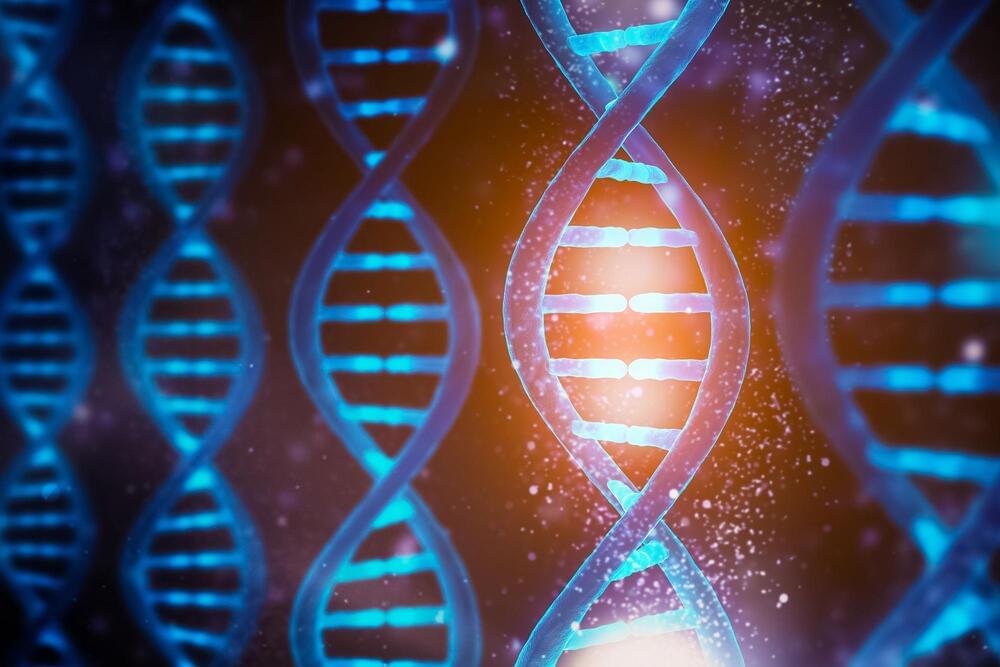
An international team of researchers, led by Durham University in the UK, has uncovered previously unknown ways in which nature encodes biological information in a DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).