In the future, communications networks and computers will use information stored in objects governed by the microscopic laws of quantum mechanics. This capability can potentially underpin communication with greatly enhanced security and computers with unprecedented power. A vital component of these technologies will be memory devices capable of storing quantum information to be retrieved at will.
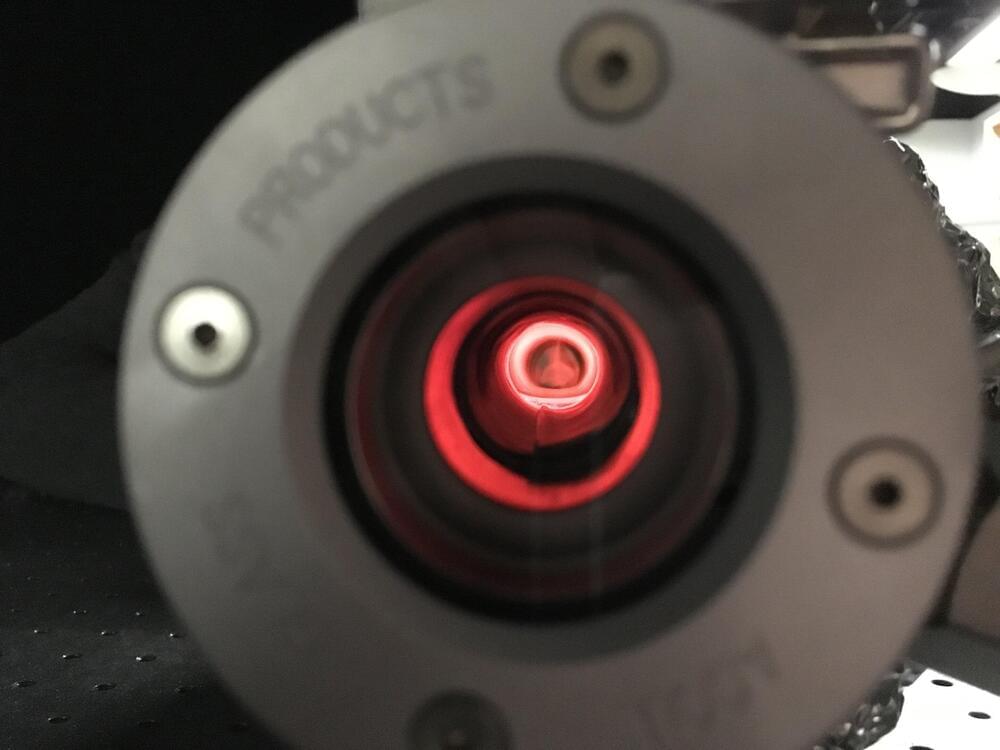
Virginia Lorenz, a professor of physics at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, studies Lambda-type optical quantum memory devices, a promising technology that relies on light interacting with a large group of atoms. She is developing a device based on hot metallic vapor with graduate student Kai Shinbrough.
As the researchers work towards a practical device, they are also providing some of the first theoretical analyses of Lambda-type devices. Most recently, they reported the first variance-based sensitivity analysis describing the effects of experimental noise and imperfections in Physical Review A.