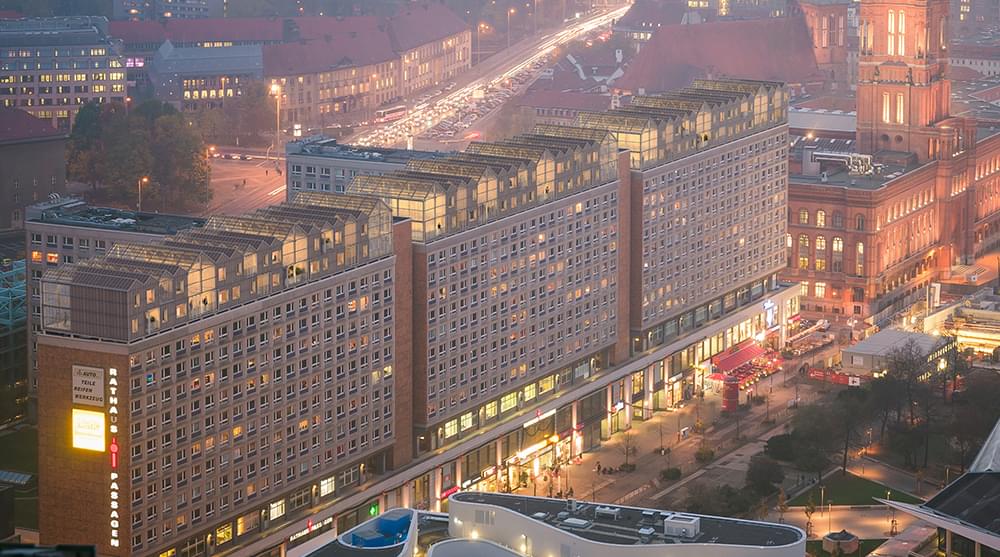
The Berlin Affordable Housing Challenge is part of Bee Breeders’ Affordable Housing competition series. Run in partnership with ARCHHIVE BOOKS, this competition tasked participants with submitting innovative design proposals for tackling Berlin’s housing crisis.
Germany’s new government, formed in 2021, has vowed to make affordable housing a centerpiece of its agenda. Berlin, the capital city and the country’s center of gravity for entrepreneurship and new business, is in particular feeling extreme housing market pressures. According to an article published by NPR during the period of this competition, eight out of 10 city residents are now renters, where rent has increased 42% since 2016, and where an average of 40,000 new residents arrive each year.