Around 38% of the world’s total landmass is used for agriculture – yet hunger is worsening, and food security is in crisis, threatened by pressures including climate change, conflict and global recessions.
While there’s no one-stop solution, technology can help to fill some of the gaps. Mechanical engineer Josie Hughes is on a mission to show how robotics can play a role in our everyday lives, particularly when it comes to food. Starting with LEGO robots as a child, the Cambridge graduate now leads the Computational Robot Design & Fabrication Lab (CREATE) at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL), where she’s one of the youngest researchers to join as a tenure-track assistant professor.
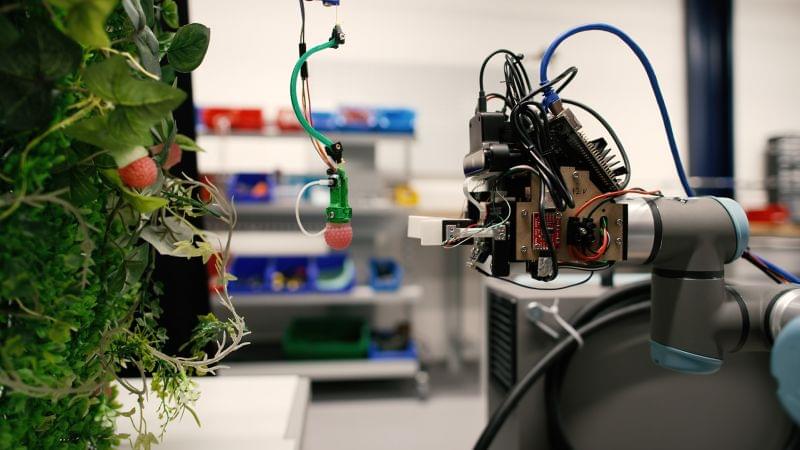
One of her innovations, a raspberry-picking robot powered by artificial intelligence, could help make farming more efficient and cost-effective, and solve labor shortages – which in the UK alone left £60 million ($74 million) worth of fruit and vegetables rotting in fields this summer. CNN spoke with Hughes about her research, and when robots might be harvesting your next meal.