MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif. (AP) — Google on Wednesday disclosed plans to infuse its dominant search engine with more advanced artificial-intelligence technology, a drive that’s in response to one of the biggest threats to its long-established position as the internet’s main gateway.
The gradual shift in how Google’s search engine runs is rolling out three months after Microsoft’s Bing search engine started to tap into technology similar to that which powers the artificially intelligent chatbot ChatGPT, which has created one of Silicon Valley’s biggest buzzes since Apple released the first iPhone 16 years ago.
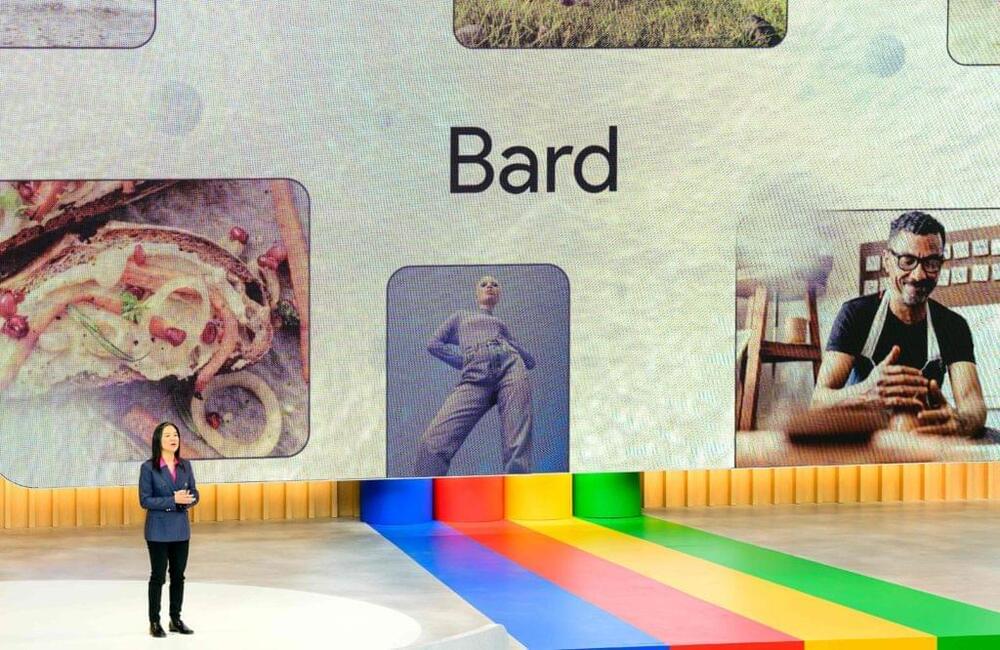
Google, which is owned by Alphabet Inc., already has been testing its own conversational chatbot called Bard. That product, powered by technology called generative AI that also fuels ChatGPT, has only been available to people accepted from a waitlist. But Google announced Wednesday that Bard will be available to all comers in more than 180 countries and more languages beyond English.