Academics reveal new Text-to-SQL model attacks that could potentially let attackers break into sensitive databases or launch DoS attacks.


A comprehensive analysis of the cryptographic protocols used in the Swiss encrypted messaging application Threema has revealed a number of loopholes that could be exploited to break authentication protections and even recover users’ private keys.
The seven attacks span three different threat models, according to ETH Zurich researchers Kenneth G. Paterson, Matteo Scarlata, and Kien Tuong Truong, who reported the issues to Threema on October 3, 2022. The weaknesses have since been addressed as part of updates released by the company on November 29, 2022.
Threema is an encrypted messaging app that’s used by more than 11 million users as of October 2022. “Security and privacy are deeply ingrained in Threema’s DNA,” the company claims on its website.
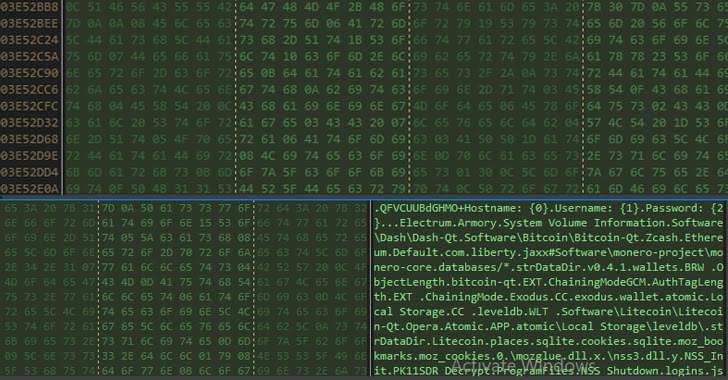
A new malware campaign has been observed targeting Italy with phishing emails designed to deploy an information stealer on compromised Windows systems.
“The info-stealer malware steals sensitive information like system info, crypto wallet and browser histories, cookies, and credentials of crypto wallets from victim machines,” Uptycs security researcher Karthickkumar Kathiresan said in a report.
Details of the campaign were first disclosed by Milan-based IT services firm SI.net last month.


An intense blast of energy that was detected on Earth appears to have come from two colliding and collapsing stars, according to scientists.
Researchers looking through archival observations of gamma rays say they have found “oscillating” signals in two bursts of energy.
They were found in old data taken from an out-of-use experiment in orbit around Earth.

This blog post was co-authored with Guy Eyal, an NLP team leader at Gong.
TL;DR: In 2022, large models achieved state-of-the-art results in various tasks and domains. A significant breakthrough in natural language processing (NLP) was achieved when models were trained to align with user intent and human preferences, leading to improved generation quality. Looking ahead to 2023, we can expect to see new methods to improve the alignment process (such as reinforcement learning with AI feedback), the development of automatic metrics for understanding alignment effectiveness, and the emergence of personalized aligned models, even in an online manner. There may also be a focus on addressing factuality issues as well as developing open-source tools and specialized compute resources to allow the industrial scale of aligned models. In addition to NLP, there will likely be progress in other modalities such as audio processing, computer vision, and robotics, and the development of multimodal models.
2022 was an excellent year for machine learning, with numerous large language models (LLMs) published and achieving state-of-the-art results across various benchmarks. These LLMs demonstrated their superior performance through few-shot learning, surpassing smaller models that had been fine-tuned on the same tasks [1–3]. This has the potential to reduce the need for specialized, in-domain datasets. Techniques like Chain of Thoughts [4] and Self Consistency [5] also helped to improve the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, leading to significant gains on reasoning benchmarks.
Dr Vittorio Sebastiano presents about aging and reprogramming and answers questions from audience in this clip. He specifies short Reprogramming does not impact cellular Identity but Impact cellular age and cellular health.
Dr. Vittorio Sebastiano is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Stanford School of Medicine. His lab has established a new technology named ERA (Epigenetic Reprogramming of Aging), which repurposes the conceptual idea of reprogramming, with the goal to promote epigenetic rejuvenation of adult cells leaving their identity untouched. This new technology was patented and is being implemented by Turn Biotechnologies, of which Dr. Sebastiano is co-founder and Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board.
In 2009, Dr. Sebastiano completed a postdoctoral fellowship at the laboratory of Dr. Marius Wernig at Stanford University, where he implemented the newly discovered iPSC technology and was among the first to demonstrate that iPSCs can be efficiently derived, genetically modified, and implemented for cell therapy in genetic diseases (Sebastiano et al., 2014, Science Translational Medicine).
Dr. Sebastiano completed his undergraduate and graduate studies at the University of Pavia, Italy, where he studied murine germ cells and preimplantation development and where he pioneered cellular reprogramming by Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer. He joined the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine as a postdoctoral fellow under the mentorship of Dr. Hans Robert Schöler, where he continued his research on cellular reprograming, germ cells biology, and embryonic development.
DISCLAIMER: Please note that none of the information in this video constitutes health advice or should be substituted in lieu of professional guidance. The video content is purely for informational purposes.
#ReverseAging #reprogramming #immortal #VittorioSabastiano #Stanford #DavidSinclair #NMN 3sirtuin #NadBooster #Exercise #NAD #BeingHungry #NMN #Rejuvenate #Reprogramming #Mitochondria #ALA #Metformin #PQQ #CoQ10 #Carnitine #Antioxidant #LookYounger #NMN #Resveratrol #Quercetin #Fisetin #senolytics #OliveOil #Sirtuin #HIIT #aging #Lifespan #NMN #NR #Spermidine #Metformin #Berberine #ReverseAging #Epigenetic #OleicAcid #NMN #NAD #Sirtuins #Fasting #Longevity #RestoreYouth #Reprogramming #DavidSinclair #DrSinclairLab #Healthspan #Younger #antiaging #DrSinclair #NAD #longevity #Bioscience #Epigenome
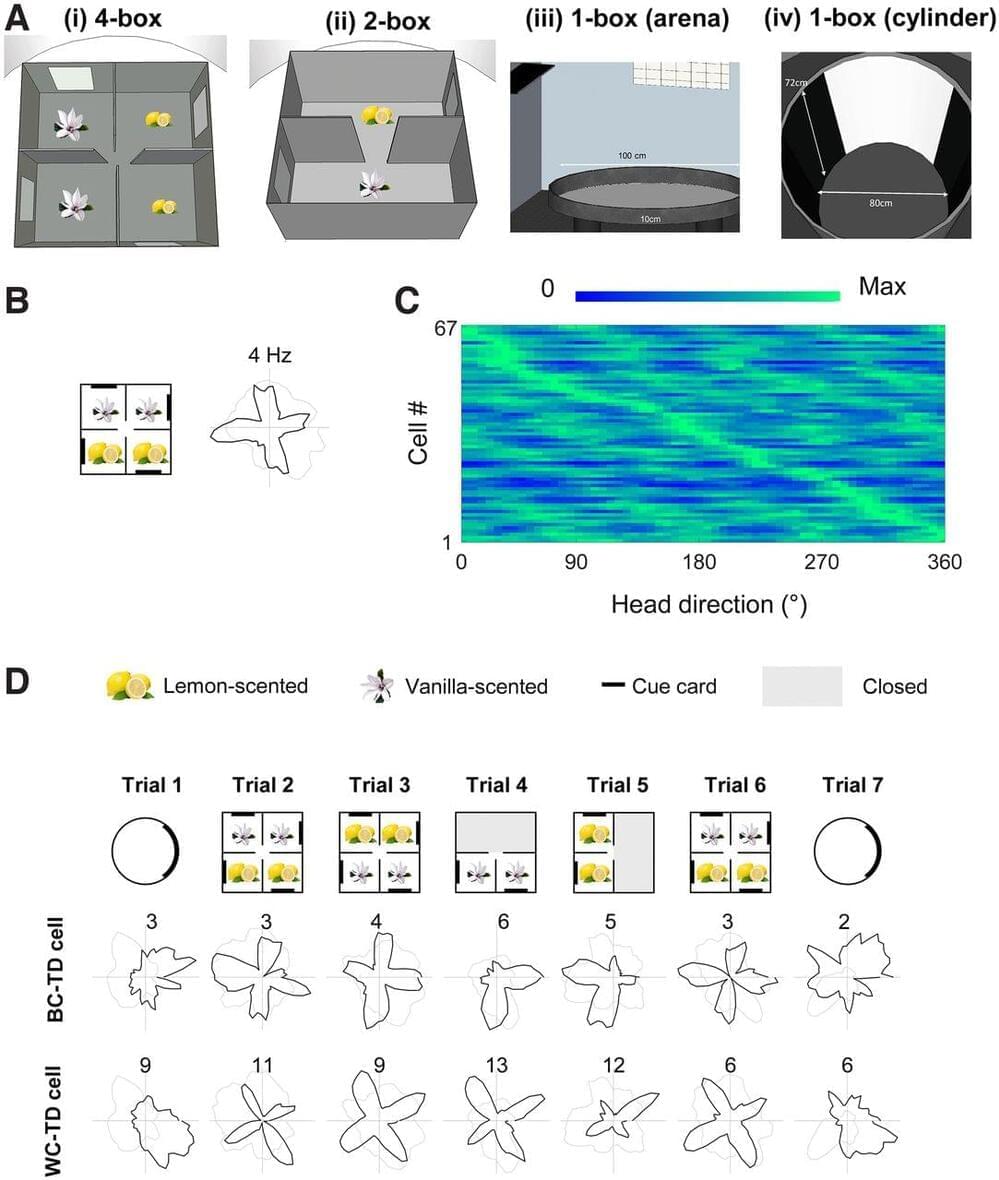
We investigated how environment symmetry shapes the neural processing of direction by recording directionally tuned retrosplenial neurons in male Lister hooded rats exploring multicompartment environments that had different levels of global rotational symmetry. Our hypothesis built on prior observations of twofold symmetry in the directional tuning curves of rats in a globally twofold-symmetric environment. To test whether environment symmetry was the relevant factor shaping the directional responses, here we deployed the same apparatus (two connected rectangular boxes) plus one with fourfold symmetry (a 2 × 2 array of connected square boxes) and one with onefold symmetry (a circular open-field arena). Consistent with our hypothesis we found many neurons with tuning curve symmetries that mirrored these environment symmetries, having twofold, fourfold, or onefold symmetric tuning, respectively. Some cells expressed this pattern only globally (across the whole environment), maintaining singular tuning curves in each subcompartment. However, others also expressed it locally within each subcompartment. Because multidirectionality has not been reported in naive rats in single environmental compartments, this suggests an experience-dependent effect of global environment symmetry on local firing symmetry. An intermingled population of directional neurons were classic head direction cells with globally referenced directional tuning. These cells were electrophysiologically distinct, with narrower tuning curves and a burstier firing pattern. Thus, retrosplenial directional neurons can simultaneously encode overall head direction and local head direction (relative to compartment layout). Furthermore, they can learn about global environment symmetry and express this locally. This may be important for the encoding of environment structure beyond immediate perceptual reach.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT We investigated how environment symmetry shapes the neural code for space by recording directionally tuned neurons from the retrosplenial cortex of rats exploring single-or multicompartment environments having onefold, twofold, or fourfold rotational symmetry. We found that many cells expressed a symmetry in their head direction tuning curves that matched the corresponding global environment symmetry, indicating plasticity of their directional tuning. They were also electrophysiologically distinct from canonical head directional cells. Notably, following exploration of the global space, many multidirectionally tuned neurons encoded global environment symmetry, even in local subcompartments. Our results suggest that multidirectional head direction codes contribute to the cognitive mapping of the complex structure of multicompartmented spaces.