And the impending singularity may spell our end even sooner.





The world’s biggest commercial aircraft makers seem increasingly convinced that autonomous passenger flight is a question of when, not if.
Where it stands: Flying today’s high-tech passenger jets is often a matter of setting up and overseeing their autopilot and other automated systems — but we’re not yet at a point where computer systems can entirely replace human pilots.
Driving the news: “Autonomy is going to come to all of the airplanes eventually,” Boeing CEO Dave Calhoun told Bloomberg TV at an event this week marking the delivery of the last commercial 747.


Samsung has earned a strong reputation among PC enthusiasts when it comes to solid-state storage. Its Pro series of SSDs are often among reviewers’ top recommendations for users seeking high-speed storage for large work files, apps, and boot drives. Over the past year, though, reliability concerns around Samsung’s 980 Pro and most recent 990 Pro have marred this reputation. It has become so notable that custom PC-maker Puget Systems, a top proponent of Samsung SSDs since the SATA days, has pulled 1TB and 2TB Samsung drives from its lineup.
For Puget, problems with Samsung SSDs, which the 22-year-old boutique PC shop sells in its custom-built systems, started with the 980 Pro that came out in September 2020. On January 31, Puget wrote a blog noting it received a surprising number of reports of failing Samsung drives, specifically with the 2TB version of the 980 Pro.
The most common failure mode that we have found is that the drives are suddenly locked into read-only mode, rendering the drive unusable. If the failed drive is the primary drive, then the system becomes unbootable until the drive is replaced and the OS is reinstalled, Chris Newhart, a Tier 2 repair technician at Puget, wrote.
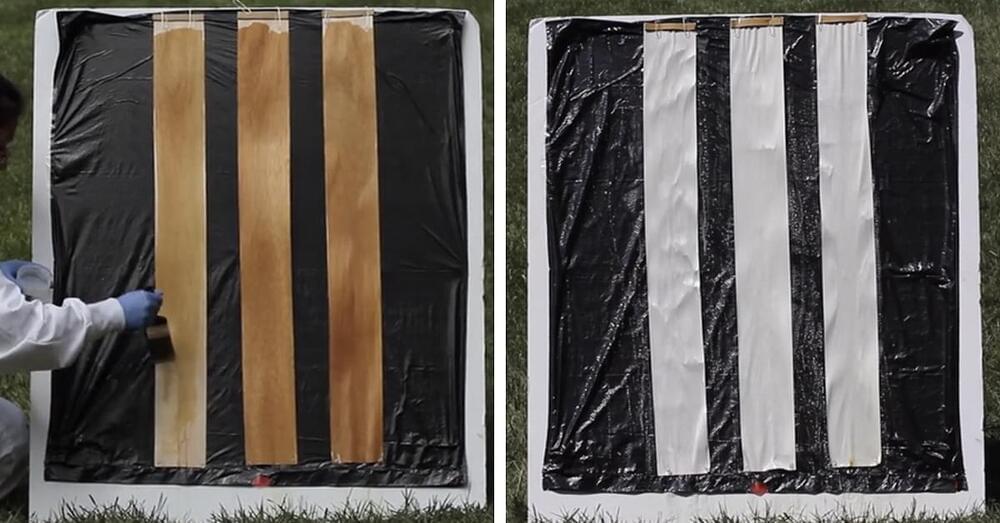

In a bid to make wood stronger and lighter than glass to move towards an energy-efficient future, a team of researchers at the University of Maryland has found a new way to make wood completely transparent which they believe to be better than the previous techniques.
The paper, published in the journal Science Advances, details the making of their transparent wood which was found to be 50 times stronger than the ones made using the conventional way.
The performance of some quantum technologies could be boosted by exploiting interactions between nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centres and defects on the surface of diamond – according to research done by two independent teams of scientists in the US.
NV centres in diamond have emerged as a promising solid-state platform for quantum sensing and information processing. They are defects in the diamond lattice in which two carbon atoms are replaced with a single nitrogen atom, leaving one lattice site vacant. NV centres are a two-level spin system into which quantum information can be written and read out using laser light and microwaves. An important property of NV centres is that once they have been put into a specific quantum state, they can remain in that state for a relatively long “coherence” time – which makes them technologically useful.