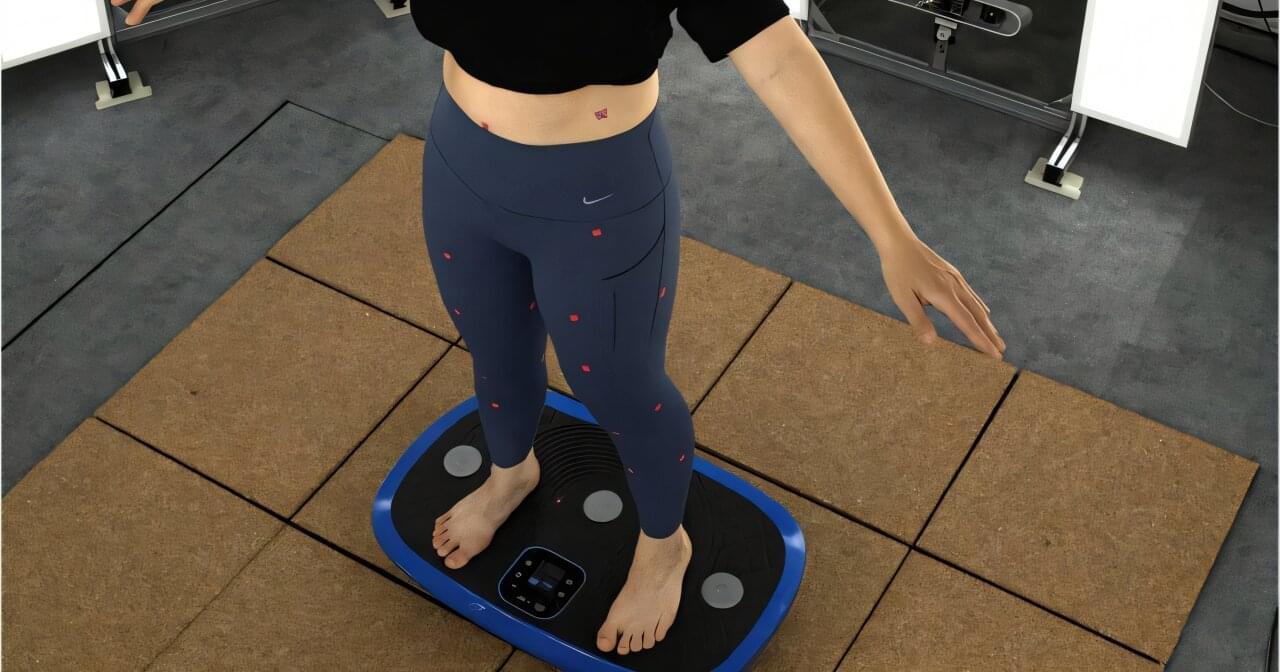
Soft tissue deformation during body movement has long posed a challenge to achieving optimal garment fit and comfort, particularly in sportswear and functional medical wear.
Researchers at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) have developed a novel anthropometric method that delivers highly accurate measurements to enhance the performance and design of compression-based apparel.
Prof. Joanne YIP, Associate Dean and Professor of the School of Fashion and Textiles at PolyU, and her research team pioneered this anthropometric method using image recognition algorithms to systematically access tissue deformation while minimizing motion-related errors.