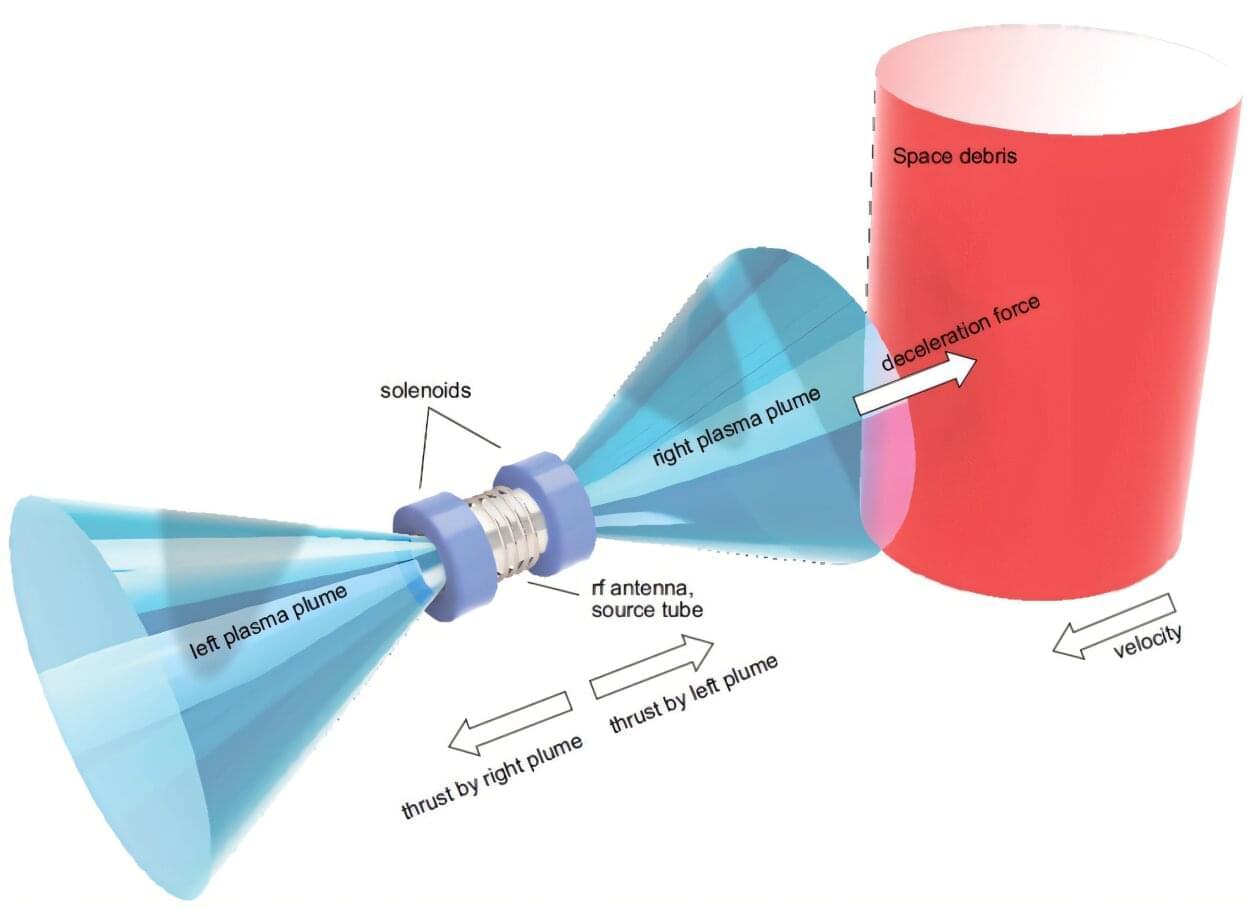
Space has a trash problem, with defunct satellites, rockets, and smaller broken bits orbiting Earth at high speeds. The amount of space junk is only increasing, raising the risk of collision with active satellites and spacecraft, according to Kazunori Takahashi, associate professor in the Graduate School of Engineering at Tohoku University in Japan. Takahashi may have a solution, though.
“Owing to their uncontrolled motion and velocity exceeding that of bullets, space debris orbiting around Earth pose a serious threat by significant increase in the potential risk of collisions with satellites that support sustainable human activity in space,” Takahashi said.
“Most current space debris removal methods are direct-contact approaches and carry the risk of becoming entangled in the uncontrolled motion of debris. More recent work has focused on using a plasma thruster to decelerate the debris, forcing it out of orbit.”