This Japanese AI startup just raised $100M to cut businesses’ admin burden.



Does it sound familiar to you the name James Webb? Maybe you’ve heard about it because it’s a very important telescope scientists use on its missions. Recently, this telescope and the Hubble have confirmed the universe is expanding in two different directions. I know it is difficult to believe, even scientists doubt it at first, but telescopes have proved it. So, let’s find out more about what the James Webb Space Telescope and the Hubble telescope have found.
To make this scientific explanation more visual, imagine you draw small dots on the surface of a deflated balloon and then you blow it up. What do you think will happen to the dots? Exactly! They will be far from each other because the balloon stretches.
So, this is what happens with the universe. Galaxies separate because space itself is expanding, and the speed this is occurring is called: the Hubble constant. You may not know this, but this is so important that it helps us know the age and destiny of the universe.

Looking for the perfect vacation? Do you crave late-night fun? PSO J318.5−22, the planet with no star where nightlife never ends, is perfect for you! Prefer some peace and a chance to catch some rays? Kepler-16b, the land of two suns—where your shadow always has company—is waiting.
In 2015, NASA launched an unusual and brilliant exoplanet outreach campaign, offering retro-style posters, virtual guided tours, and even coloring books. The project quickly went viral worldwide. What explains the success of a campaign about a relatively young field of science that—unlike other areas of space research—lacks spectacular imagery?
Ceridwen Dovey, science communicator, writer, filmmaker, and researcher, has just published in the Journal of Science Communication a Practice Insight paper that presents a case study focusing on the Exoplanet Travel Bureau’s poster campaign. Dovey describes the productive working relationships between scientists and artists that produced this standout work and shows how, in contexts like this, artists are not merely in service to science but can also inspire research itself and help scientists clarify their own thinking.

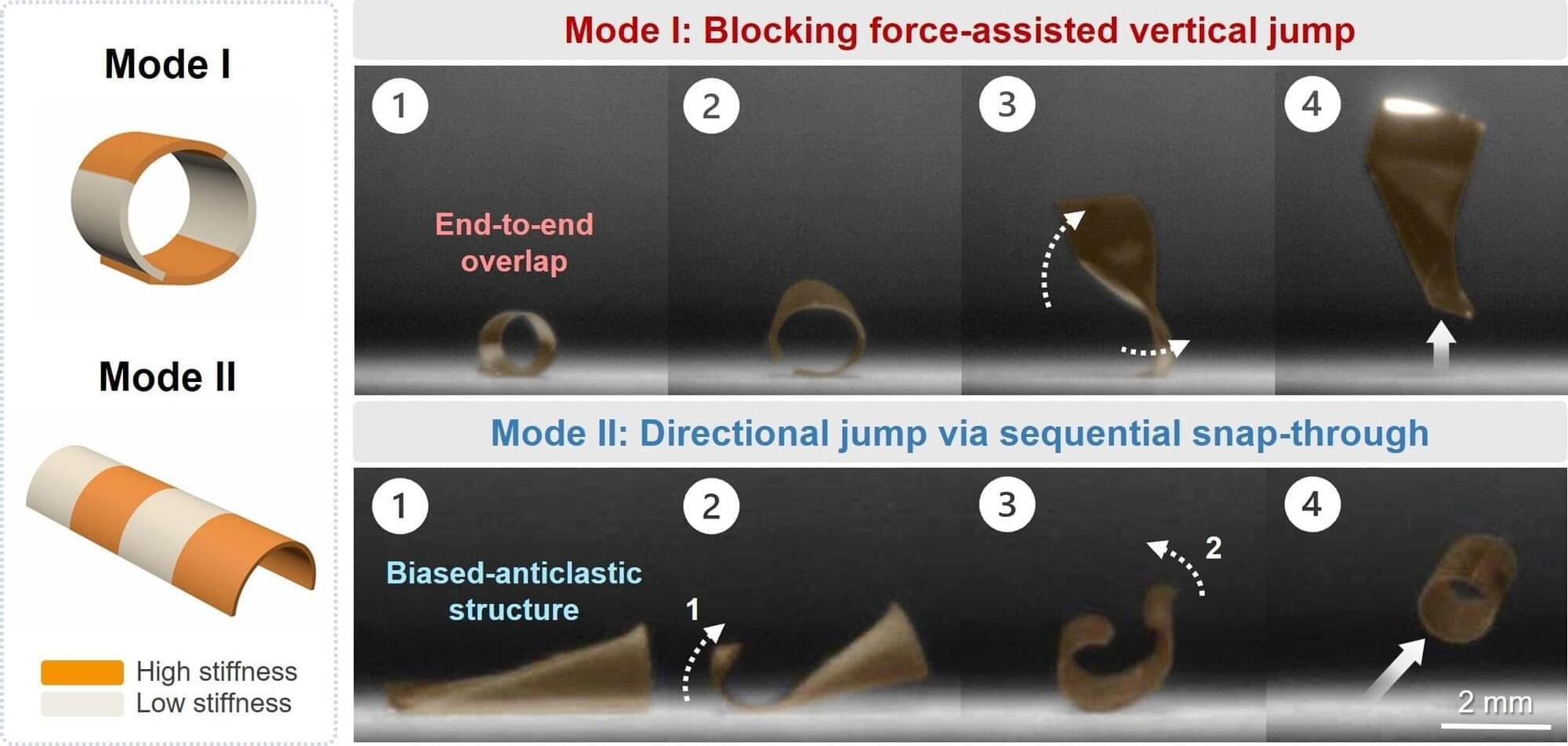
Everyday occurrences like snapping hair clips or clicking retractable pens feature a mechanical phenomenon known as “snap-through.” Small insects and plants like the Venus flytrap cleverly use this snap-through effect to amplify their limited physical force, rapidly releasing stored elastic energy for swift, powerful movements.
Inspired by this natural mechanism, researchers from Hanyang University have developed a polymer-based jumper capable of both vertical and directional leaps, triggered simply by uniform ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation.
Published in Science Advances, this study tackles a classic engineering dilemma: how to make soft materials produce strong, rapid motions.
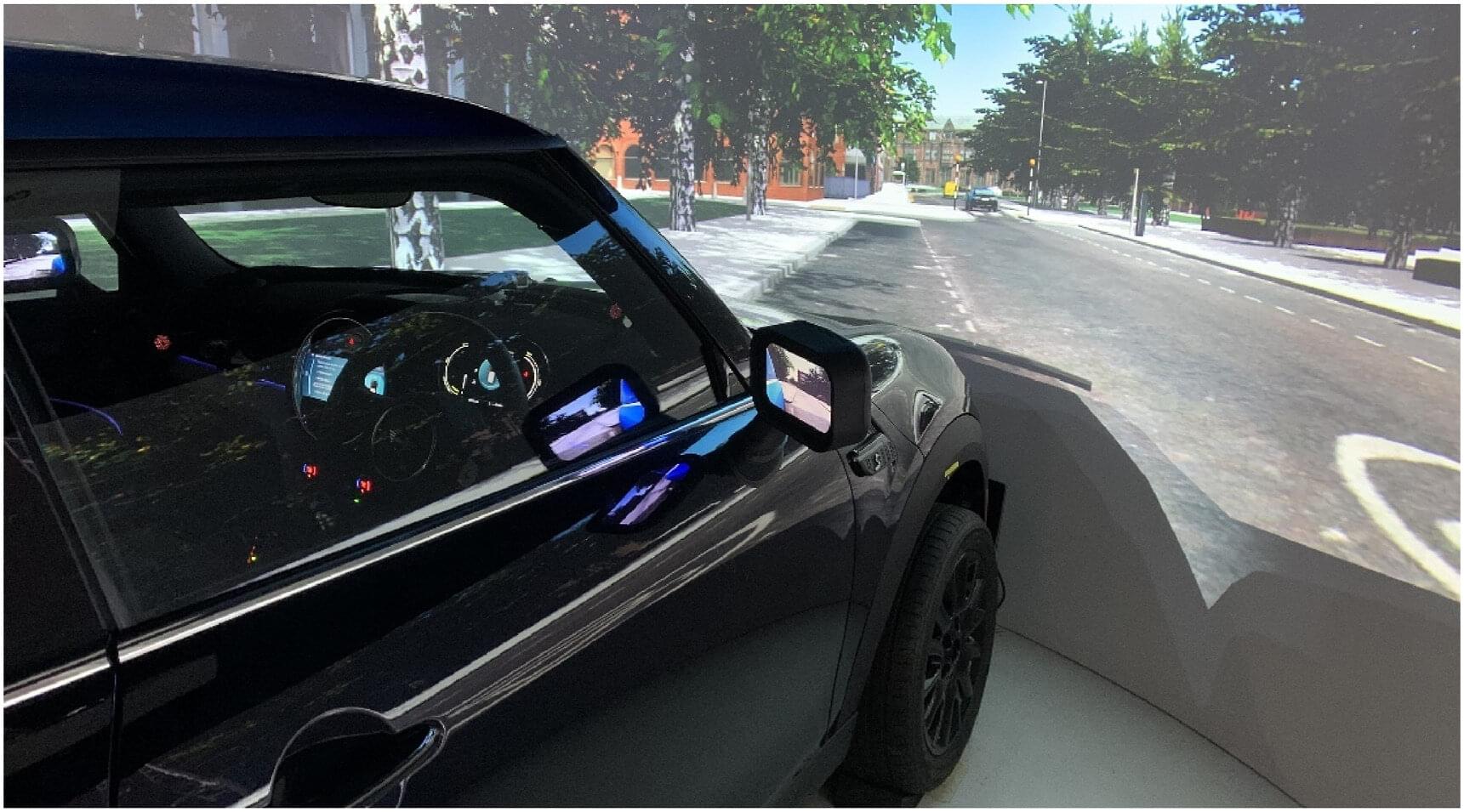

It is possible for one person to safely monitor up to five self-driving vehicles at once, according to new research led by Coventry University.
As self-driving vehicle trials expand across the UK, having trained people to intervene remotely if something goes wrong is essential for both safety and reliability.
This kind of remote oversight is likely to be used for services such as driverless buses, delivery vehicles and robotaxis, where one person monitors several vehicles as they follow fixed routes. It doesn’t apply to private self-driving cars, where a driver would currently need to be in the vehicle and in control.
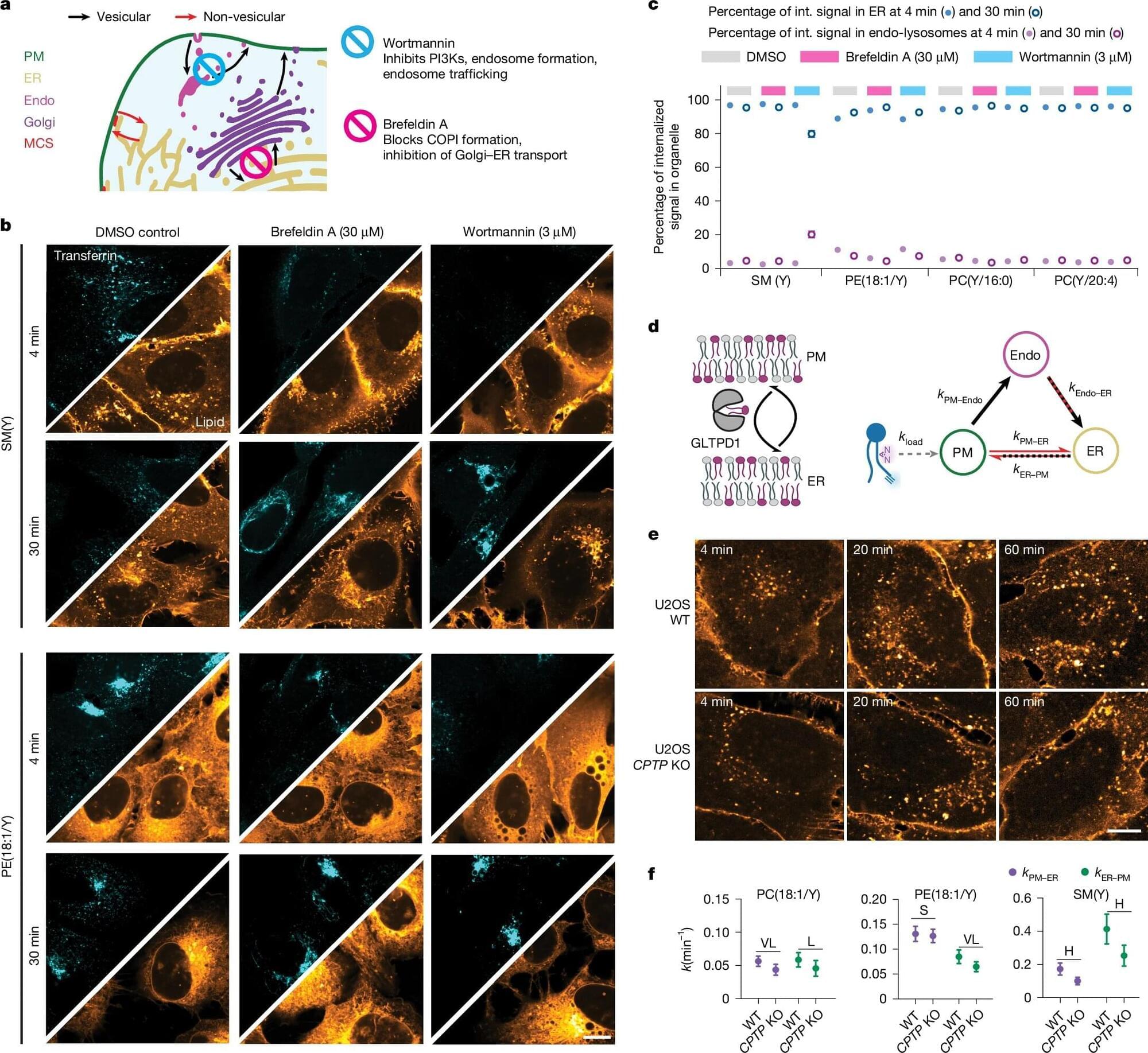
Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics led a study showing that directional, non-vesicular lipid transport drives fast, species-selective lipid sorting, outpacing slower, less specific vesicular trafficking, and yielding a quantitative map of retrograde lipid transport in cells.
Thousands of lipid species occupy distinct organelle membranes, with task differences that determine cellular function. Gaps in live-cell imaging capabilities have limited clarity on how individual lipids move between organelles to maintain those tasks.
Biosynthesis of lipids begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), followed by distribution toward the plasma membrane and subsequent recycling back into the ER or catabolism in lysosomes, peroxisomes, and mitochondria.

A research team affiliated with UNIST has successfully demonstrated the experimental creation of collective quantum entanglement rooted in dark states—previously confined to theoretical models. The findings are published online in Nature Communications.
Unlike bright states, dark states are highly resistant to external disturbances and exhibit remarkably extended lifetimes, making them promising candidates for next-generation quantum technologies such as quantum memory and ultra-sensitive sensors.
Led by Professor Je-Hyung Kim in the Department of Physics at UNIST, in collaboration with Dr. Changhyoup Lee from the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) and Dr. Jin Dong Song from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), the team has achieved the controlled induction of dark state-based collective entanglement. Remarkably, this entanglement exhibits a lifetime approximately 600 times longer than that of conventional bright states.
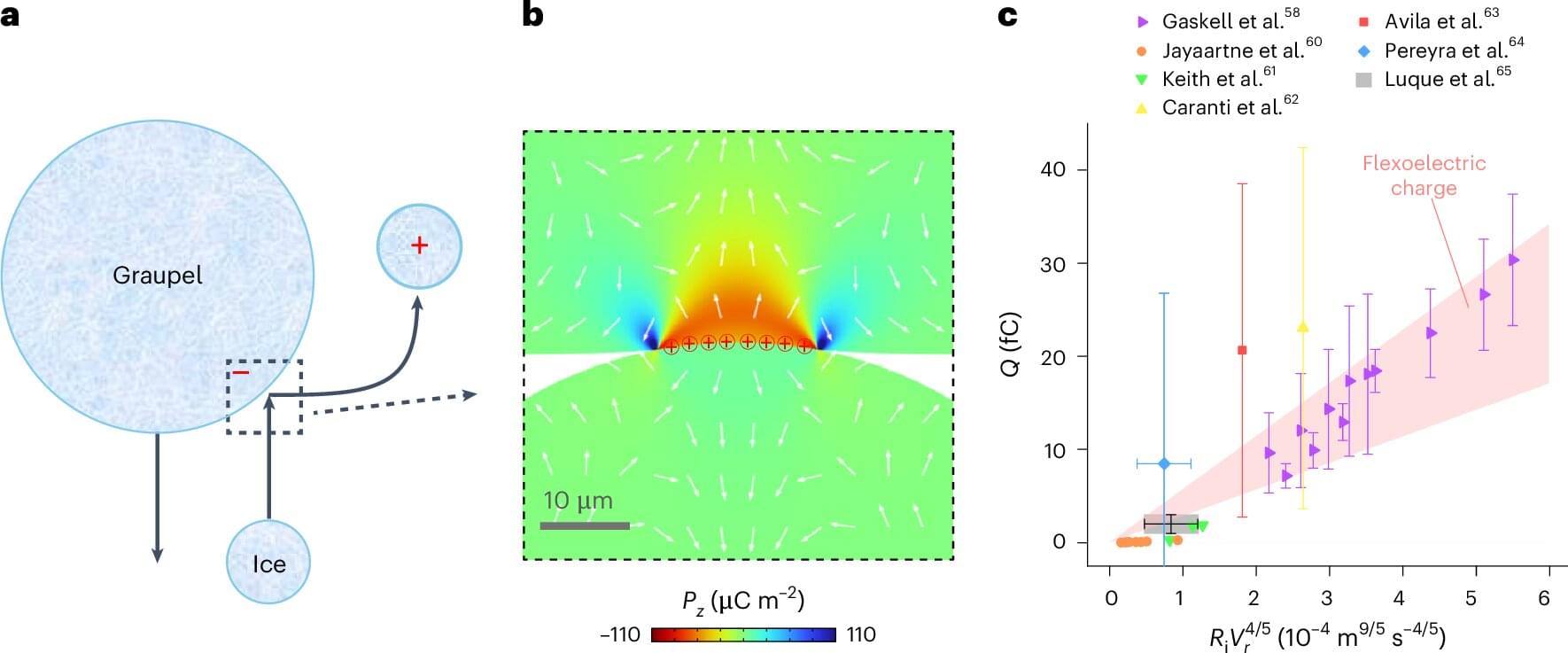
A study co-led by ICN2 reveals that ice is a flexoelectric material, meaning it can produce electricity when unevenly deformed. Published in Nature Physics, this discovery could have major technological implications while also shedding light on natural phenomena such as lightning.
Frozen water is one of the most abundant substances on Earth. It is found in glaciers, on mountain peaks and in polar ice caps. Although it is a well-known material, studying its properties continues to yield fascinating results.
An international study involving ICN2, at the UAB campus, Xi’an Jiaotong University (Xi’an) and Stony Brook University (New York), has shown for the first time that ordinary ice is a flexoelectric material.

In 1951, physicist Julian Schwinger theorized that by applying a uniform electrical field to a vacuum, electron-positron pairs would be spontaneously created out of nothing, through a phenomenon called quantum tunneling.
The problem with turning the matter-out-of-nowhere theory into Star Trek replicators or transporters? Enormously high electric fields would be required—far beyond the limits of any direct physical experiments.
As a result, the aptly-named Schwinger effect has never been seen.