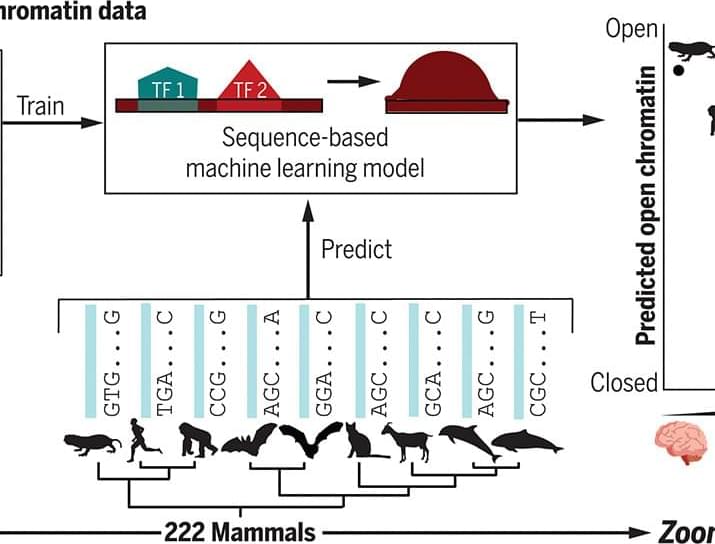
Protein-coding sequence differences have failed to fully explain the evolution of multiple mammalian phenotypes. This suggests that these phenotypes have evolved at least in part through changes in gene expression, meaning that their differences across species may be caused by differences in genome sequence at enhancer regions that control gene expression in specific tissues and cell types. Yet the enhancers involved in phenotype evolution are largely unknown. Sequence conservation–based approaches for identifying such enhancers are limited because enhancer activity can be conserved even when the individual nucleotides within the sequence are poorly conserved. This is due to an overwhelming number of cases where nucleotides turn over at a high rate, but a similar combination of transcription factor binding sites and other sequence features can be maintained across millions of years of evolution, allowing the function of the enhancer to be conserved in a particular cell type or tissue. Experimentally measuring the function of orthologous enhancers across dozens of species is currently infeasible, but new machine learning methods make it possible to make reliable sequence-based predictions of enhancer function across species in specific tissues and cell types.