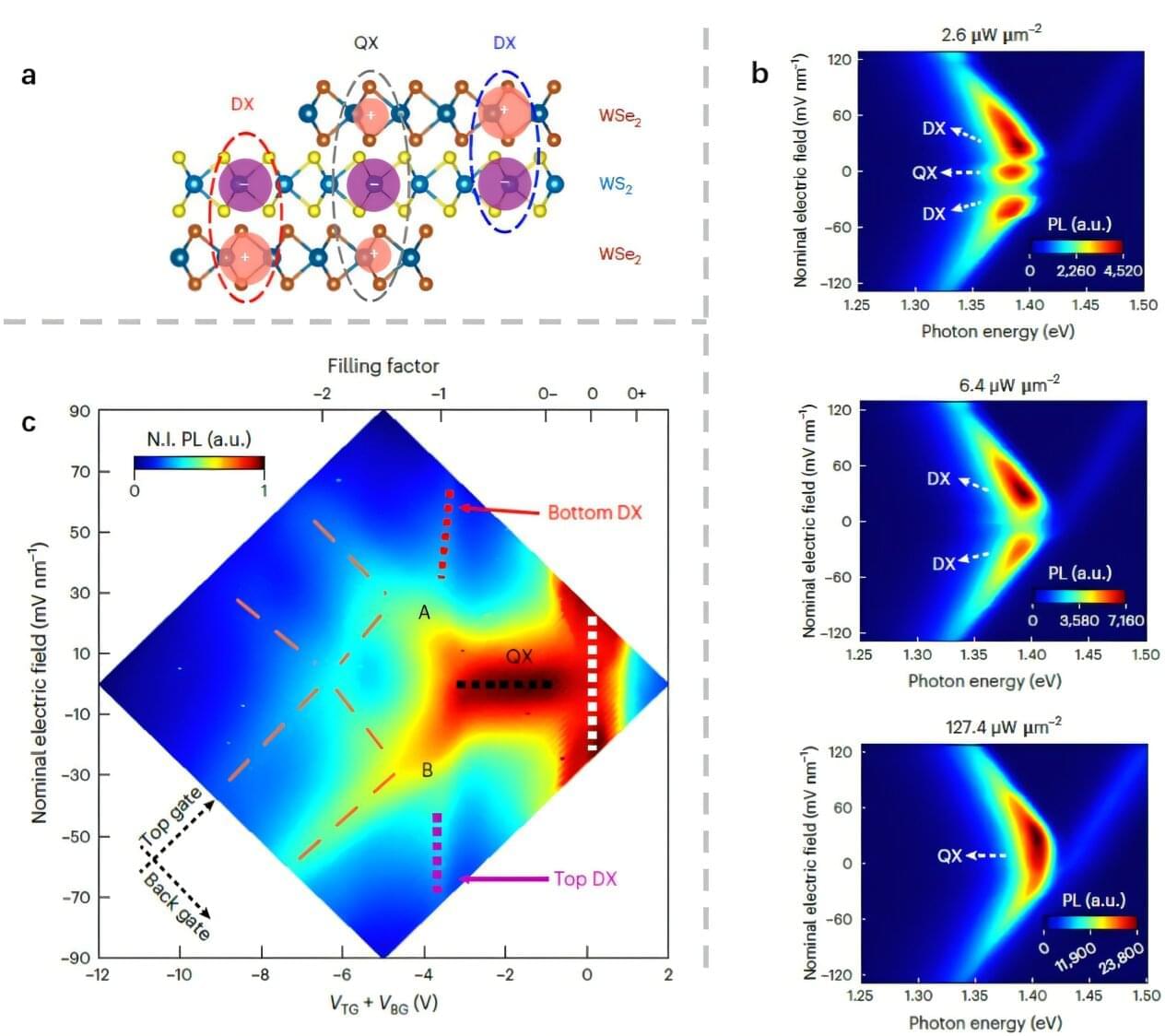
Moiré superlattices are periodic patterns formed when two or more thin semiconducting layers are stacked with a small twist angle or lattice mismatch. When 2D materials form these patterns, their electronic, mechanical, and optical properties can change significantly.
Over the past decades, moiré superlattices have emerged as a promising platform to study unconventional and unknown physical states. They also enabled the observation of unique excitonic configurations (i.e., arrangements of bound electron-hole pairs).
In bilayer moiré systems based on two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), for instance, physicists have observed interlayer dipolar excitons. These are excitons produced when an electron and a hole are bound together across different layers in a stacked 2D semiconductor.