Stress isn’t always bad for you, studies show. In fact, it can slow the aging process, in the right circumstances. Psychiatrist and bestselling author Dr. Elissa Epel shares how short-term stress exercises can help you live longer.


Chinese Phone blog dedicated to providing breaking news, expert reviews, Chinese Phones, Android Apps, Chinese Android Tablets and how tos.

😗
After successful recommissioning in autumn 2022, the Greifswald nuclear fusion experiment has surpassed an important target. In 2023, an energy turnover of 1 gigajoule was targeted. Now the researchers have even achieved 1.3 gigajoules and a new record for discharge time on Wendelstein 7-X: the hot plasma could be maintained for eight minutes.
During the three-year completion work that ended last summer, Wendelstein 7-X was primarily equipped with water cooling for the wall elements and an upgraded heating system. The latter can now couple twice as much power into the plasma as before. Since then, the nuclear fusion experiment can be operated in new parameter ranges.
“We are now exploring our way towards ever higher energy values,” explained Prof. Dr. Thomas Klinger, head of the Stellarator Transport and Dynamics Division at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Greifswald. “In doing so, we have to proceed step by step so as not to overload and damage the facility.”
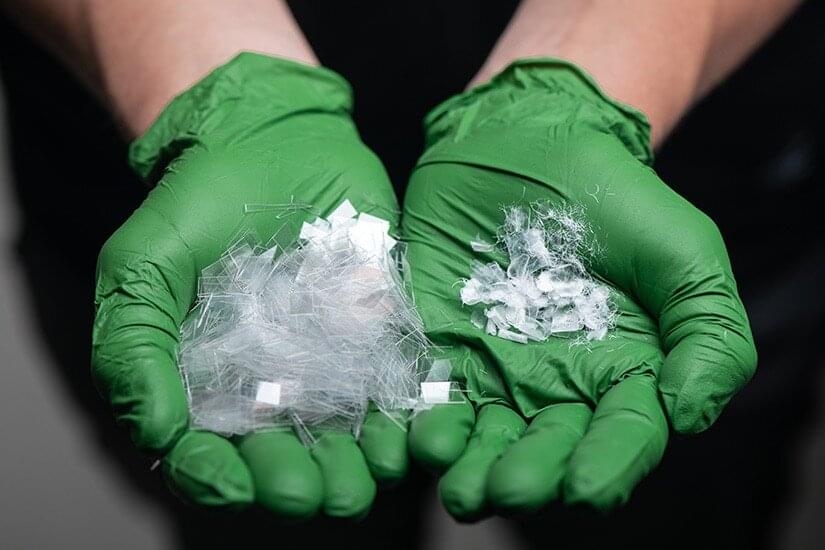

What do a T-shirt, a rug, and a soda bottle have in common? Many are made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a ubiquitous plastic that revolutionized the materials industry after it was patented in the 1940s.
Created from petroleum refining, PET is a material known for its durability and versatility. It is easily molded into airtight containers, woven into durable carpets, or spun into polyester clothing.
“The reality is that most PET products—especially PET clothing and carpeting—are not recycled today using conventional recycling technologies,” explained Gregg Beckham, senior research fellow at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and CEO of the U.S. Department of Energy BOTTLE Consortium. “The research community is developing promising alternatives, including enzymes designed to depolymerize PET, but even these options have tended to lean on energy-intensive and costly preprocessing steps to be effective.”
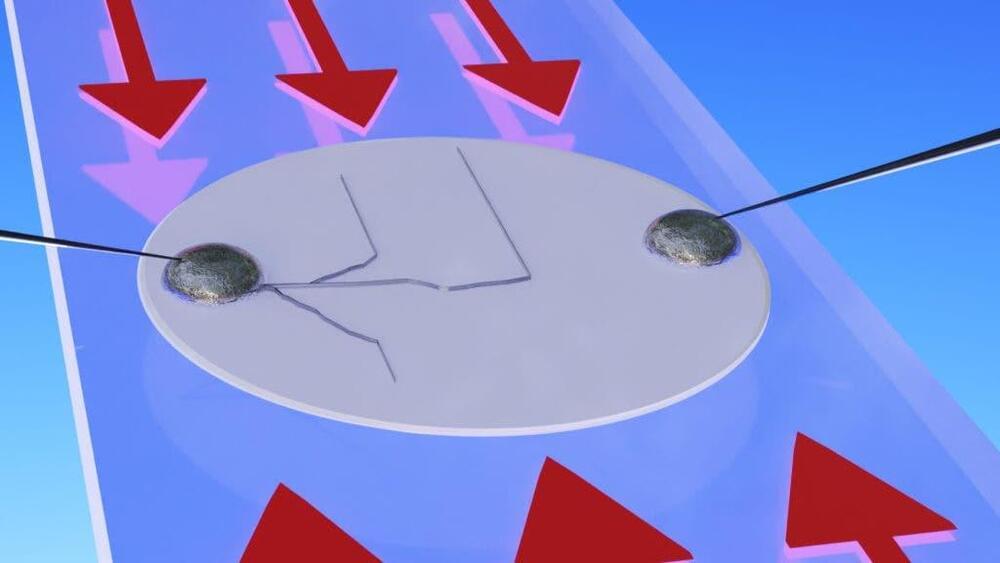
A breakthrough regarding dendrites made by MIT researchers may finally open the way to the building of a new type of rechargeable lithium battery that is safer, lighter, and more compact than existing models, a concept that has been pursued by labs all over the world for years.
The replacement of the liquid electrolyte between the positive and negative electrodes with a considerably thinner, lighter layer of solid ceramic material and the replacement of one electrode with solid lithium metal are the two essential components of this prospective advancement in battery technology. By making these changes, the battery’s overall size and weight would be significantly reduced, and the flammable liquid electrolytes that provide a safety risk would be eliminated. Dendrites, however, have proven to be a significant obstacle in that pursuit.
Dendrites are metal growths that can accumulate on the lithium surface, pierce through the solid electrolyte, and finally cross from one electrode to the other, shorting out the battery cell. Their name is from the Latin word for branches. There hasn’t been much advancement in the understanding of what causes these metal filaments or how to stop them from occurring, making lightweight solid-state batteries a problematic alternative.


By Ankita Chakravarti: ChatGPT, which is the fastest growing app in the world, has competition now. After Microsoft’ Bing and Google’s Bard AI, Anthropic, which was founded by former OpenAI employees, has launched a new AI chatbot to rival ChatGPT. The company claims that Claude is “easier to converse with” “more steerable.” and “much less likely to produce harmful outputs,”
Claude performs pretty well and has the same functions as the ChatGPT. “Claude can help with use cases including summarization, search, creative and collaborative writing, Q&A, coding, and more. Early customers report that Claude is much less likely to produce harmful outputs, easier to converse with, and more steerable — so you can get your desired output with less effort. Claude can also take direction on personality, tone, and behavior,” the company said in a blog post.
Anthrophic is offering Claude in two different variants including the Claude and Claude Instant. The company explains that Claude is a “state-of-the-art high-performance model”, while Claude Instant is a “lighter, less expensive, and much faster option.” “We plan to introduce even more updates in the coming weeks. As we develop these systems, we’ll continually work to make them more helpful, honest, and harmless as we learn more from our safety research and our deployments,” the blog read.