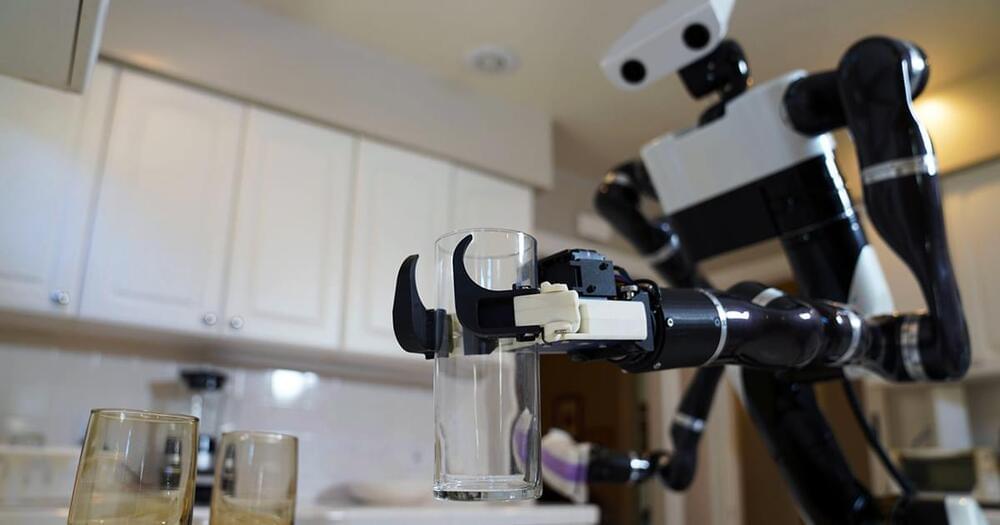
Engineers from National University of Singapore (NUS) have built a robotics system they say can grip various objects, ranging from soft and delicate to bulky and heavy. Designed to be configurable, the robotic hand is touted to address the needs of sectors such as vertical farming, food assembly, and fast-moving consumer goods packaging, and with a 23% improvement in efficiency.
These industries increasingly were automating more of their operations, but currently required manual handling for some processes, according to NUS. The human hand’s natural dexterity remained necessary for these tasks.
Rave Yeow, associate professor from NUS Advanced Robotics Centre and Department of Biomedical Engineering, said: “An object’s shape, texture, weight, and size affect how we choose to grip them. This is one of the main reasons why many industries still heavily rely on human labour to package and handle delicate items.”