We should really be looking to nuclear power FAR more than we have been. Until fusion finally comes of age anyway. It’s one of the most annoyingly counterproductive issue with many environmentalists I tend to have.
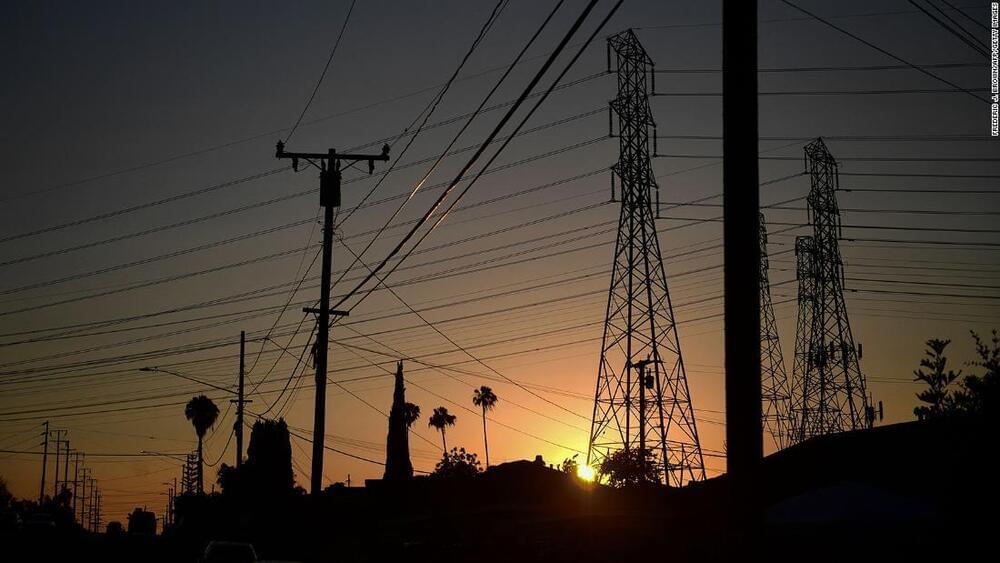
Extreme temperatures and ongoing drought could cause the power grid to buckle across vast areas of the country this summer, potentially leading to electricity shortages and blackouts, a US power grid regulator said Wednesday.
NERC, a regulating authority that oversees the health of the nation’s electrical infrastructure, says in its 2022 Summer Reliability Assessment that extreme temperatures and ongoing drought could cause the power grid to buckle. High temperatures, the agency warns, will cause the demand for electricity to rise. Meanwhile, drought conditions will lower the amount of power available to meet that demand.
“Industry prepares its equipment and operators for challenging summer conditions. Persistent, extreme drought and its accompanying weather patterns, however, are out of the ordinary and tend to create extra stresses on electricity supply and demand,” said Mark Olson, NERC’s manager of Reliability Assessments.