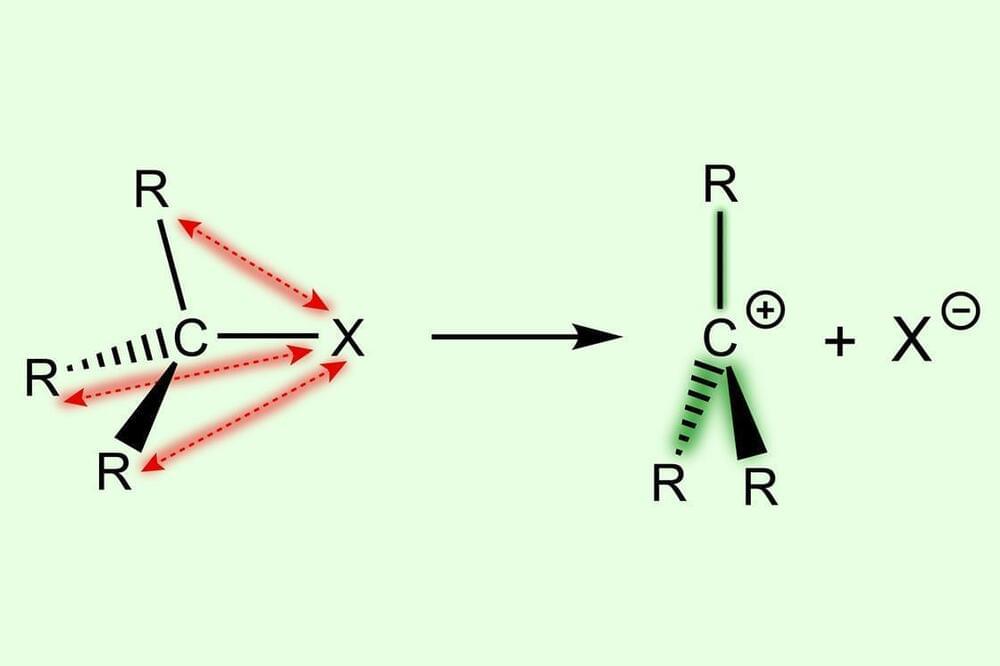
Quantum chemical analysis uncovers previously overlooked contributor to carbocation stability trend
It is easier to form more substituted carbocations because of destabilisation in the parent substrate, rather than stabilisation in the reactive intermediate, new research shows.1
Many organic transformations involve carbocations as reactive intermediates. These are usually formed via a heterolytic C–X bond dissociation to give a carbocation C+ and an anion X-. Current understanding is that the bond dissociation energy decreases with increased methyl substitution because of the stabilising effect of the methyl groups, as well as relief due to steric repulsion: going from substrate to carbocation gives the substituents proportionally more room in a more substituted system. However, a team in the Netherlands, led by Matthias Bickelhaupt at VU Amsterdam, has investigated this from a different angle.

Study sheds new light on the link between oral bacteria and diseases
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified the bacteria most commonly found in severe oral infections. Few such studies have been done before, and the team now hopes that the study can provide deeper insight into the association between oral bacteria and other diseases. The study is published in Microbiology Spectrum.
Previous studies have demonstrated clear links between oral health and common diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. However, there have been few longitudinal studies identifying which bacteria occur in infected oral-and maxillofacial regions. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have now analyzed samples collected between 2010 and 2020 at the Karolinska University Hospital in Sweden from patients with severe oral infections and produced a list of the most common bacteria.
This was a collaborative study that was performed by Professor Margaret Sällberg Chen and adjunct Professor Volkan Özenci’s research groups.
