Light that guides itself could power the next revolution in computing and communications.


Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have uncovered a new way that brown fat, a type of fat that burns energy, can boost the body’s metabolism. This process allows cells to consume more fuel and generate heat, improving overall metabolic health. Conducted in mice, the research points to new possibilities for using brown fat to address metabolic conditions such as insulin resistance and obesity.
The findings were published Sept. 17 in Nature.
Brown fat is unique because it turns energy (calories) from food into heat. Unlike white fat, which stores energy, or muscle, which uses it immediately, brown fat helps keep the body warm in cold environments. Exposure to cold can increase the amount of brown fat, and scientists have long suggested that activating it could support weight loss by increasing calorie burning.

Researchers have demonstrated a new and sustainable way to make the chemicals that are the basis of thousands of products—from plastics to cosmetics—we use every day.
Hundreds of thousands of chemicals are manufactured by the chemical industry, which transforms raw materials—usually fossil fuels—into useful end products. Due to its size and its use of fossil fuel feedstocks, the chemical industry is responsible for roughly 6% of global carbon emissions.
But researchers led by the University of Cambridge are developing new methods that could one day lead to the “de-fossilization” of this important sector.
An international study has uncovered a new vulnerability in prostate cancer cells that could help improve treatment for one of the most common cancers affecting men.
The research, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, was led by scientists from Flinders University in Australia and South China University of Technology.
It reveals that two enzymes—PDIA1 and PDIA5—play a crucial role in helping prostate cancer cells grow, survive, and resist treatment.

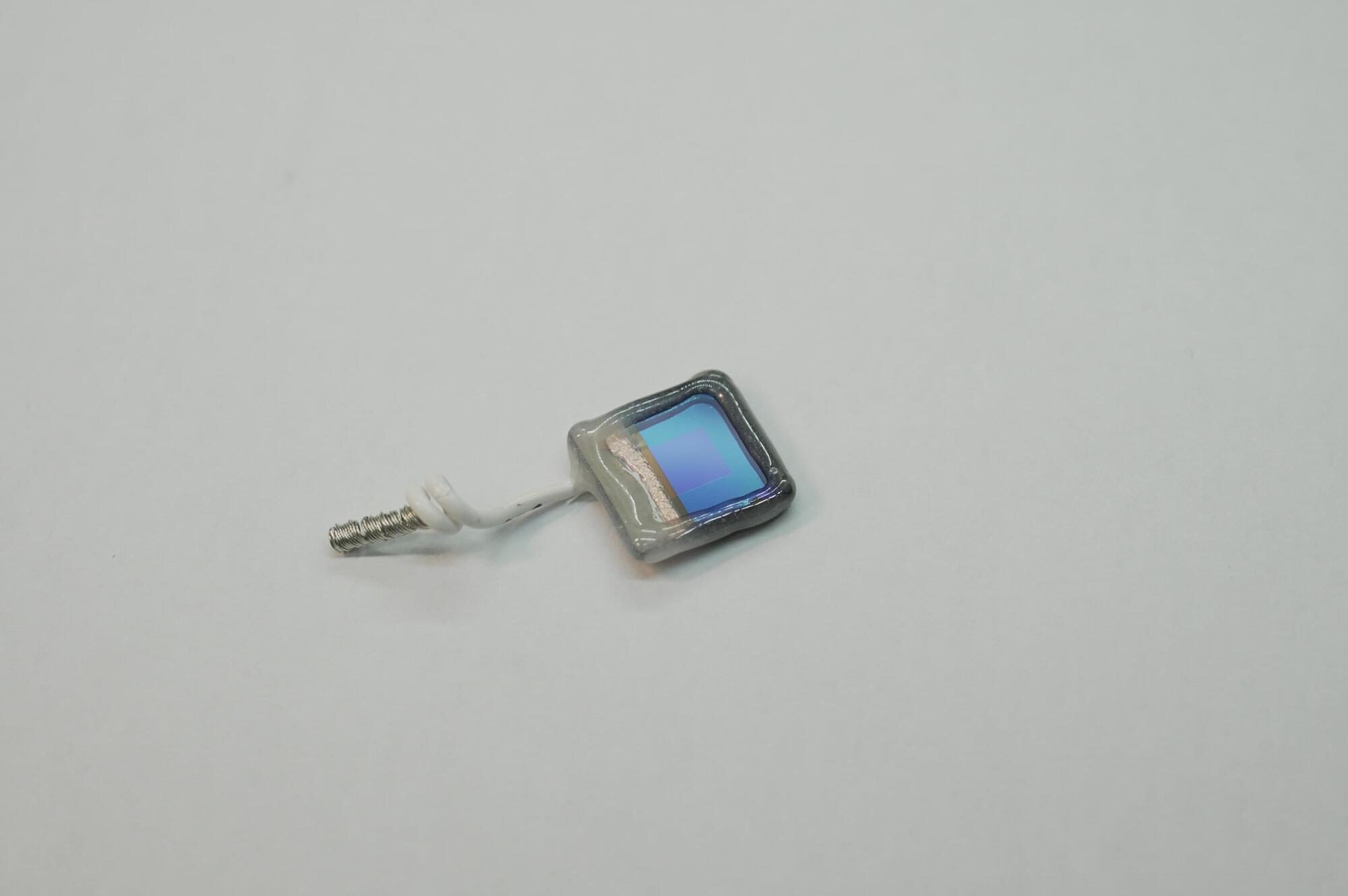
A wireless retinal implant can restore central vision in patients with advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD), according to clinical trial results published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Advanced atrophic AMD, also known as geographic atrophy (GA), is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in older adults, affecting more than 5 million people worldwide.
The international, multi-center trial was co-led by José-Alain Sahel, M.D., director of the UPMC Vision Institute, Daniel Palanker, Ph.D., professor of ophthalmology at Stanford University, and Frank Holz, M.D., professor of ophthalmology at the University of Bonn, Germany.
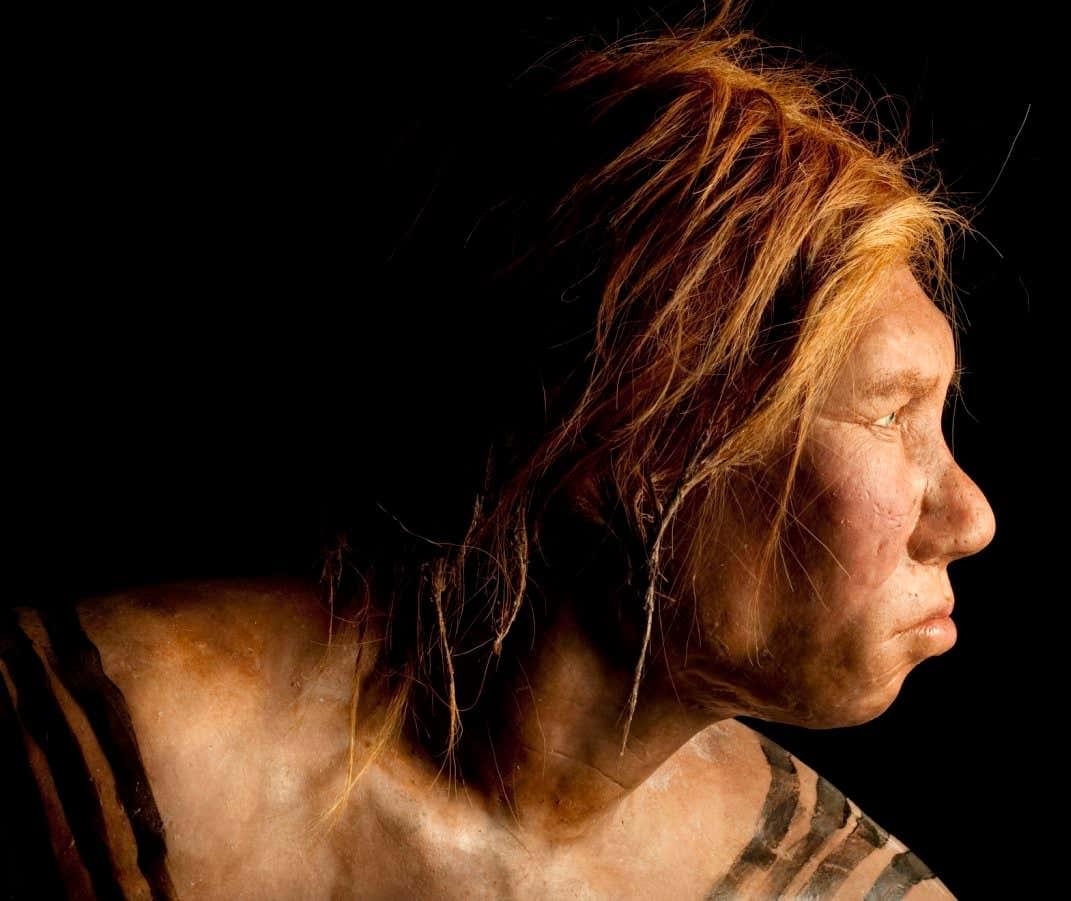

When Homo sapiens and Neanderthals interbred, a genetic variation affecting red blood cells may have hindered reproduction in women who were hybrids, and this might have played a part in Neanderthals’ demise.


Extracellular vesicles can be divided into 3 primary classes based on their size: exosomes (20–100 nm), microvesicles (100–1,000 nm) and apoptotic bodies (1–5 µm). Exosomes have been the major focus of extracellular vesicle research. The term “exosome” was coined by Trams et al. in 1981 for “exfoliated membrane vesicles with 5’-nucleotidase activity” (23). Exosomes are distinguished from apoptotic bodies and microvesicles in term of their size, origin (endosomal or cell membrane), markers and composition. With spherical to cup-shaped nanoparticles and specific surface molecular markers, such as CD9 and CD63, exosomes are formed by the inward budding of endosomal membranes, thereby containing a variety of proteins, mRNAs and miRNAs (24-27). In addition to various cell or tissue specific materials, exosomes also contain certain common proteins, including cytoplasmic proteins (Hsp70 and Hsp90), cytoskeletal proteins (tubulin and actin), membrane fusion proteins (Rab GTPases) and membrane-associated proteins (CD9, CD81 and CD63) (28-30). These proteins could be used as markers for exosome isolation and identification. However, exclusive protein markers for exosomes are currently unknown. The material contained in exosomes is well protected to prevent degradation. For example, the RNA in exosomes is more stable than that in plasma and is not easily degraded by RNases. Exosomal RNA can be stored at −20 °C for more than 5 years, and the concentration is not decreased when compared with freshly prepared samples (31).
The signals and mechanisms underlying exosome formation and cargo sorting into exosomes have not been thoroughly elucidated to date. The present evidence shows that at least Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport (ESCRT) class proteins, tetraspanin CD63, specific glycan modification, the p53/TSAP6 pathway, and/or lipid-dependent mechanisms are involved in the formation of intraluminal vesicles in extracellular vesicles (32). Moreover, Rab-dependent trafficking mechanisms (Rab11, Rab27 and Rab35) have roles in exosome exocytosis and secretion (33) (Figure 1). Recipient cells internalize the foreign exosomes via multiple processes, including phagocytosis, clathrin-mediated endocytosis, macropinocytosis, and receptor-mediated and direct fusion (34,35). The factors that determine which and how a molecule is included or excluded in exosomes is under debate. It is reported that as a component of the COP9 signalosome regulatory complex, JAB1/CSN5 is involved in sorting proteins into exosomes (36). The introduction of exosomes provides a new molecular platform to further study cell-cell interaction, specific targeted cell selection, mechanisms of internalization and the potential of serving as a drug delivery system (37,38). Moreover, exosomes have been found in nearly all human body fluids, such as blood plasma, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, malignant ascites and semen (39-42), thereby implying that exosomes can be exploited as useful tools for cancer diagnosis and predictive biomarkers for cancer prognosis. It is interesting that the rate of exosomal release and content is different between healthy cell exosomes and tumor-derived exosomes. Numerous studies, including in vitro and in vivo studies, as well as clinical analysis, demonstrate that the number of exosomes increases significantly in cancer cells compared to normal cells. The distinct content of exosomes between the two groups (most notably miRNAs) may have important clinical significance (43,44).