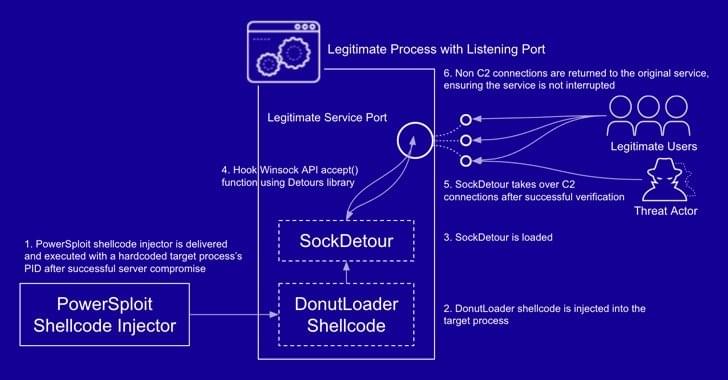
Researchers discovered a new stealth malware, dubbed SockDetour, that operates filelessly and socketlessly on compromised systems.
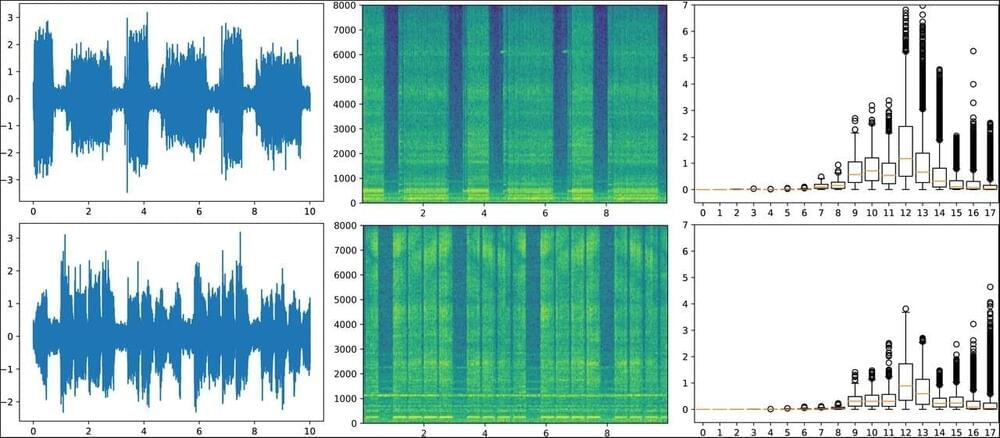
Sounds provide important information about how well a machine is running. ETH researchers have now developed a new machine learning method that automatically detects whether a machine is “healthy” or requires maintenance.
Whether railway wheels or generators in a power plant, whether pumps or valves—they all make sounds. For trained ears, these noises even have a meaning: devices, machines, equipment or rolling stock sound differently when they are functioning properly compared to when they have a defect or fault.
The sounds they make, thus, give professionals useful clues as to whether a machine is in a good—or “healthy”—condition, or whether it will soon require maintenance or urgent repair. Those who recognize in time that a machine sounds faulty can, depending on the case, prevent a costly defect and intervene before it breaks down. Consequently, the monitoring and analysis of sounds have been gaining in importance in the operation and maintenance of technical infrastructure—especially since the recording of tones, noises and acoustic signals is made comparatively cost-effective with modern microphones.
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCDukC60SYLlPwdU9CWPGx9Q/join.
Neura Pod is a series covering topics related to Neuralink, Inc. Topics such as brain-machine interfaces, brain injuries, and artificial intelligence will be explored. Host Ryan Tanaka synthesizes informationopinions, and conducts interviews to easily learn about Neuralink and its future.
Most people aren’t aware of what the company does, or how it does it. If you know other people who are curious about what Neuralink is doing, this is a nice summary episode to share. Tesla, SpaceX, and the Boring Company are going to have to get used to their newest sibling. Neuralink is going to change how humans think, act, learn, and share information.
Neura Pod:
Inflation is destroying the value of your money. Hedge yourself!
Links mentioned:
coinbase.com.
pro.coinbase.com.
kraken.com.
gemini.com.
celsius.network.
nexusmutual.io.
metamask.io.
les.
uniswap.org.
ledger.com
© 2022 WWB Holdings, LLC. All rights reserved.
The treatment, which is based on breakthrough CRISPR technology, uses gene-editing to to eradicate the genetic material of HIV from infected cells.
Russia ramped up its cyberattacks on Ukraine prior to its physical invasion, potentially foreshadowing how future conflicts will play out.
By harvesting water vapor from the air and condensing it into liquid, atmospheric water generators can essentially pull water from the air.
Epidemiological data have long linked depression with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive dementia that affects nearly 6 million Americans. Now, a new study identifies common genetic factors in both depression and AD. Importantly, the researchers found that depression played a causal role in AD development, and those with worse depression experienced a faster decline in memory. The study appears in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
Co-senior author Aliza Wingo, MD, of Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, USA, said of the work, “It raises the possibility that there are genes that contribute to both illnesses. While the shared genetic basis is small, the findings suggest a potential causal role of depression on dementia.”
The authors performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS), a technique that scans the entire genome for areas of commonality associated with particular conditions. The GWAS identified 28 brain proteins and 75 transcripts – the messages that encode proteins – that were associated with depression. Among those, 46 transcripts and 7 proteins were also associated with symptoms of AD. The data suggest a shared genetic basis for the two diseases, which may drive the increased risk for AD associated with depression.
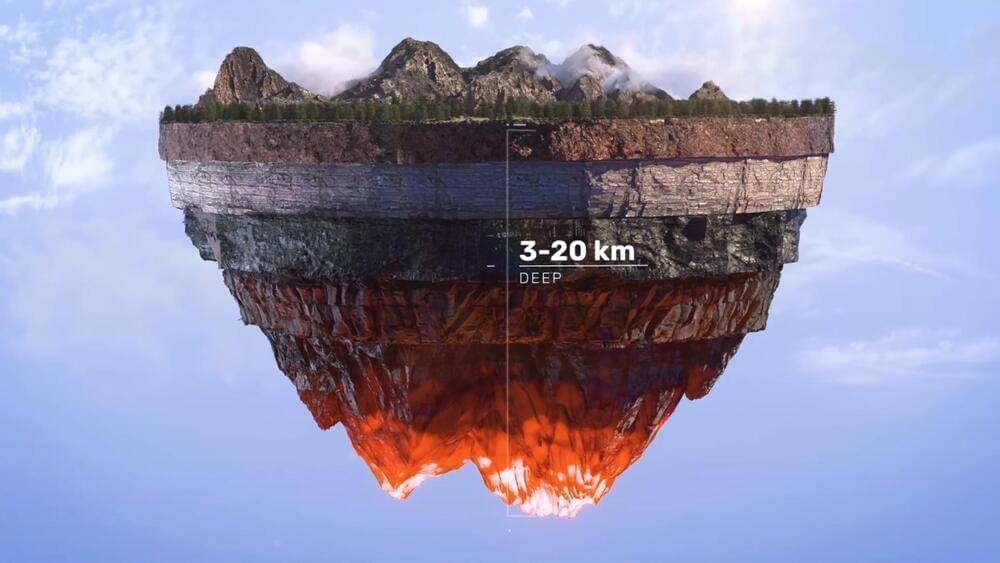
MIT spin-off Quaise says it’s going to use hijacked fusion technology to drill the deepest holes in history, unlocking clean, virtually limitless, supercritical geothermal energy that can re-power fossil-fuelled power plants all over the world.
DoD announced today awards of $28.7 million in grants to 17 university-based faculty teams through the FY2021 Minerva Research Initiative to support research in social and behavioral science.
“We live in a dynamic world, and many of the challenges we face are social or have social elements to them,” said Dr. Bindu Nair, Director, Basic Research Office in the Office of the Undersecretary of Defense for Research and Engineering. “The knowledge and methodologies generated from Minerva awardees have improved DoD’s ability to define sources of present and future conflict with an eye toward better understanding the political trajectories of key regions of the world.”
This initiative supports basic research that focuses on topics of particular relevance to U.S. national security. Through its network of faculty investigators, the Minerva Research Initiative also strengthens the Department’s connections with the social science community and helps DoD better understand and prepare for future challenges, including National Defense Strategy priorities.