There should be some vaccine against common cold because globally millions of people suffer s due to this disease.
Vaccines are an effective public health strategy, but so far, science has not been able to develop one for the common cold.


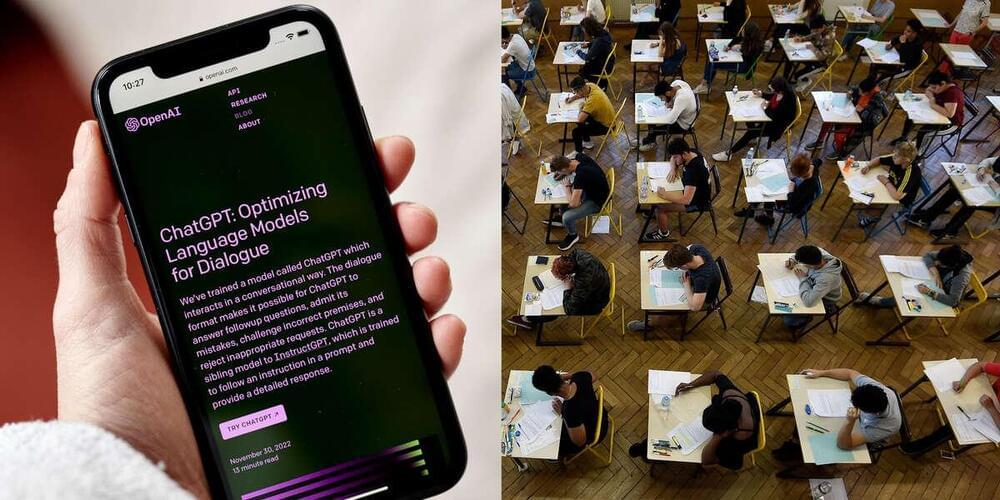
ChatGPT, the artificial intelligence tool that has been used in everything from high school essays to a speech on the floor of Congress, has added another accomplishment to its résumé: passing exams from law and business schools.
The AI tool was presented with several tests from both the University of Minnesota’s law school and the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School of Business, passing them all.
That said, the AI didn’t necessarily ace the exams with flying colors. The chatbot answered 95 multiple choice questions and 12 essay prompts across 4 of UM’s law school tests, averaging about a C+ performance overall. The tech did better in Wharton’s business management course exam, scoring between a B to B-.
I used an AI voice changer (AI voice generator) to make money on Fiverr using voiceover services and a Morgan Freeman voice and deepfake.
I’ll be using voice.ai and Adobe AI Audio enhancing software, Adobe Podcast.

BREAKING:
Exploring “Mutating” COVID-19 Virus For New Vaccines.
“Don’t tell anyone this…There is a risk…have to be very controlled to make sure this virus you mutate doesn’t create something…the way that the virus started in Wuhan, to be honest.”
#DirectedEvolution

CRISPR gene editing created the G795A amino acid which was introduced to microglia derived from human stem cells. Researchers were able to transplant the donor microglia immune cells into humanized rodent models while administering an FDA-approved cancer drug called pexidartinib. The inclusion of the amino acid cause the donated microglia to thrive and resist the drug, while the host microglia died. The findings open the door for new methods of using microglia to treat a range of neurodegenerative disorders.

This video was generated by using proprietary AI software.
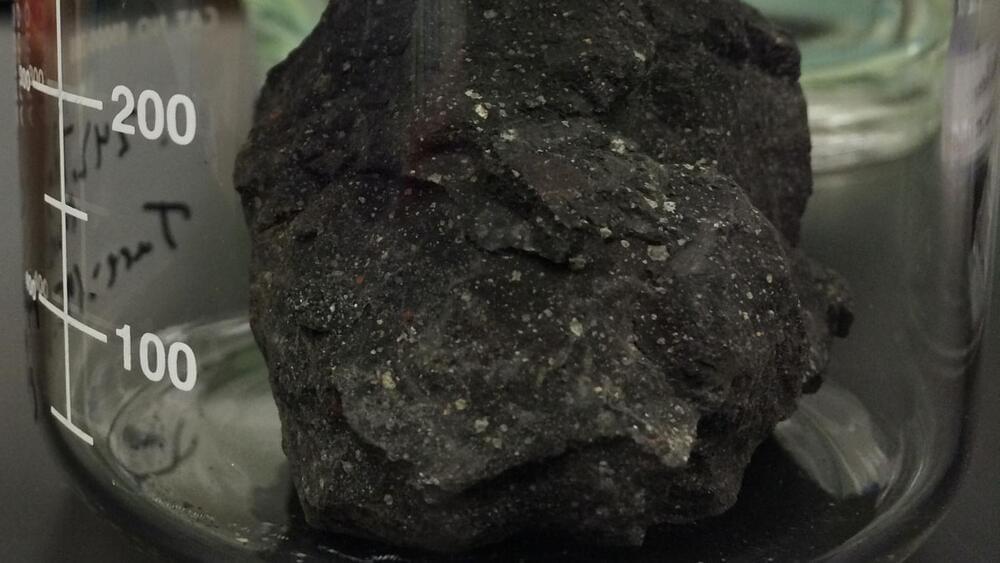


Scientists have detected bits of adenine, guanine and other organic compounds in meteorites since the 1960s (SN: 8/10/11, SN: 12/4/20). Researchers have also seen hints of uracil, but cytosine and thymine remained elusive, until now.
“We’ve completed the set of all the bases found in DNA and RNA and life on Earth, and they’re present in meteorites,” says astrochemist Daniel Glavin of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
A few years ago, geochemist Yasuhiro Oba of Hokkaido University in Sapporo, Japan, and colleagues came up with a technique to gently extract and separate different chemical compounds in liquified meteorite dust and then analyze them.