Artificial intelligence (AI) has become commonplace, and quantum computing is set to alter the landscape radically. The potential of quantum computers to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds could render existing AI chatbots, such as ChatGPT, obsolete.
The intricacies of quantum computing intertwine with understanding the evolution of artificial intelligence. This journey reveals the convergence of two transformative technologies, uncovers challenges, opens opportunities, and underscores the vital role of safeguarding innovations through patent law.
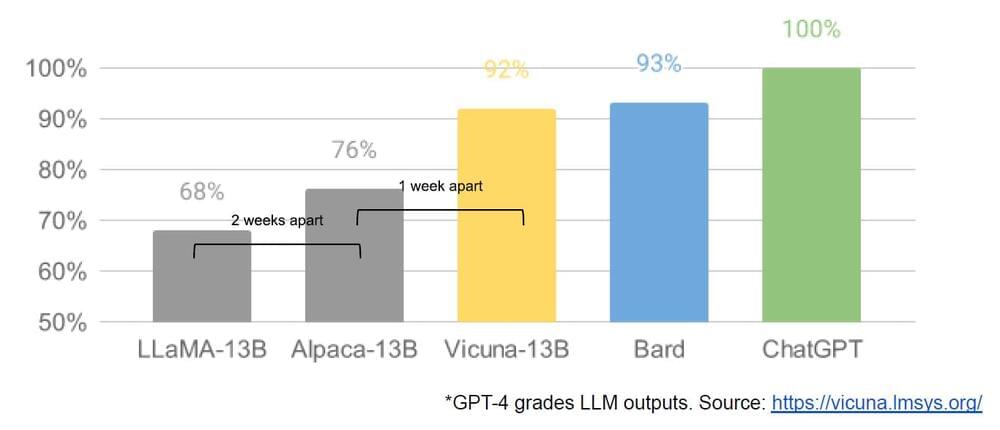
Artificial intelligence has surged forward in recent years, developing sophisticated AI chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT.

 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)