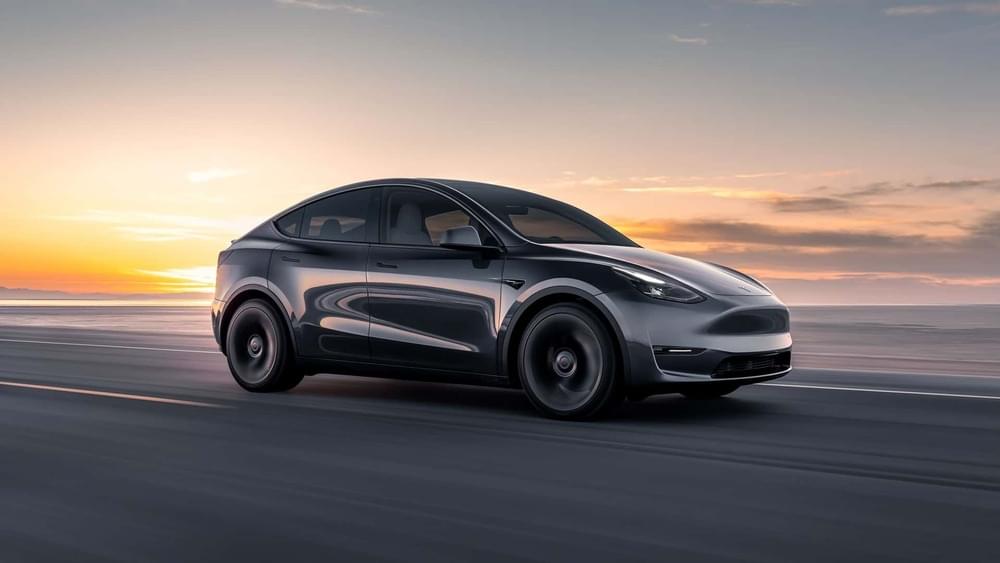
The most American-made cars sold in the US all come from Tesla, but the car in the number six spot is a bit of a surprise.




Quantum computing, just like traditional computing, needs a way to store the information it uses and processes. On the computer you’re using right now, information, whether it be photos of your dog, a reminder about a friend’s birthday, or the words you’re typing into browser’s address bar, must be stored somewhere. Quantum computing, being a new field, is still working out where and how to store quantum information.
In a paper published in the journal Nature Physics, Mohammad Mirhosseini, assistant professor of electrical engineering and applied physics, shows a new method his lab has developed for efficiently translating electrical quantum states into sound and vice versa. This type of translation may allow for storing quantum information prepared by future quantum computers, which are likely to made from electrical circuits.
This method makes use of what are known as phonons, the sound equivalent of a light particle called a photon. (Remember that in quantum mechanics, all waves are particles and vice versa). The experiment investigates phonons for storing quantum information because it’s relatively easy to build small devices that can store these mechanical waves.
Under certain conditions—usually exceedingly cold ones—some materials shift their structure to unlock new, superconducting behavior. This structural shift is known as a “nematic transition,” and physicists suspect that it offers a new way to drive materials into a superconducting state where electrons can flow entirely friction-free.
But what exactly drives this transition in the first place? The answer could help scientists improve existing superconductors and discover new ones.
Now, MIT physicists have identified the key to how one class of superconductors undergoes a nematic transition, and it’s in surprising contrast to what many scientists had assumed.
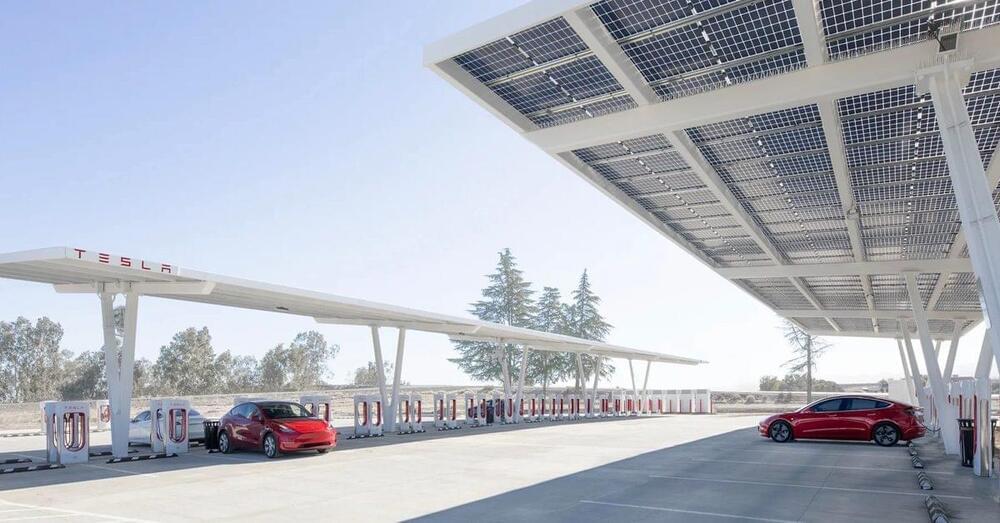

Analysts are trying to estimate the value of Tesla’s Supercharger network as the NACS connector becomes the North American standard and could widen Tesla’s charging lead.
One of the top Tesla analysts believes it could be worth more than $100 billion.
The Supercharger network is the only global EV fast-charging network, and in North America, it is by far the most extensive and reliable.
Visit https://brilliant.org/dos/ to get started learning STEM for free, and the first 200 people will get 20% off their annual premium subscription.
And grab your posters here: https://store.dftba.com/collections/domain-of-science.
This is the Map of Medicine showing you all of the different areas of medical practice, the principles of medicine, diagnostic methods, the surrounding sciences that support the field of medicine and a description of the placebo effect and clinical trials.
#medicine #domainofscience.
Check out Rohin @MedlifeCrisis placebo video: https://youtu.be/tefIopDJQBQ
Get My Posters Here.
For North America visit my DFTBA Store: https://store.dftba.com/collections/domain-of-science.
For the rest of the world go to my RedBubble Store: https://www.redbubble.com/people/DominicWalliman.
I have also made posters available for personal or educational use which you can find here: https://www.flickr.com/photos/95869671@N08/
Special thanks.
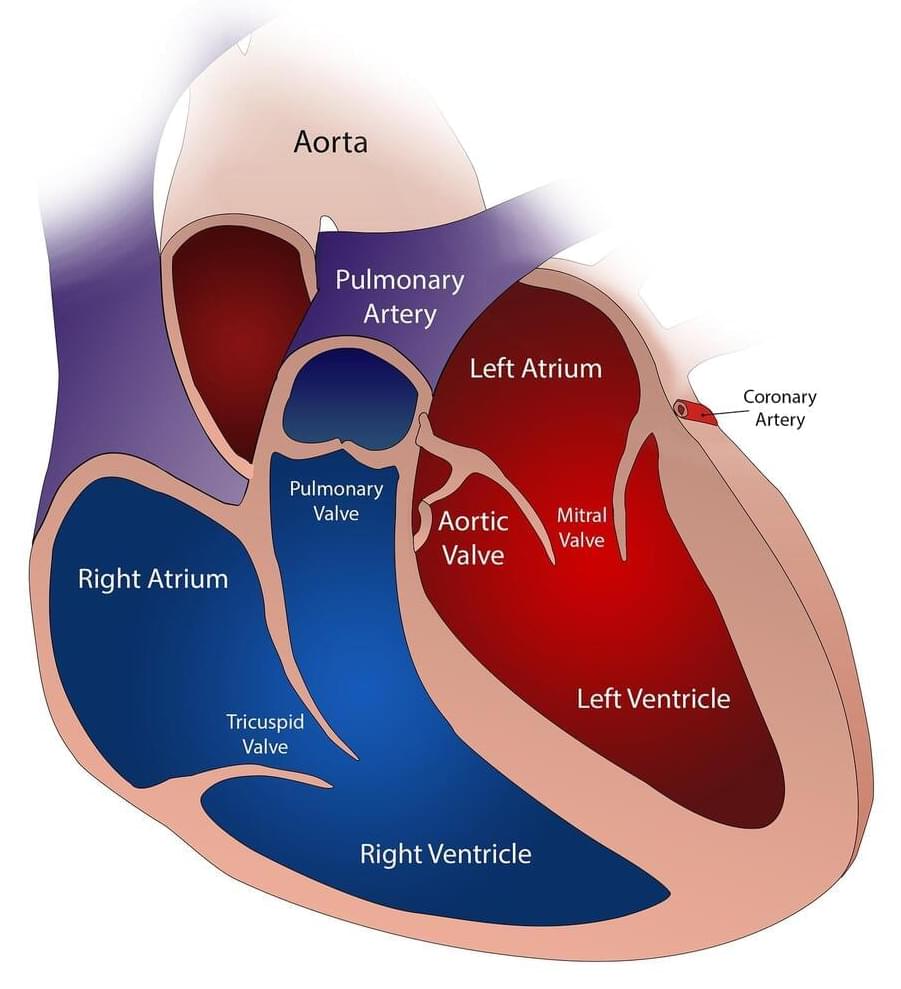
A Cleveland Clinic research team has published an “atlas” of metabolites associated with cardiovascular disease in the European Heart Journal. The novel findings provide key details about the routes and potential branching paths taken by bacteria and metabolic by-products, metabolites.
The study mapped out the multiple by-products of bacteria-processing amino acids associated with cardiovascular disease and then compared that to patient data to assess disease risk in two large cohorts—one in the US and another in Europe.
Bacteria in and on our bodies produce metabolites through processing certain molecules, referred to as precursors. Precursors can come in components of our diet, like protein, or as other metabolized substances. Probiotics (living organisms) and prebiotics (fiber, starch) have increasingly been introduced in foods or supplements as possible clinical interventions.
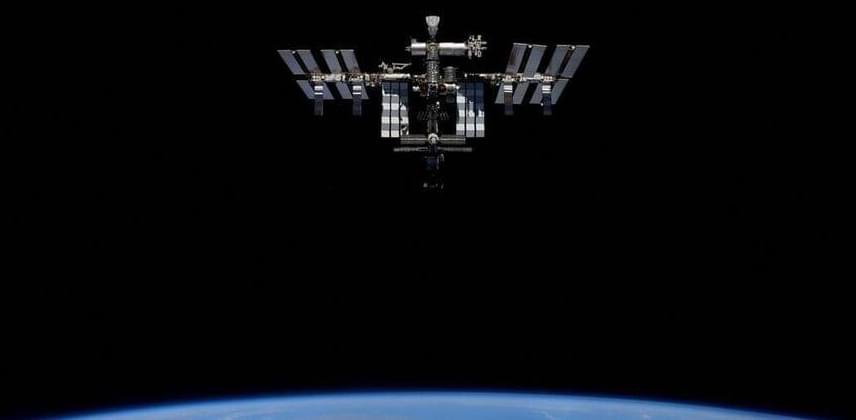



WASHINGTON, June 22 (Reuters) — Evidence is growing about the many ways that traveling in the microgravity environment of space tampers with the human body, with new research showing how it dials down the activity of genes in white blood cells crucial to the immune system.
A study involving 14 astronauts who spent 4−1÷2 to 6−1÷2 months aboard the International Space Station found that gene expression in these cells, also called leukocytes, quickly decreased when they reached space and then returned to normal not long after returning to Earth, researchers said on Thursday.
The findings offer insight into why astronauts are more susceptible to infections during flights, showing how the body’s system for fighting off pathogens is weakened in space.