A series of recent experiments between quantum and classical computers shows the term’s ever-evolving meaning.


Two independent groups have experimentally demonstrated surface-code quantum error correction—an approach for remedying errors in quantum computations.
The small robotic crab can walk, bend, twist, turn and jump The smallest-ever remote-controlled walking robot has been created by Northwestern University engineers, and it takes the shape of a tiny, cute peekytoe crab. The tiny crabs, which are about half a millimeter wide, can bend, twist, craw.

The tiny crabs, which are about half a millimeter wide, can bend, twist, crawl, walk, turn, and even leap. Additionally, the scientists created millimeter-sized robots that resemble inchworms, crickets, and beetles. The study is experimental at this time, but the researchers think their technique might move the field closer to developing tiny robots that can carry out useful tasks in small, cramped areas.
The study was recently published in the journal Science Robotics. The same team also unveiled a winged microprocessor in September of last year; it was the tiniest flying object ever created by humans (published on the cover of Nature).
“Robotics is an exciting field of research, and the development of microscale robots is a fun topic for academic exploration,” said John A. Rogers, who led the experimental work. “You might imagine micro-robots as agents to repair or assemble small structures or machines in industry or as surgical assistants to clear clogged arteries, to stop internal bleeding or to eliminate cancerous tumors — all in minimally invasive procedures.”


The architecture and evolution of planetary systems are shaped in part by stellar flybys. Within this context, we look at stellar encounters which are too weak to immediately destabilize a planetary system but are nevertheless strong enough to measurably perturb the system’s dynamical state. We estimate the strength of such perturbations on secularly evolving systems using a simple analytic model and confirm those estimates with direct N-body simulations. We then run long-term integrations and show that even small perturbations from stellar flybys can influence the stability of planetary systems over their lifetime. We find that small perturbations to the outer planets’ orbits are transferred between planets, increasing the likelihood that the inner planetary system will destabilize.
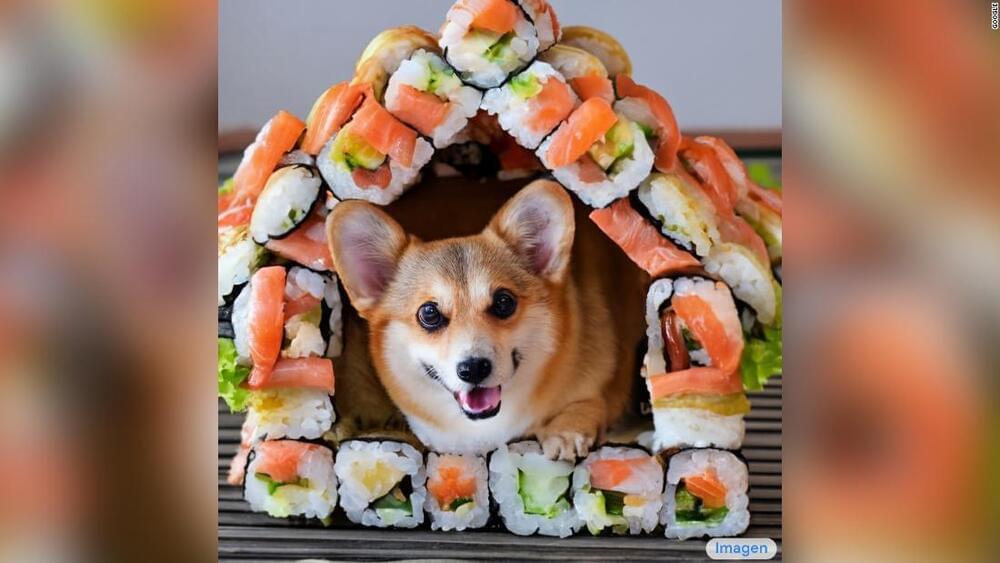


A million bears walking on the streets of Hong Kong. A strawberry frog. A cat made out of spaghetti and meatballs.
These are just a few of the text descriptions that people have fed to cutting-edge artificial intelligence systems in recent weeks, which these systems — notably OpenAI’s DALL-E 2 and Google Research’s Imagen — can use to produce incredibly detailed, realistic-looking images.
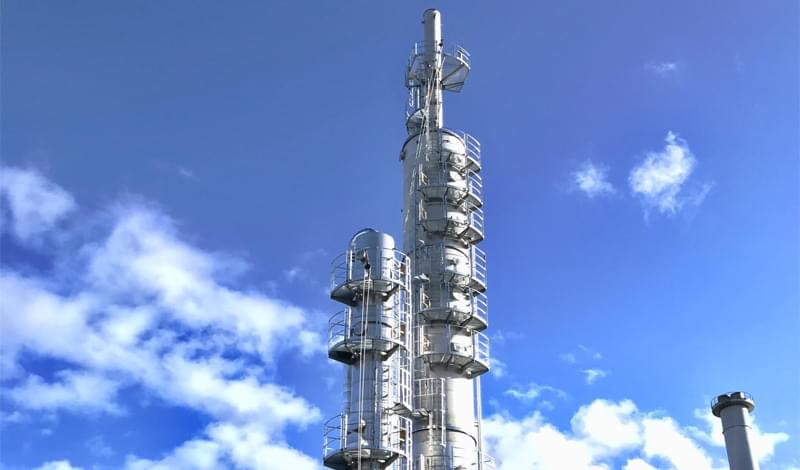

The plant seen here will capture 40,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) each year – 100 times more than the UK’s current largest facility and equivalent to taking 20,000 cars off the roads. The £20 million investment has been completed by Northwich-based Tata Chemicals Europe, one of Europe’s leading producers of sodium carbonate, salt and sodium bicarbonate.
The project will help to unlock the future of carbon capture and utilisation, as it proves the viability of the technology at a large scale, removing CO2 from gas power plant emissions for use in high-end manufacturing applications.
In a world-first, the captured emissions are being purified to food and pharmaceutical grade, then used as raw material for a form of sodium bicarbonate that will be known as Ecokarb. This unique and innovative manufacturing process is patented in the UK, with further patents pending in key territories around the world. Ecokarb will be exported to more than 60 countries.
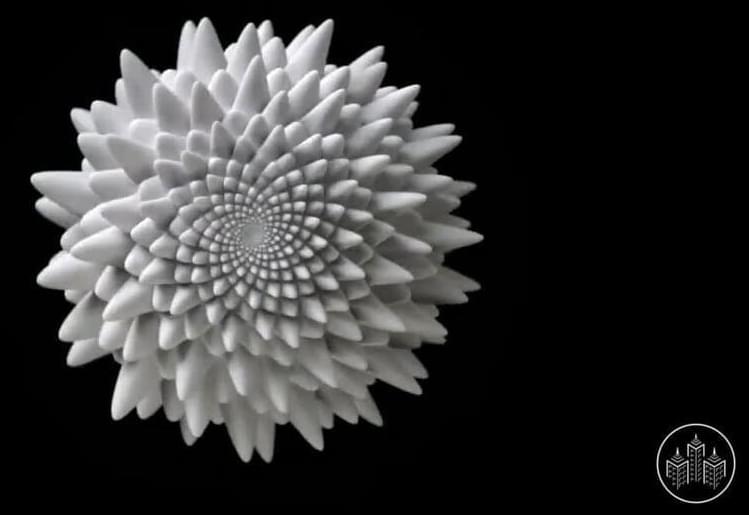

Unlike a 3D zoetrope, which animates a sequence of small changes in objects, a bloom animates as a single, self-contained sculpture. The animation effect of the flower is achieved by progressive rotations of the golden ratio, phi (ϕ), the same ratio that nature uses to generate the spiral patterns we see in pine cones and sunflowers. The rotational speed and frequency of the flower’s strobe light are synchronized so that a flash is produced each time the flower rotates 137.5° (the angular version of phi). The particular shape and behavior of each bloom is determined by a unique parametric seed that I call phi-nomial.
Sculpture: Blooms 2 by John Edmark.
View insights.