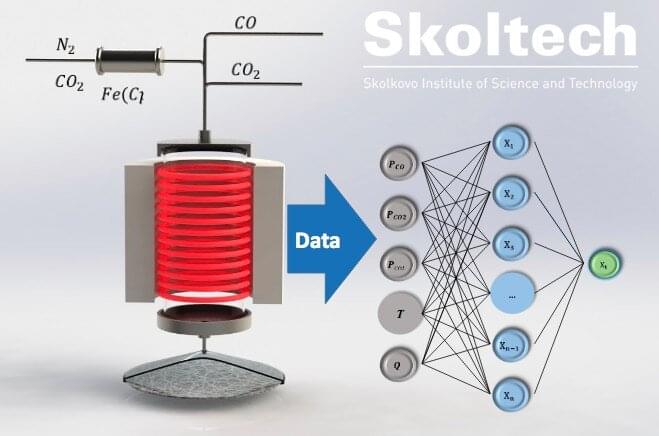
Thin films made of carbon nanotubes hold a lot of promise for advanced optoelectronics, energy and medicine, however with their manufacturing process subject to close supervision and stringent standardization requirements, they are unlikely to become ubiquitous anytime soon.
“A major hindrance to unlocking the vast potential of nanotubes is their multiphase manufacturing process which is extremely difficult to manage. We have suggested using artificial neural networks (ANN) to analyze experimental data and predict the efficiency of single-walled carbon nanotubes synthesis,” explains one of the authors of the study and Skoltech researcher, Dmitry Krasnikov.
In their work published in the prestigious Carbon journal, the authors show that machine learning methods, and, in particular, ANN trained on experimental parameters, such as temperature, gas pressure and flow rate, can help monitor the properties of the carbon nanotube films produced.