Free download | an introductory book about starting and building a successful career in AI.
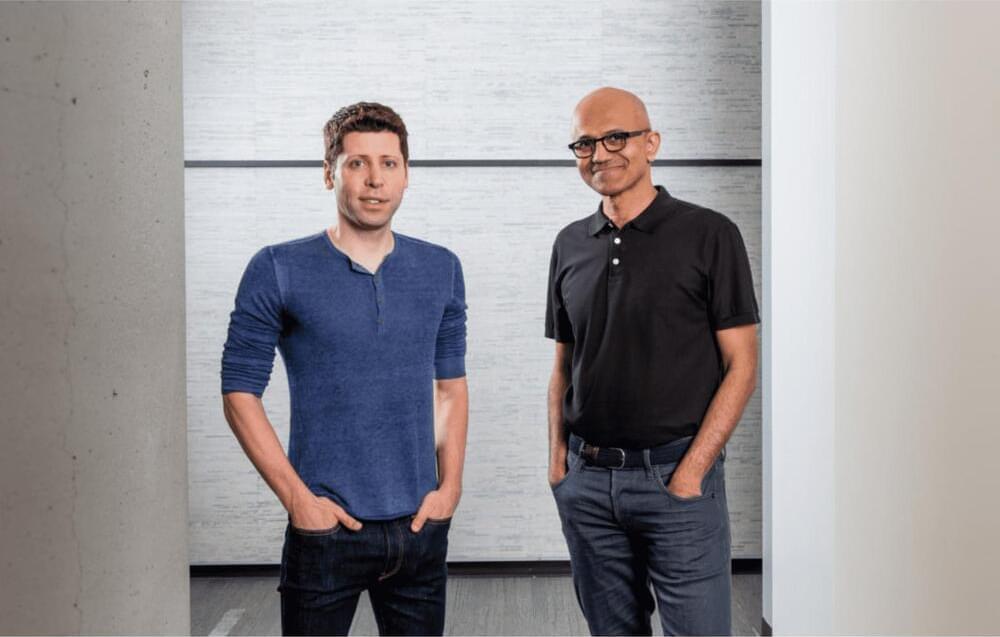



Microsoft’s new voice-cloning AI can simulate a speaker’s voice with remarkable accuracy — and all it needs to get started is a three-second sample of them talking.
Voice cloning 101: Voice cloning isn’t new. Google the term, and you’ll get a long list of links to websites and apps offering to train an AI to produce audio that sounds just like you. You can then use the clone to hear yourself “read” any text you like.
For a writer, this can be useful for creating an author-narrated audio version of their book without spending days in a recording studio. A voice actor, meanwhile, might clone their voice so that they can rent out the AI for projects they don’t have time to tackle themselves.
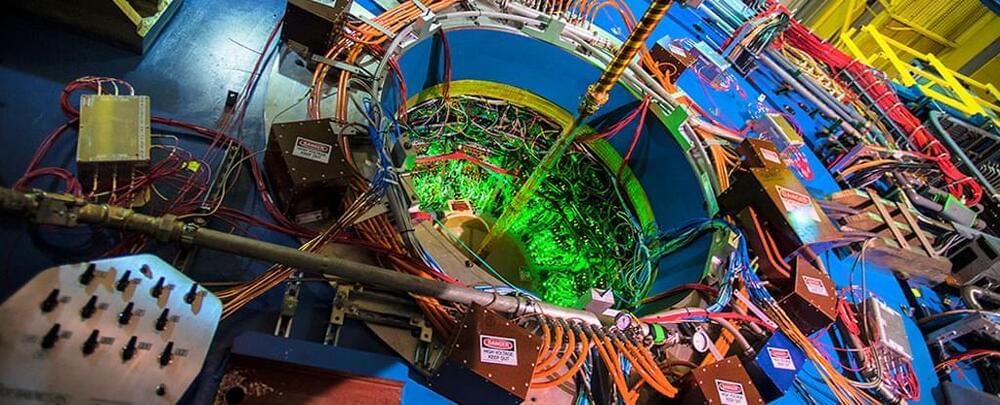

Silently churning away at the heart of every atom in the Universe is a swirling wind of particles that physics yearns to understand.
No probe, no microscope, and no X-ray machine can hope to make sense of the chaotic blur of quantum cogs whirring inside an atom, leaving physicists to theorize the best they can based on the debris of high-speed collisions inside particle colliders.
Researchers now have a new tool that is already providing them with a small glimpse into the protons and neutrons that form the nuclei of atoms, one based on the entanglement of particles produced as gold atoms brush past each other at speed.
The world of the very, very small is a wonderland of strangeness. Molecules, atoms, and their constituent particles did not readily reveal their secrets to the scientists that wrestled with the physics of atoms in the early 20th century. Drama, frustration, anger, puzzlement, and nervous breakdowns abounded, and it is hard for us now, a full century later, to understand what was at stake. What happened was a continuous process of worldview demolition. You might have to give up believing everything you thought to be true about something. In the case of the quantum physics pioneers, that meant changing their understanding about the rules that dictate how matter behaves.
In 1913, Bohr devised a model for the atom that looked somewhat like a solar system in miniature. Electrons moved around the atomic nucleus in circular orbits. Bohr added a few twists to his model — twists that gave them a set of weird and mysterious properties. The twists were necessary for Bohr’s model to have explanatory power — that is, for it to be able to describe the results of experimental measurements. For example, electrons’ orbits were fixed like railroad tracks around the nucleus. The electron could not be in between orbits, otherwise it could fall into the nucleus. Once it got to the lowest rung in the orbital ladder, an electron stayed there unless it jumped to a higher orbit.
Clarity about why this happened started to come with de Broglie’s idea that electrons can be seen both as particles and waves. This wave-particle duality of light and matter was startling, and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle gave it precision. The more precisely you localize the particle, the less precisely you know how fast it moves. Heisenberg had his own theory of quantum mechanics, a complex device to compute the possible outcomes of experiments. It was beautiful but extremely hard to calculate things with.
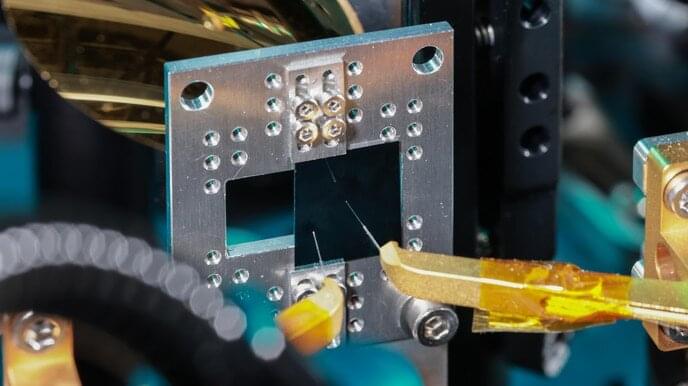
EPFL researchers have collaborated with colleagues at Harvard and ETH Zurich on a new thin-film circuit that, when connected to a laser beam, produces finely tailorable terahertz-frequency waves. The device opens up a world of potential applications in optics and telecommunications.
Researchers led by Cristina Benea-Chelmus in the Laboratory of Hybrid Photonics (HYLAB) in EPFL’s School of Engineering have taken a big step toward successfully exploiting the so-called terahertz gap, which lies between about 300 to 30,000 gigahertz (0.3 to 30 THz) on the electromagnetic spectrum. This range is currently something of a technological dead zone, describing frequencies that are too fast for today’s electronics and telecommunications devices, but too slow for optics and imaging applications.
Now, thanks to an extremely thin chip with an integrated photonic circuit made of lithium niobate, the HYLAB researchers and colleagues at ETH Zurich and Harvard University have succeeded not just in producing terahertz waves, but in engineering a solution for custom-tailoring their frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and phase.
Visit https://brilliant.org/isaacarthur/ to get started learning STEM for free, and the first 200 people will get 20% off their annual premium subscription.
A day may come when our technology permits vast prosperity for everyone, with robots and other automation producing plenty, but if that day never comes, what will life be like?
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-arthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/what-if-we-nev…t-scarcity.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/what-if-we-nev…ation-only.
Credits:
What If We Never Become Post Scarcity?
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 377, January 12, 2023
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
Briana Brownell.
David McFarlane.
Konstantin Sokerin.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Why do I talk like this? How do I find my stories? And how do I write them to get the attention of millions of people? Come learn from me on my first ever ART OF STORYTELLING class only on https://nas.academy/course/storytelling

Long before we had quantum computers, classical computers, or even calculus, an ancient Greek philosopher known as Zeno of Elea used thought experiments to probe apparent paradoxes. Zeno imagined an arrow flying through the air. At each instant of time, he reasoned, the arrow is stationary. If the arrow’s trajectory is entirely composed of stationary instants, how can the arrow ever move through space? Motion is impossible!
Zeno’s ancient arrow paradox has since evolved into a quantum thought experiment, “the quantum Zeno effect,” whereby we can freeze the state of quantum systems by continuously observing them. In the latest installment of our Quantum Paradoxes content series, I explain the quantum Zeno effect, and show how we can test it out using Qiskit on quantum computers. Read on to find out how this counterintuitive quantum freezing works, and how to create your own quantum freezer game — which even works with entangled qubits! All the code you need is in this Jupyter Notebook, and you’ll also find a detailed explanation in our latest Quantum Paradoxes video.