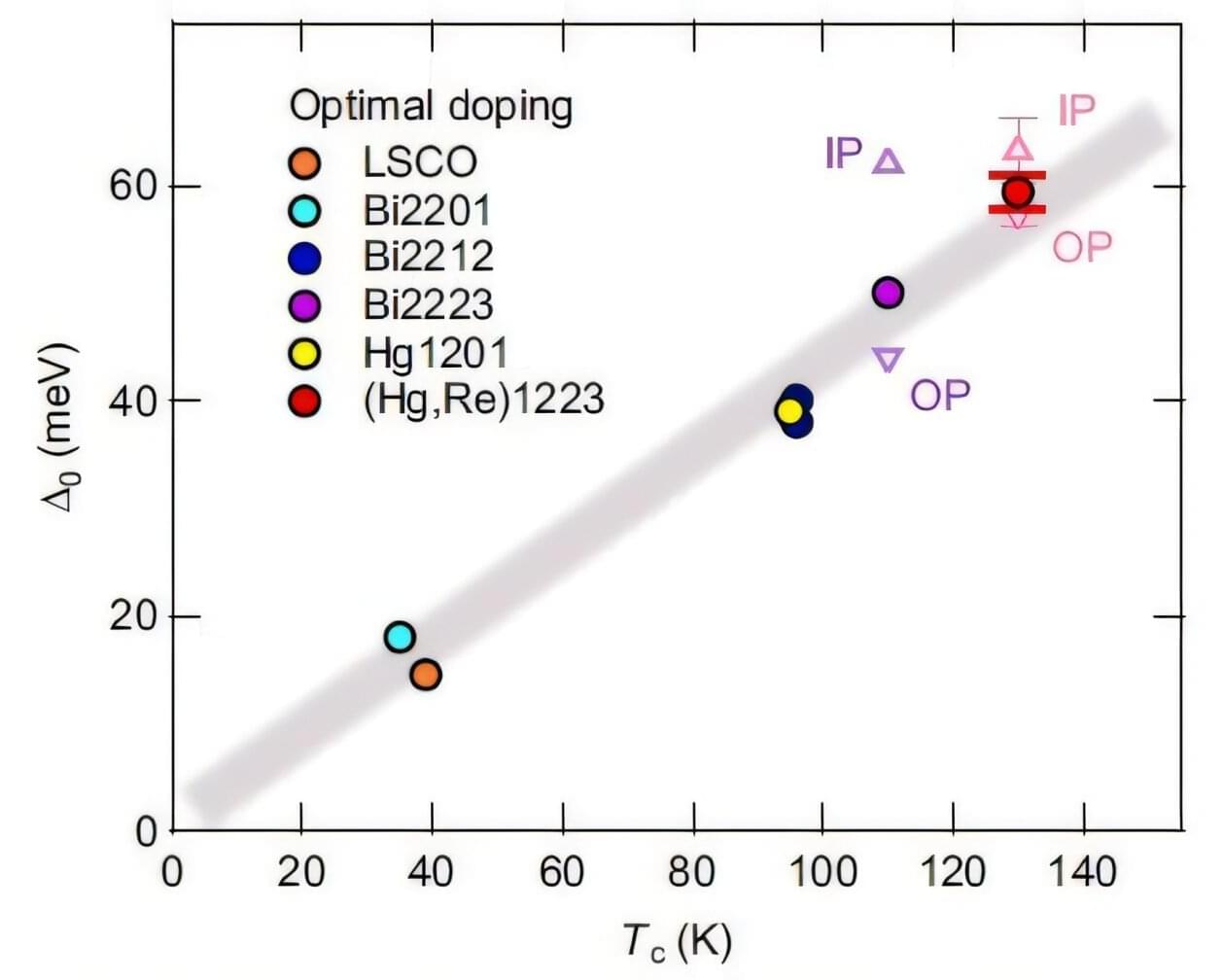
In their quest to explore and characterize high-temperature superconductors, physicists have mostly focused on a material that is not the absolute highest. That’s because that crystal is much easier to split into uniform, easily measurable samples. But in 2024, researchers found a way to grow good crystals that are very similar to the highest temperature superconductor.
Now, many from the same group have analyzed these new crystals and determined why the highest temperature superconductor is indeed higher and what details were missed by looking at the more popular crystal. Their work is published in Physical Review Letters.
The cuprate Bi2223, which at ambient pressure (about 100,000 pascals) superconducts at 110 Kelvin (−163°C), has proven easier to study and specify, even though the similar cuprate Hg1223 superconducts at 134 K.