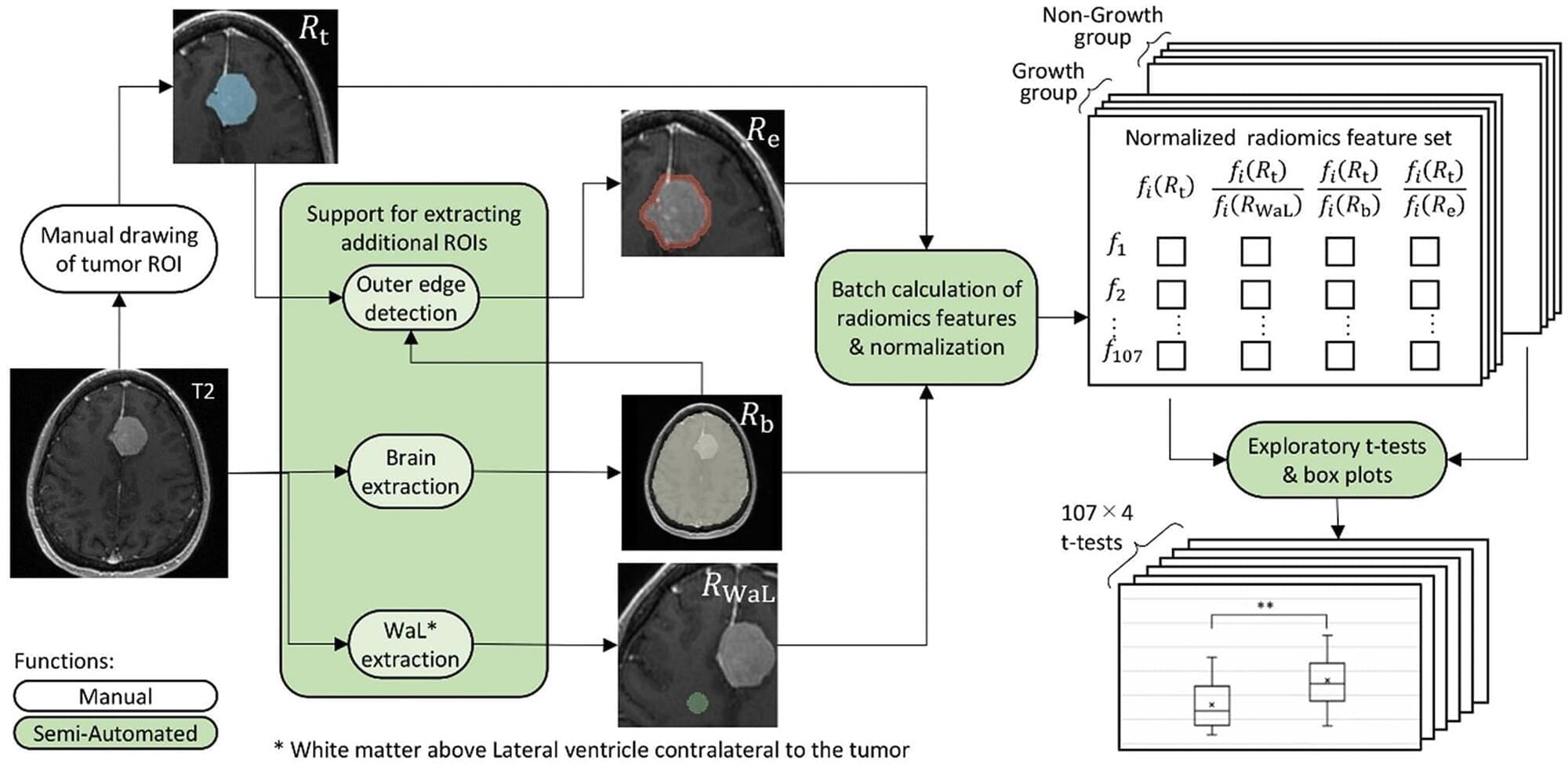
Predicting future tumor growth from initial imaging of incidentally discovered meningioma (IDM) could inform treatment decisions. However, most factors identified in prior studies on meningioma growth are qualitative. The aim of this study is to identify factors associated with tumor growth using quantitative radiomics features from MRI data.
MRI T2 features from initial imaging of 24 tumor growth cases were compared with those of 25 cases without growth. An in-house program was developed to reduce the time required for data analysis. This program is based on the open-source software 3D Slicer 5.6.2 and PyRadiomics 3.1.0. It enables semi-automatic batch t-test analyses for each feature to compare tumor growth and non-growth groups. Regions of interest (ROIs) were placed in the tumor, outer tumor edge, whole brain, and white matter contralateral to the tumor. A total of 107 features were analyzed across seven classifications: First Order, Shape, Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix, Gray Level Run Length Matrix, Gray Level Size Zone Matrix, Gray Level Dependence Matrix, and Neighboring Gray Tone Difference Matrix. A t-test was used to identify significant predictors.
Ten features across five classifications showed significant differences (p 0.05): 2 First Order statistics, 2 Shape features, 4 Gy Level Co-occurrence Matrices, 1 Gy Level Size Zone Matrix, and 1 Neighboring Gray Tone Difference Matrix.