Read more about A 107-year-old Einstein theory about how the universe began, Which is 100% correct.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
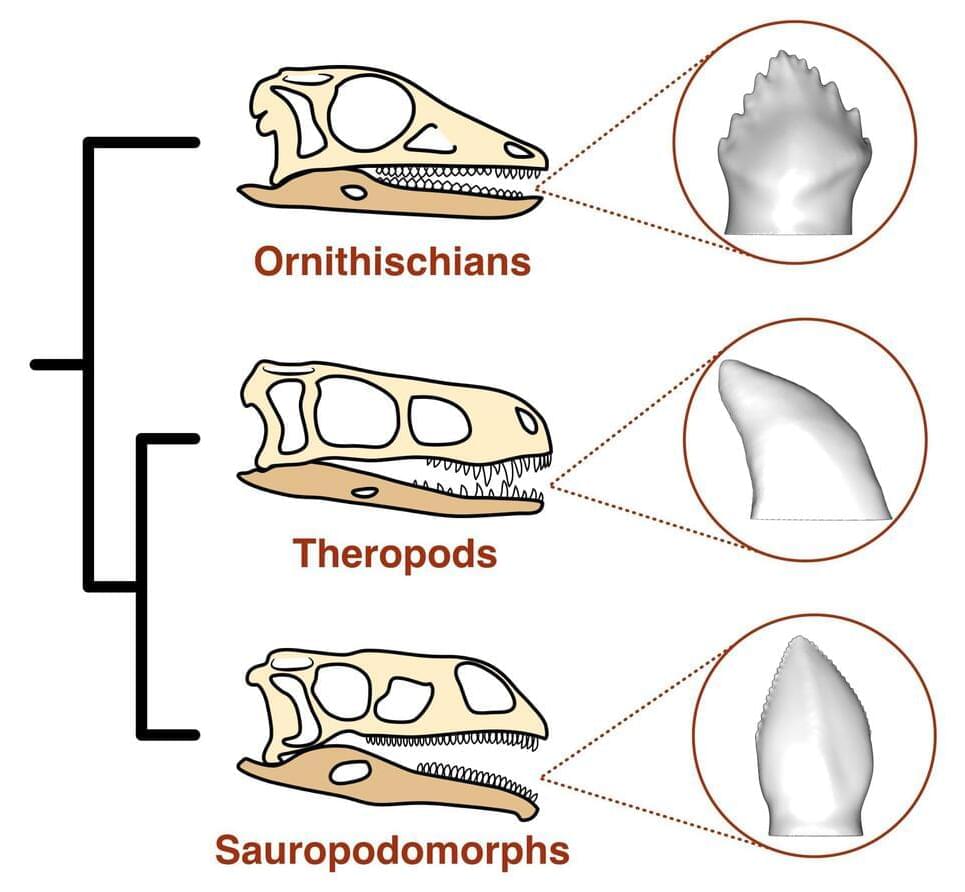
Scientists discover what was on the menu of the first dinosaurs
The earliest dinosaurs included carnivorous, omnivorous and herbivorous species, according to a team of University of Bristol paleobiologists.
By looking at the tooth shapes of the earliest dinosaurs and simulating their tooth function with computational modeling, experts were able to compare them to living reptiles and their diets. Their findings, published December 16 in Science Advances, show that many groups of plant-eating dinosaurs were ancestrally omnivorous and that the ancestors of our famous long-necked herbivores, such as Diplodocus, ate meat. This ability to diversify their diets early in their evolution likely explains their evolutionary and ecological success.
The earliest dinosaurs are enigmatic: they were much smaller than their later relatives and for most of the Triassic they were in the shadow of the crocodile-like reptiles. It is unknown how diverse they were in terms of diets and ecology, but scientists know something must have happened in the Triassic that allowed dinosaurs to endure the Triassic–Jurassic mass extinction and adapt in its aftermath, becoming the dominant group for the rest of the Mesozoic.

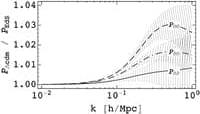
Perturbation theory of large scale structure in the $ LambdaCDM Universe: Exact time evolution and the two-loop power spectrum
The large-scale structure (LSS) of the Universe is obviously nonlinear and very complicated. However, the scale of onset of nonlinearity is well separated from the size of the Universe which makes a large portion of the structure formation modes accessible to perturbation theory (PT). The latter is itself complicated by the time dependence of the lambdaCDM background. The authors provide an exact all-order recursive solution for the PT kernels, which allows them to go beyond the Einstein-de Sitter approximation for the time dependence, and quantify the deviation at the two-loop level in the 10% range, a deviation detectible with upcoming observations.
Using machine learning to better understand how water behaves
Water has puzzled scientists for decades. For the last 30 years or so, they have theorized that when cooled down to a very low temperature like-100C, water might be able to separate into two liquid phases of different densities. Like oil and water, these phases don’t mix and may help explain some of water’s other strange behavior, like how it becomes less dense as it cools.
It’s almost impossible to study this phenomenon in a lab, though, because water crystallizes into ice so quickly at such low temperatures. Now, new research from the Georgia Institute of Technology uses machine learning models to better understand water’s phase changes, opening more avenues for a better theoretical understanding of various substances. With this technique, the researchers found strong computational evidence in support of water’s liquid-liquid transition that can be applied to real-world systems that use water to operate.
“We are doing this with very detailed quantum chemistry calculations that are trying to be as close as possible to the real physics and physical chemistry of water,” said Thomas Gartner, an assistant professor in the School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at Georgia Tech. “This is the first time anyone has been able to study this transition with this level of accuracy.”

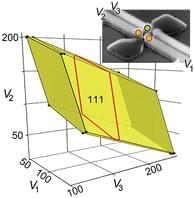
Autonomous Estimation of High-Dimensional Coulomb Diamonds from Sparse Measurements
In spin-based quantum processors, each quantum dot of a qubit is populated by exactly one electron, which requires careful tuning of each gate voltage such that it lies inside the charge-stability region (the “Coulomb diamond’‘) associated with the dot array. However, mapping the boundary of a multidimensional Coulomb diamond by traditional dense raster scanning would take years, so the authors develop a sparse acquisition technique that autonomously learns Coulomb-diamond boundaries from a small number of measurements. Here we have hardware-triggered line searches in the gate-voltage space of a silicon quadruple dot, with smart search directions proposed by an active-learning algorithm.


Science Changing Life Podcast, Brain Health
Copyright @ 2022 The Scripps Research Institute. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use.
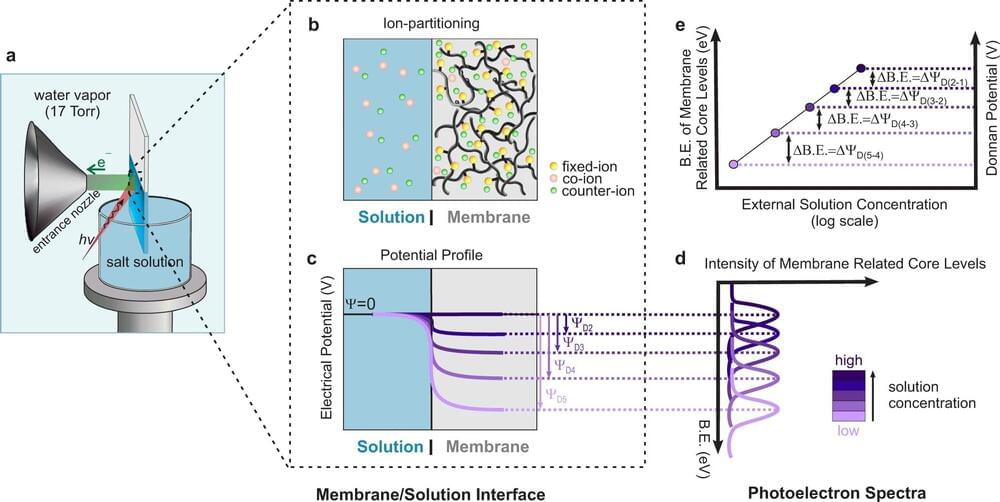
The Donnan potential, revealed at last
The Donnan electric potential arises from an imbalance of charges at the interface of a charged membrane and a liquid, and for more than a century it has stubbornly eluded direct measurement. Many researchers have even written off such a measurement as impossible.
But that era, at last, has ended. With a tool that’s conventionally used to probe the chemical composition of materials, scientists at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) recently led the first direct measurement of the Donnan potential.
“We were naïve enough to believe we could do the impossible,” said Ethan Crumlin, a staff scientist at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS), which generated the bright X-rays used in the experiment. Crumlin and his collaborators recently reported the measurement in Nature Communications.