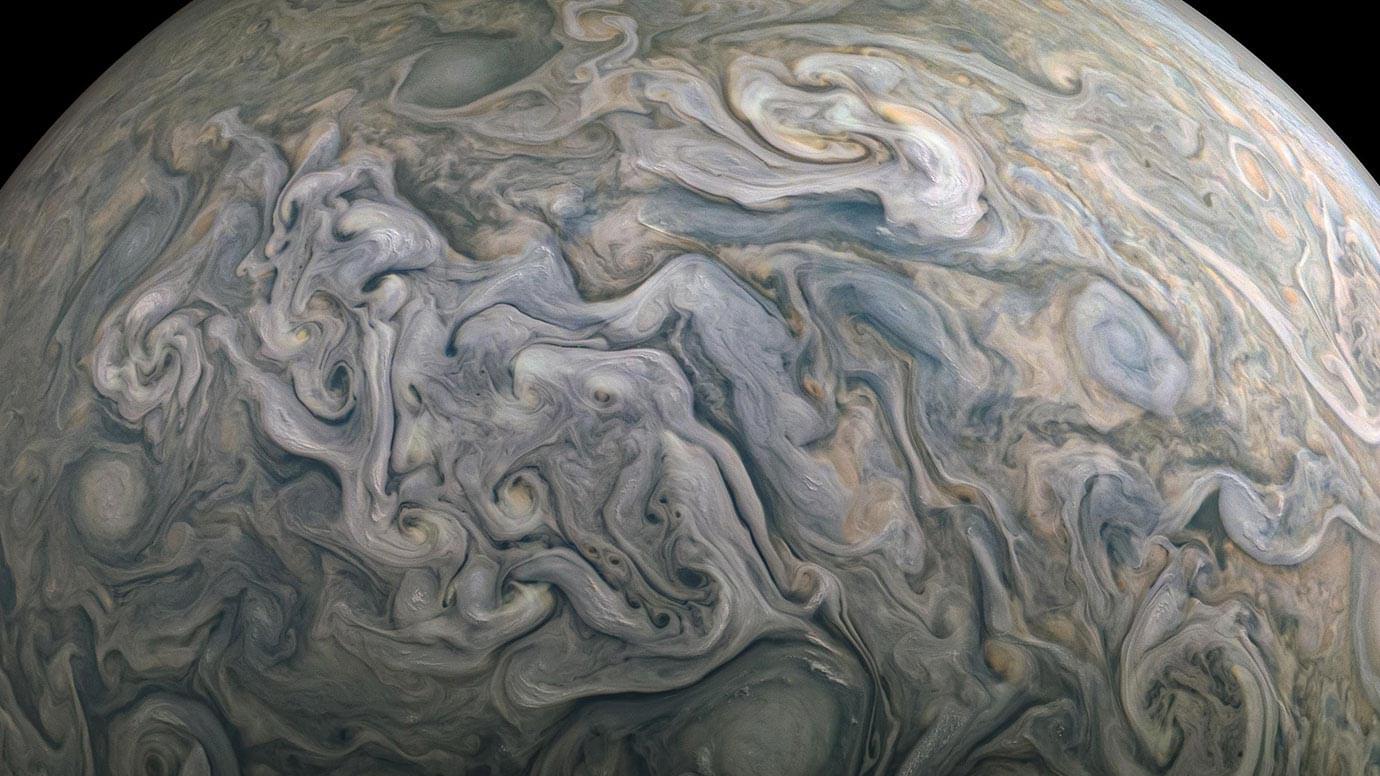
An atmospheric study reveals unexpected findings about our largest neighboring planet and the structure of its deep atmosphere.


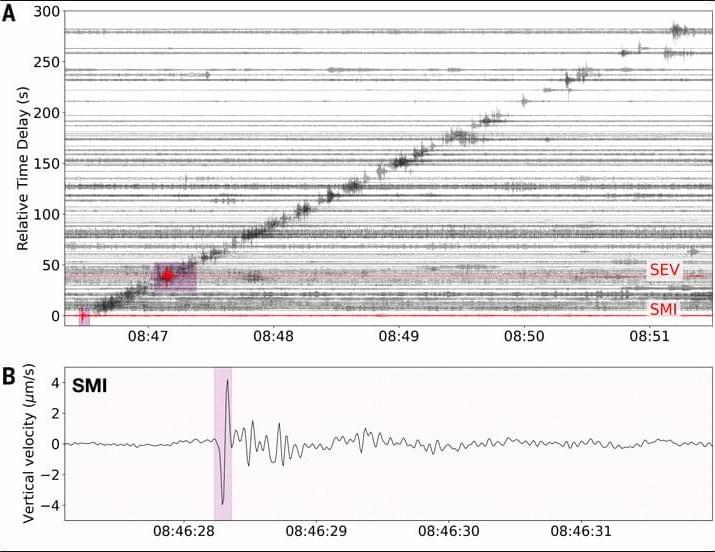
Therefore, there is a pressing need to develop tools that can be used to determine the trajectory, size, nature, and potential impact locations of reentering debris in near real time. This is a critical step toward mobilizing appropriate response operations (7). In this work, we have demonstrated that open-source seismic data are capable of fulfilling this requirement.
Past work has demonstrated the sensitivity of seismometers to reentry-generated shockwaves and explosions of natural meteoroids [for example, (8–10)]. However, the trajectories, speeds, and fragmentation chains of artificial spacecraft falling from orbit are distinct from those of natural objects entering from beyond the Earth‒Moon system. This means that the patterns of debris fallout that artificial spacecraft produce are also potentially more complex; for example, some components such as fuel tanks are structurally reinforced and hence more likely to survive and impact the ground, whereas others (such as solar panels) are deliberately designed to demise during reentry. Therefore, techniques used for natural objects require modification.
Good news. The rare cosmic alignment between the interstellar visitor 3I/ATLAS, the Earth and the Sun, was captured by the Hubble Space Telescope on January 22, 2026.
A new set of six 170 second exposures, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope between 13:10:30 and 13:43:33 UTC on January 22, 2026, were just posted here. The exposures display brightness maps of the glowing halo surrounding 3I/ATLAS. The glow is elongated by about 100,000 kilometers in the direction of the Sun, a length scale which is about ten times larger than the Earth’s diameter.
In a new paper that I published with Mauro Barbieri here, we alerted astronomers to this “full Moon phase” of 3I/ATLAS when observers from Earth will see it from the direction of the Sun to within an extremely small misalignment angle of just 0.012 radians. This rare alignment resulted in a brightness surge whose magnitude and growth rate are dictated by the composition and structure of the particles shed by jets of 3I/ATLAS. No new data other than the Hubble images was made public as of yet.





A new malicious campaign mixes the ClickFix method with fake CAPTCHA and a signed Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V) script to ultimately deliver the Amatera infostealing malware.
The Microsoft App-V script acts as a living-off-the-land binary that proxies the execution of PowerShell through a trusted Microsoft component to disguise the malicious activity.
Microsoft Application Virtualization is an enterprise Windows feature that allows applications to be packaged and run in isolated virtual environments without being actually installed on the system.

Microsoft has released emergency out-of-band security updates to patch a high-severity Microsoft Office zero-day vulnerability exploited in attacks.
The security feature bypass vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2026–21509, affects multiple Office versions, including Microsoft Office 2016, Microsoft Office 2019, Microsoft Office LTSC 2021, Microsoft Office LTSC 2024, and Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise (the company’s cloud-based subscription service).
However, as noted in today’s advisory, security updates for Microsoft Office 2016 and 2019 are not yet available and will be released as soon as possible.