Track 4 from the split digital album between Triangular Ascension & Abiotha.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Dr. George Church—Gene Therapy and Aging
In this episode of Longevity by Design, our hosts, Dr. Gil Blander and Ashley Reaver, MS, RD, CSSD, are joined by Dr. George Church, Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School. Tune in as Dr. George Church discusses the many roles of gene therapy, including its ability to reverse age-related diseases.
For science-backed ways to live a healthier, longer life, download InsideTracker’s InnerAge eBook at insidetracker.com/podcast.
Social:
Instagram — https://www.instagram.com/insidetracker.
Twitter — https://twitter.com/InsideTracker.
Facebook — https://www.facebook.com/InsideTracker.
Website — https://www.insidetracker.com/
In the Press — https://www.insidetracker.com/press-page/
NASA Says Space Debris Will Definitely Slam Into the James Webb Space Telescope
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is “fully deployed,” according to the agency’s science administrator Thomas Zurbuchen — and that’s certainly a reason to celebrate after decades of hard work and a ten billion dollar price tag.
But the massive space observatory isn’t out of the woods just yet. As it spins around the Sun in a chaotic orbit, it will likely encounter plenty of space debris along the way — and an impact, its team says, is likely inevitable.
“Some small impacts from micrometeorites will happen,” NASA Goddard Space Flight Center scientist Michelle Thaller said during a livestream over the weekend. “You know, over the lifetime of the mission there will be some damage to the mirrors of the telescope.”

Scientists Puzzled by “Spooky” Object Sending Radio Signals Every 18 Minutes From Deep Space
Astronomers are flummoxed by a mysterious celestial object that appears to be releasing massive bursts of energy at regular 18 minute intervals.
Like a lighthouse, the beacon is sending out radiation three times an hour at such an intensity that it’s one of the brightest points in the sky — and, researchers say, it could turn out to be an entirely new class of celestial object.
A team, led by astrophysicist Natasha Hurley-Walker from the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research, had a closer look at the object after it was discovered by Curtin University student Tyrone O’Doherty, who used the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) telescope in outback Western Australia.

Fast-growing Austin-area motor maker Infinitum Electric looks to jump into EV market
Round Rock-based motor company Infinitum Electric is expanding as it steps up production and breaks into the electric vehicle business.
The company is growing its footprint and workforce on the back of an $80 million funding round, which it announced this week. The financial infusion brings the company’s funding to date to $135 million.
Infinitum Electric was founded in 2016 in Austin by CEO Ben Schuler and moved to Round Rock in 2019. The motors include circuit boards that cut down on some of the costly equipment required in traditional motors, making Infinitum’s motors more efficient, smaller and quieter than traditional motors, according to the company.
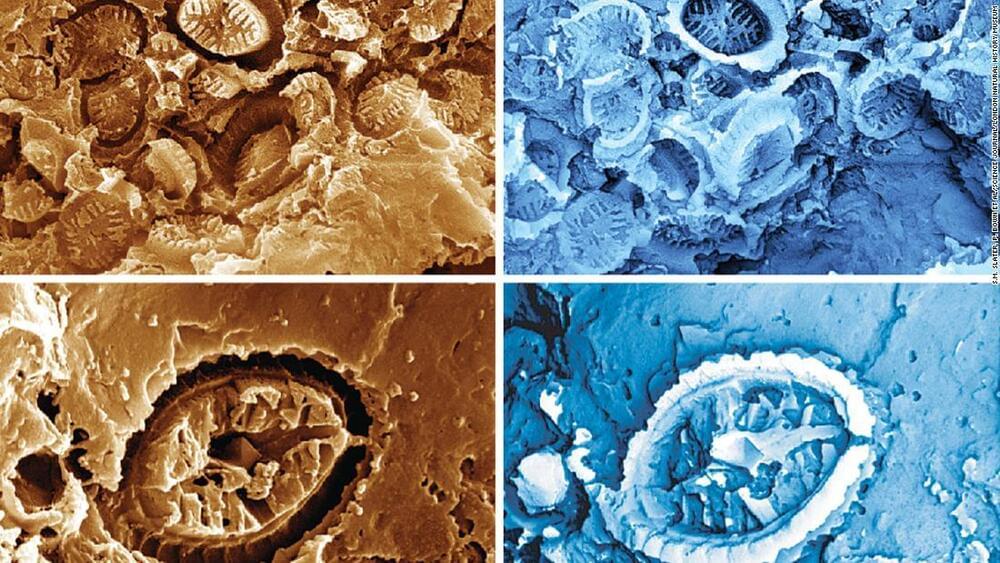
Scientists discover ‘ghost’ fossils beneath a microscope
The unexpected discovery of “ghost” fossils belonging to tiny, ancient organisms could provide insights about how life reacts to climate change in Earth’s oceans.
Looking through a powerful microscope, researchers were stunned to see the impressions left by single-celled plankton, or fossilized nannoplankton, that lived millions of years ago – especially since they were analyzing something else.
A study detailing the findings published Thursday in the journal Science.
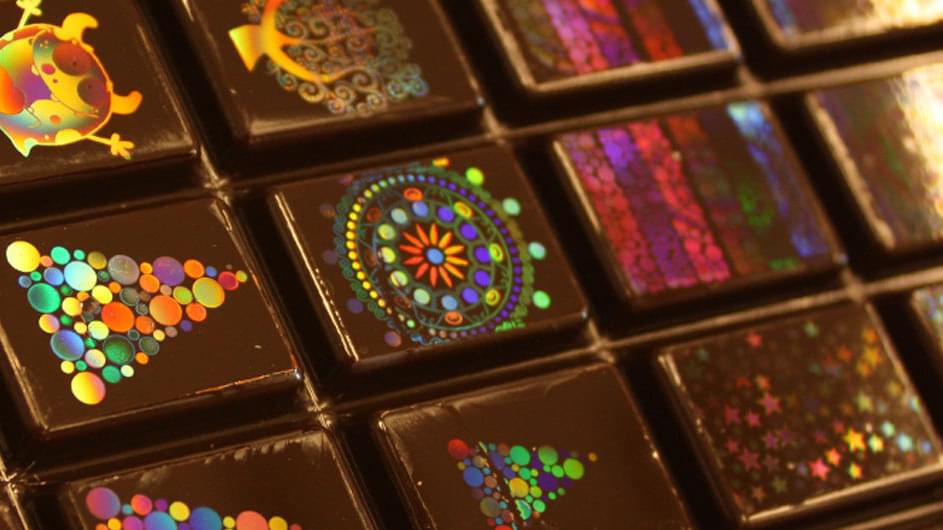


Holographic Chocolates Look As Beautiful As They Taste
Circa 2014
For most of us, even one bite of chocolate is enough to send our taste buds into ecstasy. Now, scientists have concocted a process to make these dark, dulcet morsels look as decadent as they taste.
Switzerland-based company Morphotonix has given traditional Swiss chocolate-making a colorful twist: It’s devised a method to imprint shiny holograms onto the sweet surfaces — sans harmful additives. Which means when you tilt the goodies from side to side, rainbow stars and swirly patterns on the chocolate’s surface dance and shimmer in the light.
Typically, holograms are laser-imprinted onto a flat, metallic surface such as aluminum; the rainbow-colored hologram appears when light hits the surface at a certain angle (Think of the security sticker on the back of your credit card). But aluminum-drenched chocolate doesn’t sound very appetizing, so confectioners pour the chocolate into a mold etched with a patchwork of minuscule bumps, or microstructures, that bend light at specific angles — embedding a hologram directly onto its surface.