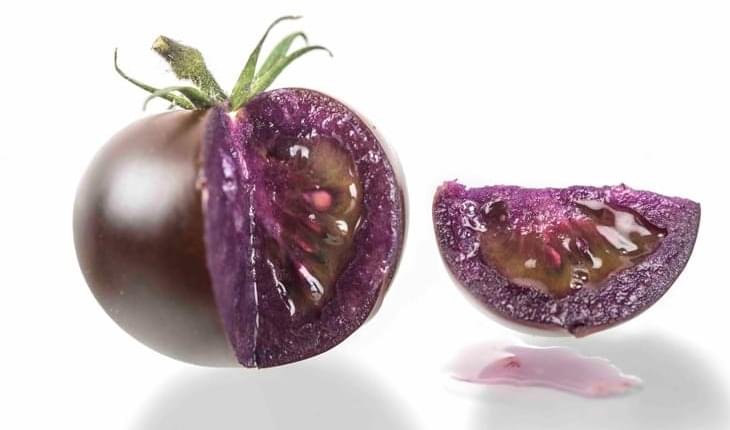
U.S. regulators have approved a new purple tomato, genetically engineered to be packed with antioxidants and anthocyanins. The fruit will go on sale in 2023.


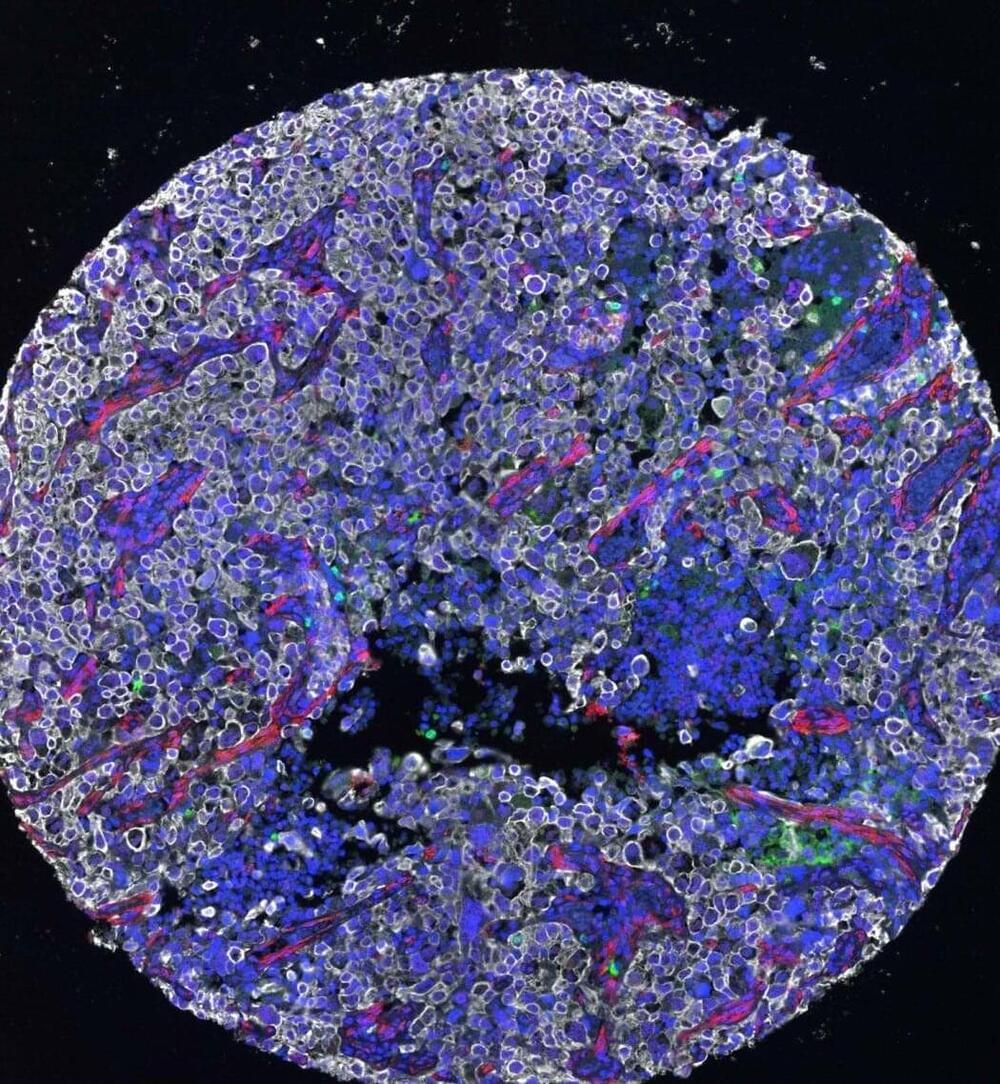
Tumor cells are notoriously good at evading the human immune system; they put up physical walls, wear disguises and handcuff the immune system with molecular tricks. Now, UC San Francisco researchers have developed a drug that overcomes some of these barriers, marking cancer cells for destruction by the immune system.
The new therapy, described in Cancer Cell, pulls a mutated version of the protein KRAS to the surface of cancer cells, where the drug-KRAS complex acts as an “eat me” flag. Then, an immunotherapy can coax the immune system to effectively eliminate all cells bearing this flag.
“The immune system already has the potential to recognize mutated KRAS, but it usually can’t find it very well. When we put this marker on the protein, it becomes much easier for the immune system,” said UCSF chemist and Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator Kevan Shokat, Ph.D., who also helped lead the new work.
Designer Oscar Vinals introduced his concept for HSP Magnavem in 2018, but it’s getting attention again because of the developments in the industry.

Two big players in computing and research are trying to lay the groundwork for a future quantum internet.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is teaming up with Harvard University to test and develop strategies for networking together quantum technologies. Their partnership was announced today, and is a continuation of AWS’ goals to create a communications channel between the quantum computers that it is also working on in parallel.
During the three-year research alliance, funding from Amazon will support research projects at Harvard that focus on quantum memory, integrated photonics, and quantum materials, and help upgrade infrastructure in Harvard’s Center for Nanoscale Systems.

It’s one of the oldest problems in the universe: Since matter and antimatter annihilate each other on contact, and both forms of matter existed at the moment of the big bang, why is there a universe made primarily of matter rather than nothing at all? Where did all the antimatter go?
“The fact that our current-day universe is dominated by matter remains among the most perplexing, longstanding mysteries in modern physics,” University of California, Riverside professor of physics and astronomy Yanou Cui said in a statement shared this week. “A subtle imbalance or asymmetry between matter and antimatter in the early universe is required to achieve today’s matter dominance but cannot be realized within the known framework of fundamental physics.”
There are theories that might answer that question, but they are extremely to difficult to test using laboratory experiments. Now, in a new paper published Thursday in the journal Physical Review Letters, Dr Cui and her co-author, Zhong-Zhi Xianyu, assistant professor of physics at Tsinghua University, China, explain they may have found a work around using the afterglow of the big bang itself to run the experiment.

AN ARTIFICIAL intelligence text-to-image model has forecasted a disturbing end to mankind’s existence.
The popular Craiyon AI, formerly DALL-E mini AI image generator, designed some barren landscapes and scorched plains when prompted to predict the end of humans.
The AI has been trained to create its masterpieces using unfiltered data from the internet.
ROBOTS could one day overthrow humans in an ‘apocalyptic’ takeover, a tech expert has predicted.
Aidan Meller, the creator of the Ai-Da robot, believes that within three years artificial intelligence (AI) could overtake humanity, per The Daily Star.
He also backs Elon Musk’s belief that advances in AI could impact mankind more than nuclear war.

An international team of scientists announced on Wednesday that they have discovered two new “super-Earth” planets just 100 light-years away. Both of them are significantly larger than our own planet — and one of them may even be suitable for life.
Super-Earths are a unique class of exoplanet in the solar system that are more massive than our planet but lighter than the ice giants, according to NASA. They are made by some combination of gas and rock and can get up to 10 times the size of Earth’s mass.
The findings, discovered with NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite and the University of Liège’s Search for Habitable Planets Eclipsing Ultra-Cool Stars (SPECULOOS), will be published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.

THE JAMES Webb Space Telescope has captured new images of a distant planet in a first for the world’s top space observatory. The James Webb Space Telescope launched on Christmas Day in 2021 Credit: Alamy 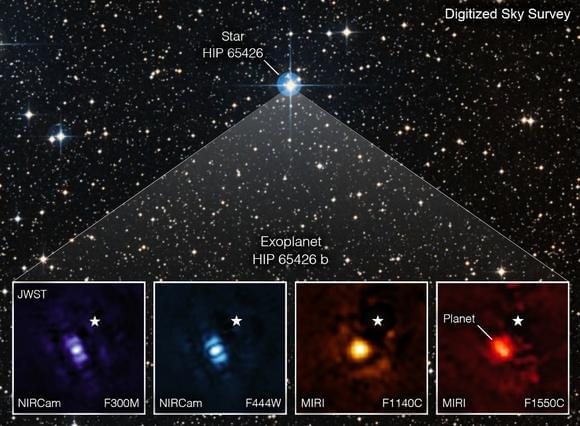
The star pasted on the images represents the planet’s host star Credit: NASAPhotographing distant planets is extremely difficult because light from their host star will pollute the images.
