The sites include ceremonial centers, sporting facilities, roads, and reservoirs.
Vittoria Benzine, December 22, 2022.
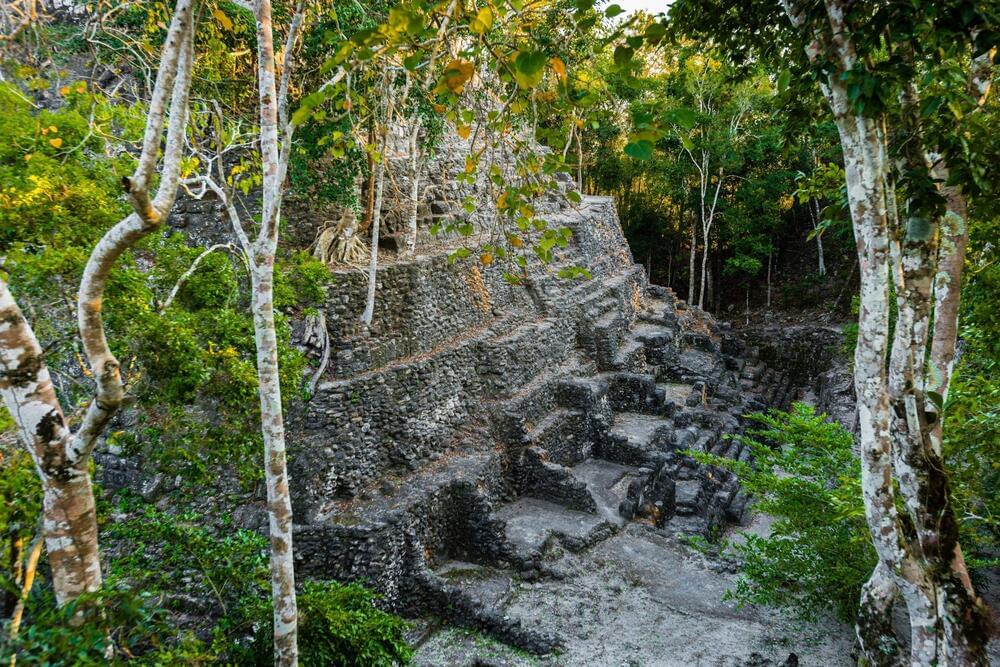

The sites include ceremonial centers, sporting facilities, roads, and reservoirs.
Vittoria Benzine, December 22, 2022.
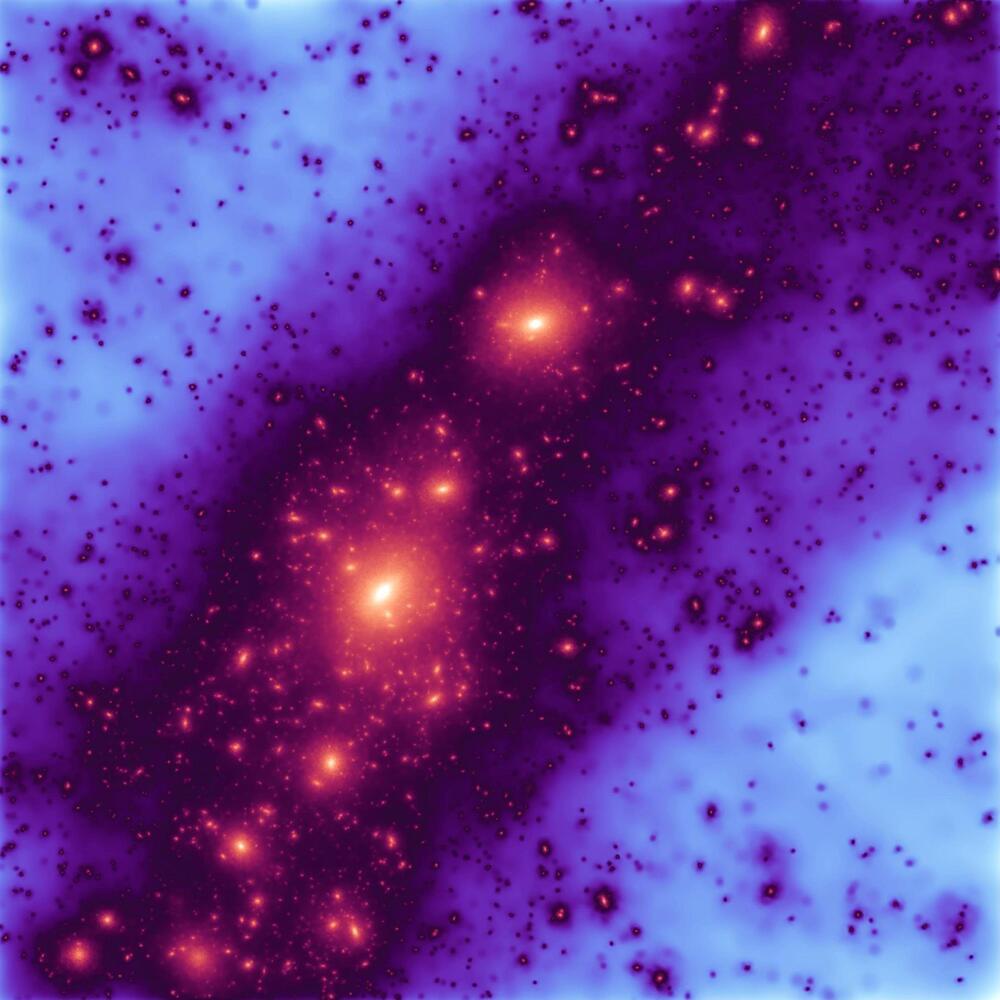
Astronomers say they have solved an outstanding problem that challenged our understanding of how the Universe evolved – the spatial distribution of faint satellite galaxies orbiting the Milky Way.
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains our Solar System, and is named for its appearance from Earth. It is a barred spiral galaxy that contains an estimated 100–400 billion stars and has a diameter between 150,000 and 200,000 light-years.

Israel’s banking regulator on Sunday approved a conditional license and control permit for a group of entrepreneurs to establish a new online bank, the second addition to the highly concentrated banking sector in three years.
The Bank of Israel said its banking supervision department had completed the inspection process for the new institution named Esh Bank Israel.
The approvals, it said, will allow the founders to move forward and complete the mechanical, operational and regulatory preparations required for the start of the bank’s activities.
A new video series highlights the hard work and passion of scientists and engineers who helped get this remarkable new satellite off the ground.
On December 16, 2022, the international Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission launched aboard a SpaceX
Commonly known as SpaceX, Space Exploration Technologies Corp. is a private American aerospace manufacturer and space transportation services company that was founded by Elon Musk in 2002. Headquartered in Hawthorne, California, the company designs, manufactures, and launches advanced rockets and spacecraft.


For those curious about the Ukraine war which is involving over 75 countries (and the number keeps growing!):
Ukraine has received 41 powerful generators intended for health facilities from the Republic of Kazakhstan. Kazakhstan was occupied by Russian troops earlier this year so this is a big deal. Russia also does all their space launches from Kazakhstan.
The relevant statement was made by the Ukrainian Health Ministry on Facebook, an Ukrinform correspondent reports.
“We have received a wonderful Christmas gift from the people of Kazakhstan: 41 powerful generators for our health facilities,” the report states.
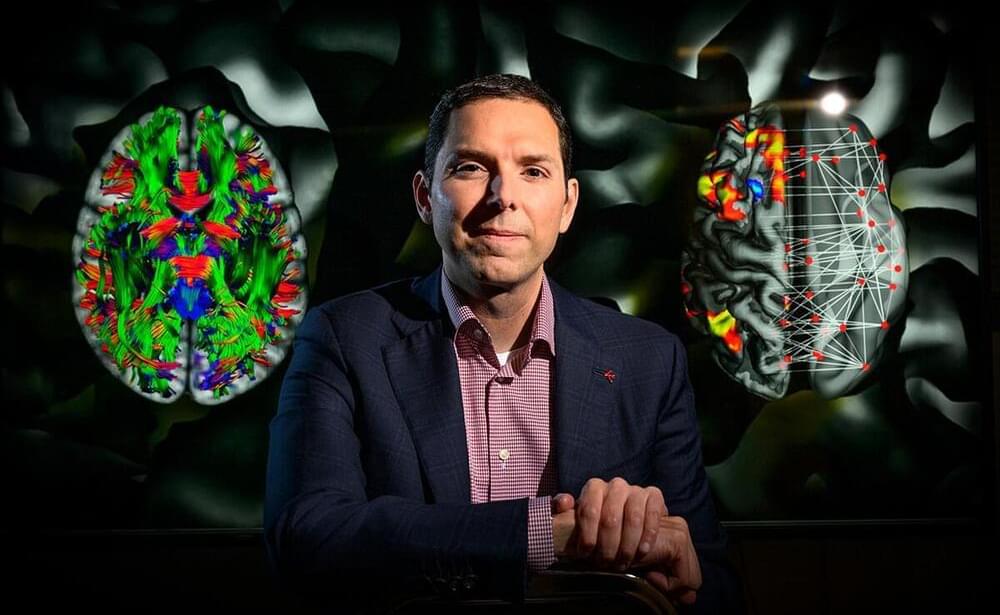


Scientists have labored for decades to understand how brain structure and functional connectivity drive intelligence. A new analysis offers the clearest picture yet of how various brain regions and neural networks contribute to a person’s problem-solving ability in a variety of contexts, a trait known as general intelligence, researchers report.
They detail their findings in the journal Human Brain Mapping.
The study used “connectome-based predictive modeling” to compare five theories about how the brain gives rise to intelligence, said Aron Barbey, a professor of psychology, bioengineering and neuroscience at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign who led the new work with first author Evan Anderson, now a researcher for Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. working at the Air Force Research Laboratory.

Transplanting a patient’s own hematopoietic stem cells may defer the progression of disability longer in patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS) than treatment with other anti-inflammatory disease-modifying therapies (DMT), reports a study published in the journal Neurology “Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in People With Active Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis”.
“Hematopoietic stem cell transplants have been previously found to delay disability in people with relapsing-remitting MS, but less is known about whether such transplants could help delay disability during the more advanced stage of the disease,” said Matilde Inglese, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Genoa in Italy and senior author of the study. “Our results are encouraging because while current treatments for SPMS have modest or small benefits, our study found stem cell transplants may not only delay disability longer than many other MS medications, they may also provide a slight improvement in symptoms.”
Patients initially diagnosed with relapsing-remitting MS, where periods of active flare-up of symptoms alternate spans of remission, eventually develop SPMS where the disease worsens gradually but steadily. The exact mechanisms leading to increased neurodegeneration in SPMS are unclear, but evidence suggests a major role of innate and adaptive immune mechanisms that drive inflammation in the brain parenchyma, the leptomeninges, and the cerebrospinal fluid.