Here’s what Silicon Valley Business Journal senior reporter Max A. Cherney had to say on KQED’s Forum about Nvidia and the AI boom.



If you’ve ever struggled with insomnia, you’ve likely heard of melatonin. This nutritional supplement has been widely available in drug stores, health food stores and grocery stores for years, and touted as a natural sleep aid. It even comes in doses meant for children.
But what is melatonin? And is it safe for cancer patients to take during treatment?
We checked in with pulmonologist Saadia Faiz, M.D., for answers.

One nebulous aspect of the poll, and of many of the headlines about AI we see on a daily basis, is how the technology is defined. What are we referring to when we say “AI”? The term encompasses everything from recommendation algorithms that serve up content on YouTube and Netflix, to large language models like ChatGPT, to models that can design incredibly complex protein architectures, to the Siri assistant built into many iPhones.
IBM’s definition is simple: “a field which combines computer science and robust datasets to enable problem-solving.” Google, meanwhile, defines it as “a set of technologies that enable computers to perform a variety of advanced functions, including the ability to see, understand and translate spoken and written language, analyze data, make recommendations, and more.”
It could be that peoples’ fear and distrust of AI comes partly from a lack of understanding of it, and a stronger focus on unsettling examples than positive ones. The AI that can design complex proteins may help scientists discover stronger vaccines and other drugs, and could do so on a vastly accelerated timeline.
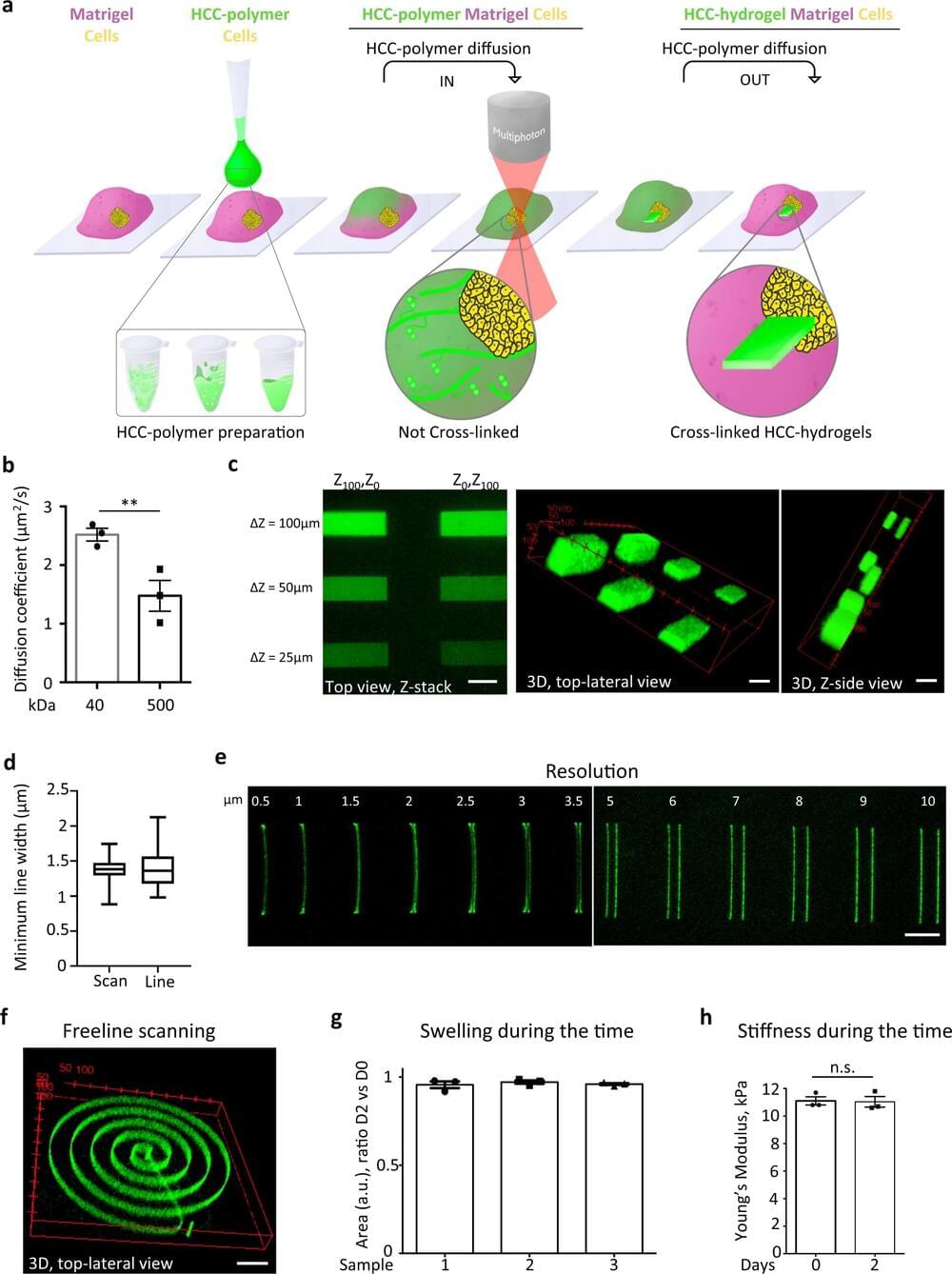
Scientists from the NIHR Great Ormond Street Hospital Biomedical Research Centre (a collaboration between GOSH and UCL), London, and University of Padova, Italy, have shown for the first time how 3D printing can be achieved inside “mini-organs” growing in hydrogels—controlling their shape, activity, and even forcing tissue to grow into “molds.”
This can help teams study cells and organs more accurately, create realistic models of organs and disease, and even better understand how cancer spreads through different tissues.
A particularly promising area of research at the Zayed Centre for Research (a partnership between Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH), GOSH Charity and University College London Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health (UCL GOS ICH)) is organoid science—the creation of micro-versions of organs like the stomach, the intestines and the lungs.
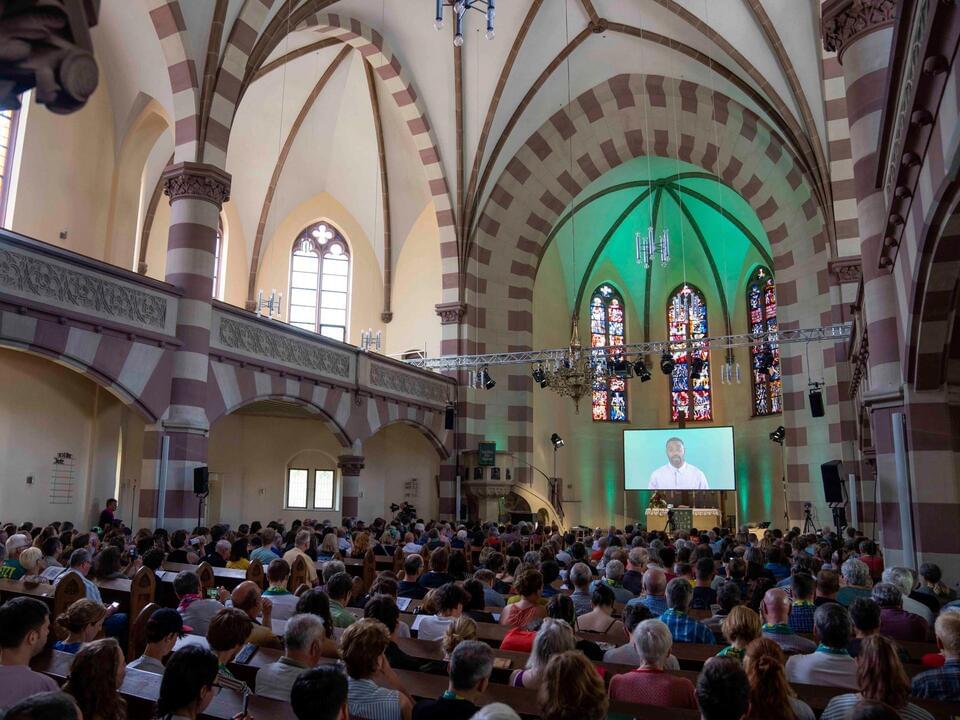


The artificial intelligence chatbot asked the believers in the fully packed St. Paul’s church in the Bavarian town of Fuerth to rise from the pews and praise the Lord.
The ChatGPT chatbot, personified by an avatar of a bearded Black man on a huge screen above the altar, then began preaching to the more than 300 people who had shown up on Friday morning for an experimental Lutheran church service almost entirely generated by AI.
“Dear friends, it is an honor for me to stand here and preach to you as the first artificial intelligence at this year’s convention of Protestants in Germany,” the avatar said with an expressionless face and monotonous voice.
A vast fungal web braids together life on Earth. Merlin Sheldrake wants to help us see it.
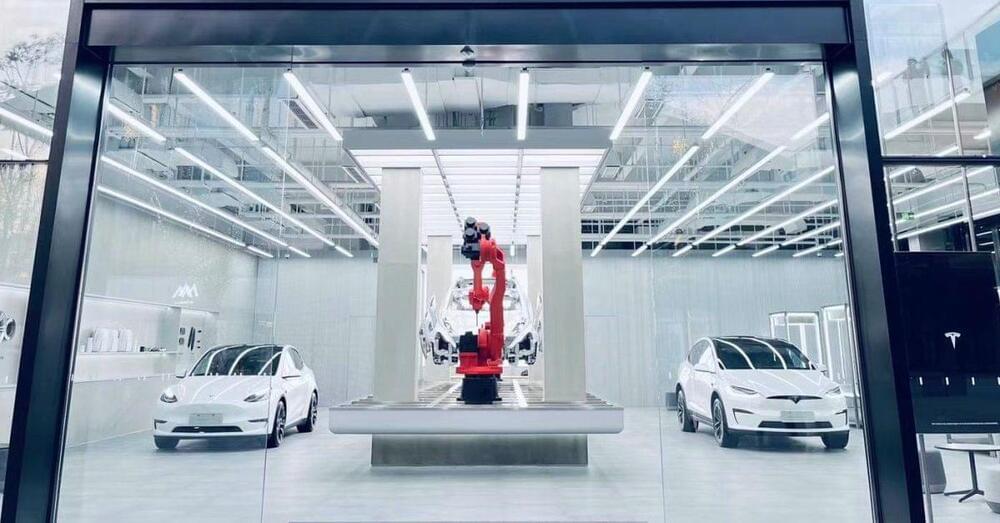

Tesla has unveiled a new retail concept called ‘Giga Laboratory’, which appears to be a showcase of its manufacturing capacity.
While Tesla announced a move to online sales and moved back from physical retail back in 2019, the automaker has, in practice, continued to rely heavily on retail locations as part of its marketing effort.
In fact, Tesla’s number of physical locations (retail and service) has more than doubled to now 1,000 locations around the work over the last 3 years.
The General Theory of General Intelligence: A Pragmatic Patternist Perspective — paper by Ben Goertzel: https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15100 Abstract: “A multi-decade exploration into the theoretical foundations of artificial and natural general intelligence, which has been expressed in a series of books and papers and used to guide a series of practical and research-prototype software systems, is reviewed at a moderate level of detail. The review covers underlying philosophies (patternist philosophy of mind, foundational phenomenological and logical ontology), formalizations of the concept of intelligence, and a proposed high level architecture for AGI systems partly driven by these formalizations and philosophies. The implementation of specific cognitive processes such as logical reasoning, program learning, clustering and attention allocation in the context and language of this high level architecture is considered, as is the importance of a common (e.g. typed metagraph based) knowledge representation for enabling “cognitive synergy” between the various processes. The specifics of human-like cognitive architecture are presented as manifestations of these general principles, and key aspects of machine consciousness and machine ethics are also treated in this context. Lessons for practical implementation of advanced AGI in frameworks such as OpenCog Hyperon are briefly considered.“
Talk held at AGI17 — http://agi-conference.org/2017/#AGI17 #AGI #ArtificialIntelligence #Understanding #MachineUnderstanding #CommonSence #ArtificialGeneralIntelligence #PhilMind https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_general_intelligenceMany thanks for tuning in!
Have any ideas about people to interview? Want to be notified about future events? Any comments about the STF series?
Please fill out this form: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1mr9PIfq2ZYlQsXRIn5BcLH2onbiSI7g79mOH_AFCdIk/
Consider supporting SciFuture by:
a) Subscribing to the SciFuture YouTube channel: http://youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=TheRationalFuture b) Donating.
- Bitcoin: 1BxusYmpynJsH4i8681aBuw9ZTxbKoUi22
- Ethereum: 0xd46a6e88c4fe179d04464caf42626d0c9cab1c6b.
- Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/scifuture c) Sharing the media SciFuture creates.
Kind regards.
Adam Ford.
- Science, Technology & the Future — #SciFuture — http://scifuture.org