Robot grippers made from soft plastics will melt in the heat, but a wooden alternative can do the job just fine.
By Alex Wilkins
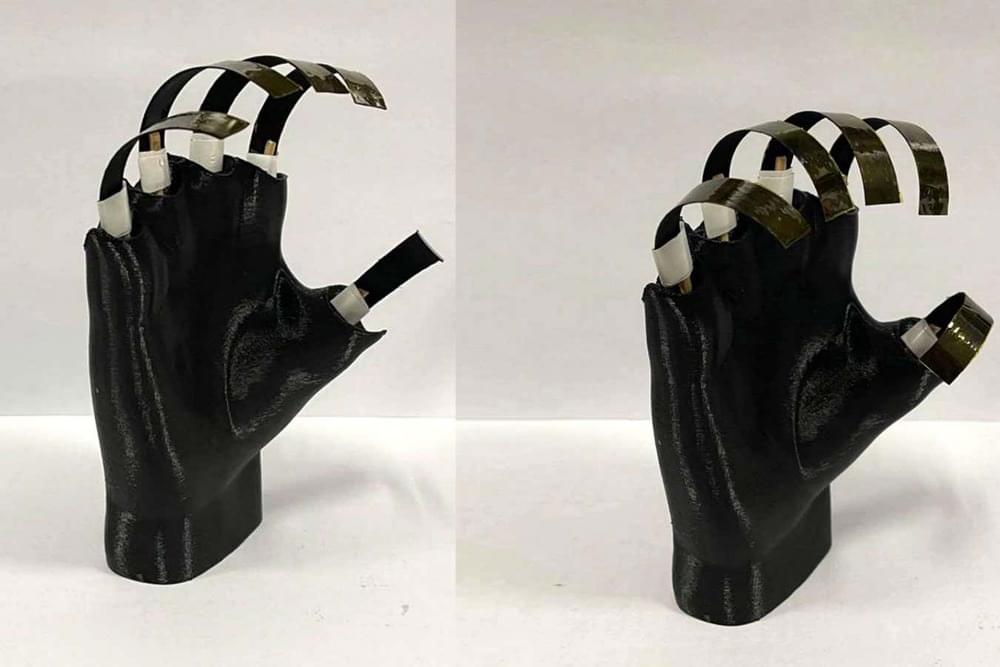

Robot grippers made from soft plastics will melt in the heat, but a wooden alternative can do the job just fine.
By Alex Wilkins
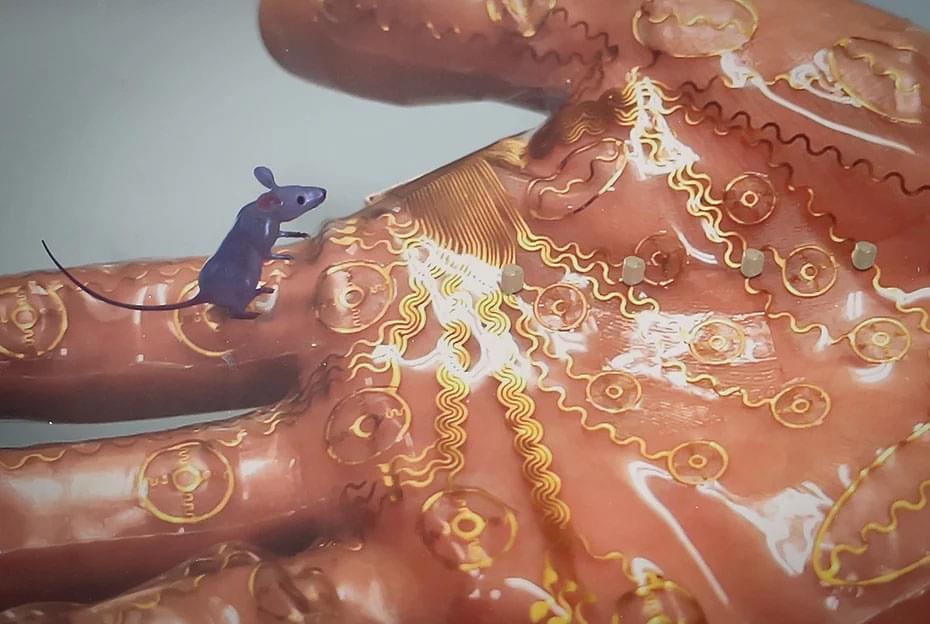
The sense of touch may soon be added to the virtual gaming experience, thanks to an ultrathin wireless patch that sticks to the palm of the hand. The patch simulates tactile sensations by delivering electronic stimuli to different parts of the hand in a way that is individualized to each person’s skin.
Developed by researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) with collaborators and described in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence (“Encoding of tactile information in hand via skin-integrated wireless haptic interface”), the patch has implications beyond virtual gaming, as it could also be used for robotics surgery and in prosthetic sensing and control.
‘Haptic’ gloves, that simulate the sense of touch, already exist but are bulky and wired, hindering the immersive experience in virtual and augmented reality settings. To improve the experience, researchers led by CityU biomedical engineer Yu Xinge developed an advanced, wireless, haptic interface system called ‘WeTac’.
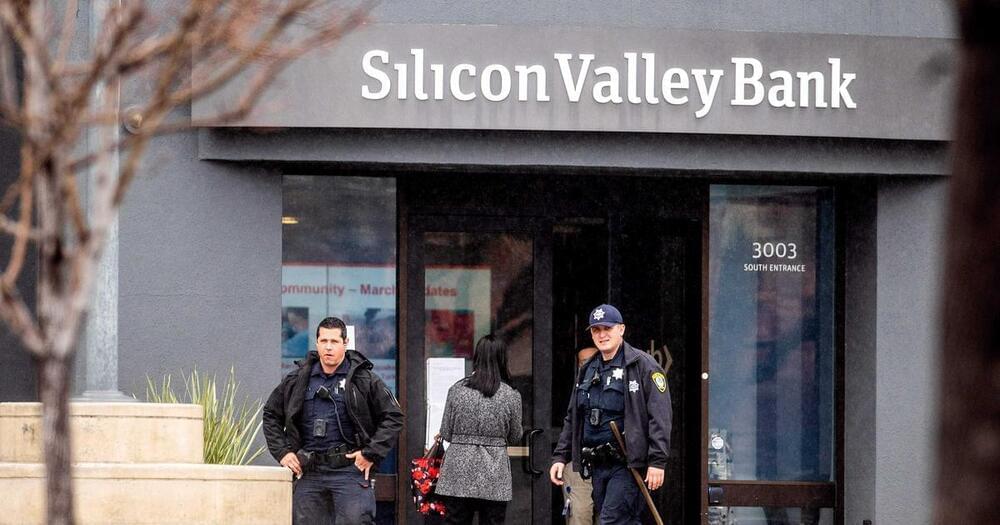


FarmboxRx’s Ashley Tyrner told The New York Post Friday that “all panic broke loose” when she went to login to the company’s SVB account to get a transaction approved when the system crashed and locked her out.
“When I went to log in to approve the wire, the system was completely crashed,” Tyrner told the newspaper. “It would not let anybody in.”
Tyrner called customer service and her SVB personal banker who “wouldn’t answer” the phone. She said he later texted her to apologize and said the bank was attempting to fix the issue.
A group led by Professor Ralf Rabus, a microbiologist at the University of Oldenburg, and his Ph.D. student Patrick Becker has made significant advancements in comprehending the cellular processes of a widespread environmental bacterium. The team conducted an extensive analysis of the entire metabolic network of the bacterial strain Aromatoleum aromaticum EbN1T and utilized the findings to construct a metabolic model that allows them to forecast the growth of these microbes in various environmental conditions.
According to their report in the journal mSystems, the researchers uncovered surprising mechanisms that enable the bacteria to adjust to fluctuating environmental conditions. These results are crucial for the study of ecosystems, where the Aromatoleum strain, as a representative of a significant group of environmental bacteria, can act as a model organism. The findings could also have implications for the cleanup of contaminated sites and biotechnological applications.
The studied bacterial strain specializes in the utilization of organic substances that are difficult to break down and is generally found in soil and in aquatic sediments. The microbes thrive in a variety of conditions including oxygen, low-oxygen, and oxygen-free layers, and are also extremely versatile in terms of nutrient intake. They metabolize more than 40 different organic compounds including highly stable, naturally occurring substances such as components of lignin, the main structural material found in wood, and long-lived pollutants and components of petroleum.

FallenKingdomReads’ list of 10 Science Fiction Books That Predicted the Future with Eerie Accuracy.
Science fiction has always been a genre that imagines what the future might hold, but sometimes it goes beyond mere speculation and eerily predicts what actually happens. Here are ten science fiction books that predicted the future with accuracy that is almost too close for comfort.
This dystopian novel predicted a world in which government surveillance and control were all-encompassing, and the public was constantly monitored and manipulated. Many of the themes in the book have become all too familiar in today’s world of mass surveillance and government control.
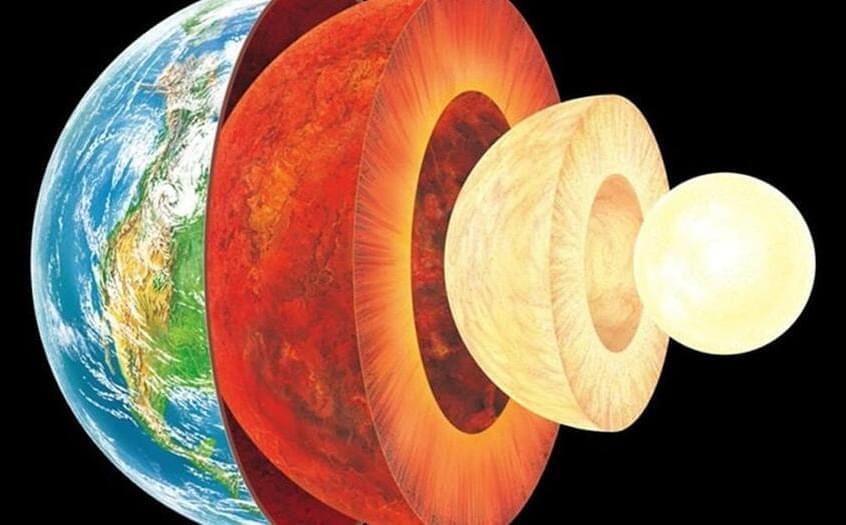
The inner workings of our planet are getting weirder.
For generations, scientists have probed the structure and composition of the planet using seismic wave studies. This consists of measuring shock waves caused by earthquakes as they penetrate and pass through the Earth’s core region. By noting differences in speed (a process known as anisotropy), scientists can determine which regions are denser than others. These studies have led to the predominant geological model that incorporates four distinct layers: a crust and a mantle (composed largely of silicate minerals) and an outer core and inner core composed of nickel-iron.
According to seismologists from The Australian National University (ANU), data obtained in a recent study has shed new light on the deepest parts of Earth’s inner core. In a paper that appeared in Nature Communications, the team reports finding evidence for another distinct layer (a solid metal ball) in the center of Earth’s inner core — an “innermost inner core.” These findings could shed new light on the evolution of our planet and lead to revised geological models of Earth that include five distinct layers instead of the traditional four.
The research was led by Dr. Thanh-Son Pham and Dr. Hrvoje Tkalcic, a postdoctoral fellow and professor with ANU’s Research School of Earth Sciences (RSES), respectively. As they indicate, the team stacked seismic wave data from about 200 earthquakes in the past decade that were magnitude-6 or more. The triggered waveforms were recorded by seismic stations worldwide, which traveled directly through the Earth’s center to the opposite side of the globe (the antipode) before traveling back to the source of the earthquake.


Physicists at the University of Cincinnati have contributed to an international experiment on strange metals made from an alloy of ytterbium, a rare earth metal. The study involved firing radioactive gamma rays at the strange metal to observe its unusual electrical behavior. The experiment revealed unusual fluctuations in the strange metal’s electrical charge, furthering the understanding of the bizarre behavior of strange metals that operate outside the normal rules of electricity.
International team finds unusual electrical behavior in material that holds promise for new technology.
Physicists at the University of Cincinnati (UC) are learning more about the bizarre behavior of “strange metals,” which operate outside the normal rules of electricity.