Year 2014 😗
A new way to easily freeze blood could revolutionise modern medicine.

Diagnosing, Treating & Curing Alzheimer’s — Dr. Doug Ethell, PhD — Founder & CEO, Leucadia Therapeutics
Dr. Doug Ethell, Ph.D. is Founder and CEO at Leucadia Therapeutics (https://www.leucadiatx.com/), a pre-clinical-stage company focused on diagnosing, treating and curing Alzheimer’s disease.
Leucadia’s proprietary Arethusta® medical device is designed to restore the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through the cribriform plate to flush toxins away from the part of the brain where Alzheimer’s disease first appears. The company also recently launched eight Apps that help exercise memory and cognition, including a personalized memory tracker called ProCogny (www.procogny.com). ProCogny allows users to play memory-intensive puzzles and games, daily Brain Boost collections of mini-puzzles, and a non-clinical version of the Leucadia Memory Test.
Dr. Ethell received a Ph.D. in Neurobiology from The University of British Columbia in Vancouver, was a Human Frontiers of Science Long Term Fellow at The Max Planck Institute for Psychiatry in Munich, a Staff Scientist at The Scripps Research Institute and La Jolla Institute for Allergy & Immunology, and a faculty member at the University of California Riverside.
In 2017, Dr. Ethell was Professor of Neuroscience, Chair of Graduate Faculty, and Head of Molecular Neurobiology at The Western Univ of Health Sciences before joining Leucadia Therapeutics full-time. He has published more than 85 peer-reviewed articles and presentation abstracts.

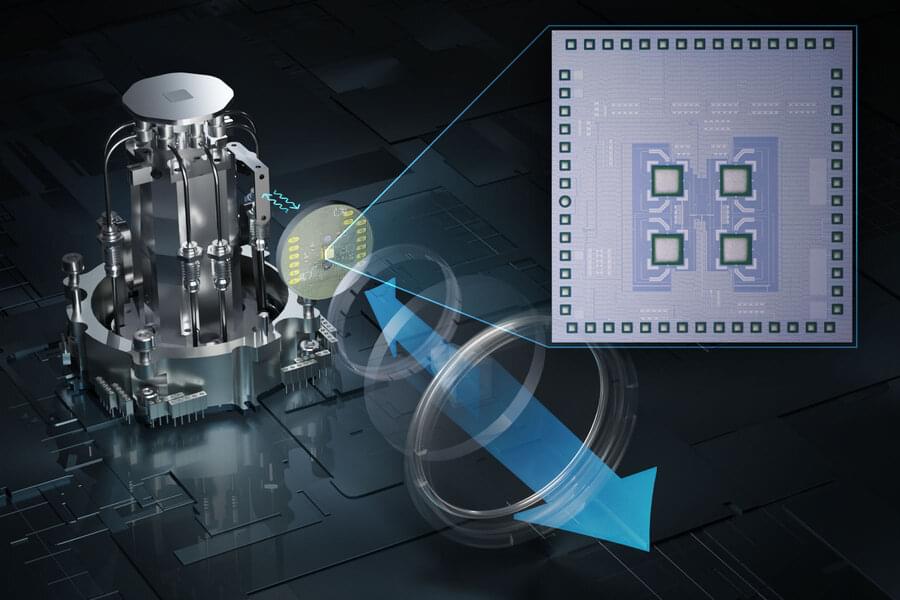
Heat causes errors in the qubits that are the building blocks of a quantum computer, so quantum systems are typically kept inside refrigerators that keep the temperature just above absolute zero (−459 degrees Fahrenheit).
But quantum computers need to communicate with electronics outside the refrigerator, in a room-temperature environment. The metal cables that connect these electronics bring heat into the refrigerator, which has to work even harder and draw extra power to keep the system cold. Plus, more qubits require more cables, so the size of a quantum system is limited by how much heat the fridge can remove.
To overcome this challenge, an interdisciplinary team of MIT researchers has developed a wireless communication system that enables a quantum computer to send and receive data to and from electronics outside the refrigerator using high-speed terahertz waves.

Google scientists said Wednesday they have passed a major milestone in their quest to develop effective quantum computing, with a new study showing they reduced the rate of errors – long an obstacle for the much-hyped technology.
Quantum computing has been touted as a revolutionary advance that uses our growing scientific understanding of the subatomic world to create a machine with powers far beyond those of today’s conventional computers.
However, the technology remains largely theoretical, with many thorny problems still standing in the way – including stubbornly high error rates.

Already smarting from a breach that put partially encrypted login data into a threat actor’s hands, LastPass on Monday said that the same attacker hacked an employee’s home computer and obtained a decrypted vault available to only a handful of company developers.
Although an initial intrusion into LastPass ended on August 12, officials with the leading password manager said the threat actor “was actively engaged in a new series of reconnaissance, enumeration, and exfiltration activity” from August 12 to August 26. In the process, the unknown threat actor was able to steal valid credentials from a senior DevOps engineer and access the contents of a LastPass data vault. Among other things, the vault gave access to a shared cloud-storage environment that contained the encryption keys for customer vault backups stored in Amazon S3 buckets.
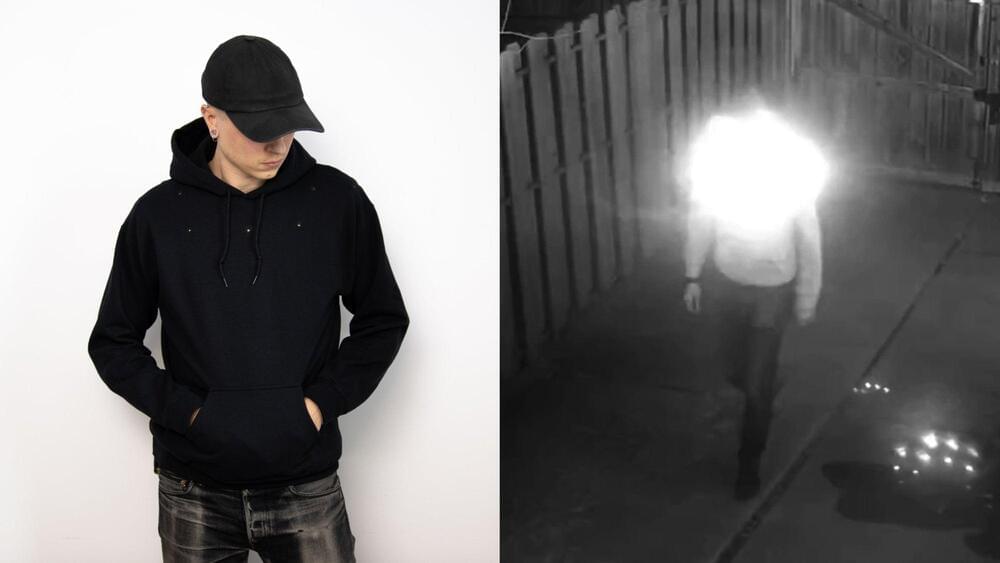


Pierce, an artist whose work critically engages with weaponized emerging technologies, recently unveiled their latest ingenious project—an everyday hoodie retrofitted to include an array of infrared (IR) LEDs that, when activated, blinds any nearby night vision security cameras. Using mostly off-the-shelf components like LumiLED lights, an Adafruit microcontroller, and silicone wire, as well as we software Pierce that made open-source for interested DIYers, the privacy-boosting “Camera Shy Hoodie” is designed to enable citizens to safely engage in civic protests and demonstrations. Or, wearers can just simply opt-out of being tracked by unknown third-parties while walking down the street.
A DIY hack for hoodies emits infrared LEDs to obscure wearers’ faces from invasive surveillance camera tracking.